

























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This is a part of quantitative techniques management. The purpose of this is to explain how decision theory takes place.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 33

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


























Most management decisions are
made in an environment of
uncertainty.
Decision theory provides a orderly
way of choosing among several
alternative strategies when decisions
are made under uncertainty or risk.
States of Nature
j
s
1
s
2
s
3
s 4 a 1 a 2 a 3
Alternatives
i
States of Nature
j
s
1
s
2
s
3
s 4 a 1 a 2 a 3
Alternatives
i
c
11
c
12
c
13
c
14
c
21
c
22
c
23
c
24
c
31
c
32
c
33
c
34
Suppose a home health agency is considering adding
physical therapy (PT) services for its clients. There
are three ways to do this:
Option A : contract with an independent practitioner
at $60 per visit.
Option B : hire a staff PT at a monthly salary of $
plus $400/mo. for a leased car plus $7/visit for
supplies and travel.
Option C : independent practitioner at $35/visit but
pay for fringe benefits at $200/mo. and cover the car
and expenses as in Option B.
Source: Austin, CJ and Boxerman, SB, Quantitative Analysis for Health Services
Administration, AUPHA/Health Administration Press, Ann Arbor, Michigan, 1995
States of Nature
j
s
1
s
2
s
3
s
4
Demand of
Patient
Services:
Visits/ mo.
30 90 140 150
Assumption: Probabilities of States of Nature are
unknown.
Alternatives
i a 1 a 2 a 3
Net Profit = (75 - 60) * D = 15*D
Assumption: Charge $75 per visit.
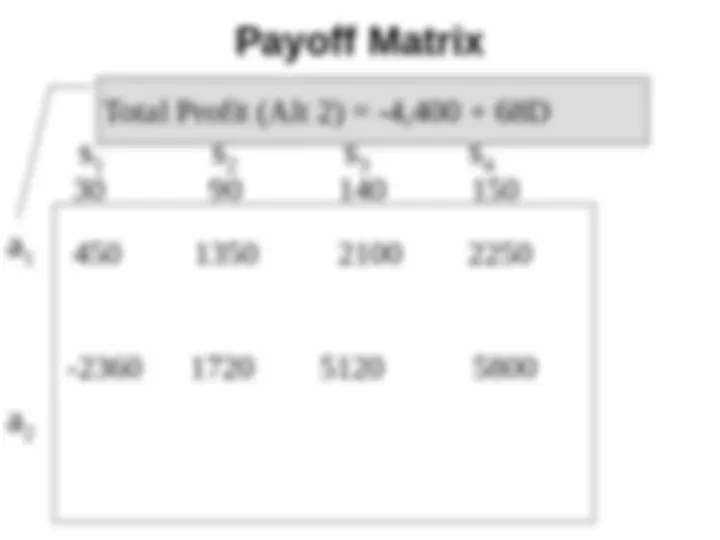
Net Profit = - 4,000 - 400 + (75 - 7) * D = -4,400 + 68*D
Alternatives
i a 1 a 2 a 3
Net Profit = (75 - 60) * D = 15*D
Assumption: Charge $75 per visit.
Net Profit = - 4,000 - 400 + (75 - 7) * D = -4,400 + 68*D
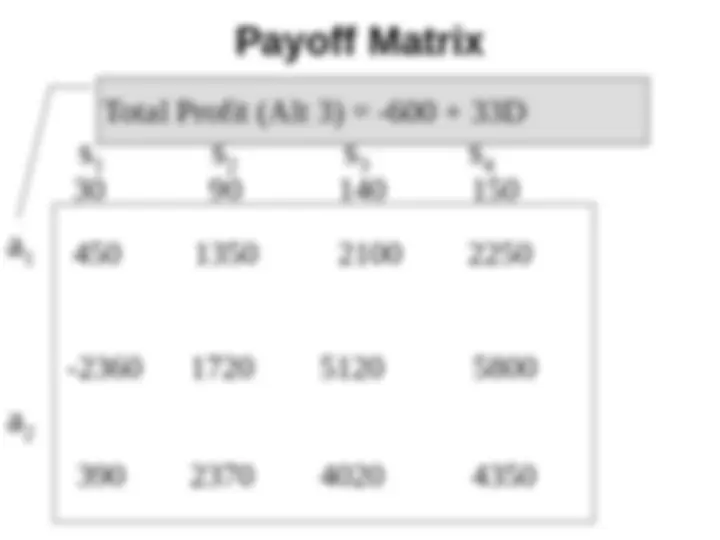
Net Profit = -400 -200+ (75 - 35 -7) * D = -600 + 33*D
s
1
s
2
s
3
s
4
450 1350 2100 2250
30 90 140 150
Total Profit (Alt 2) = -4,400 + 68D
-2360 1720 5120 5800
a
1
a
2
s
1
s
2
s
3
s 4 a 1 a 2
450 1350 2100 2250
30 90 140 150
Total Profit (Alt 3) = -600 + 33D
-2360 1720 5120 5800
390 2370 4020 4350
s
1
s
2
s
3
s 4 a 1 a 2
450 1350 2100 2250
30 90 140 150
-2360 1720 5120 5800
390 2370 4020 4350
No alternative dominates any other alternative
Criteria for Decision Making
Maximin Criterion- criterion that
maximizes the minimum payoff for each
alternative.
Steps:
alternative.