














Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This lecture was delivered by Dr. Radha Ram at Anand Agricultural University for Advanced Research Methods subject. Its main points are: Data, Analysis, SPSS, Cronbach, Alphas, Individual, Variables, Exploratory, Statistics, Regression, Correlation
Typology: Slides
1 / 21

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!














˃ Writing requires sustained concentration, so create time for writing
˃ One cannot write in unfamiliar surroundings. Find a place where you cannot be interrupted, so remove all distractions including TV, magazines, computer games, etc.
˃ So that it is easy to restart next time
˃ Ask friends to read to point out difficult things that are not easy to understand, along with all omissions, spelling, punctuations and grammatical errors Docsity.com
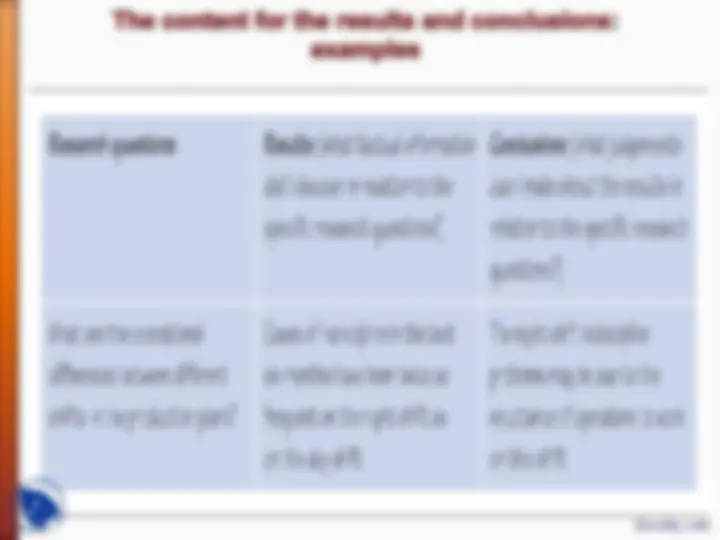
Suggested structure
b. Participants/sampling:
c. Materials:
d. Procedures
Saunders et al. (2009)
This section/chapter provides the second major opportunity to researcher to shine, and demonstrate the real originality of thought; he gets the first opportunity to shine and demonstrate real opportunity of thought when he chooses the research topic.
The difference between the „Findings chapter‟ and „Conclusion chapter‟ is that you make judgements in the latter while you report facts in the former.
For each finding, there should be at least one conclusion. Answering the research questions, meeting the objectives, and supporting or otherwise the research hypothesis is the main purpose of the conclusion chapter.
A copy of Appendix 2 on Harvard and APA style of referencing Is provided in your class „Reading Materials‟,
SPSS Exercise 6(b)
What is an outlier? “An outlying observation, or outlier, is an observation that is much different (either very small or very large) in relation to the observations in the sample. More precisely, an outlier is an observation from a different population to that generating the remaining sample observations. The inclusion or exclusion of such an observation, especially if
the sample size is small, can substantially alter
the results of regression analysis”.
(Gujarati, 2007; p.399)
SPSS Exercise 6(c)
Let‟s use the following SPSS commands, which may help us to identify certain outliers in our data set.
(Go-to-Statistics).....DESCRIPTIVES.....OUTLIERS.....
CONTINUE.....(on-display, pick).....STATISTICS.....OK.
Study the output; it contains 2-parts: (i) Descriptives (ii) Extreme cases (Gives both