


















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of web application security, focusing on a multi-tier approach that utilizes various security techniques such as sql injection prevention, role based access control (rbac), n-tier architecture, and encryption. The concepts behind each technique, their importance, and why they are used. It also includes references to additional resources for further learning.
Typology: Slides
1 / 25

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


















Topics Covered
Background Our Project Components N-Tier Encryption Quick Demo (After each component) Future Conclusion References
Our Project
Web Application Security
(database driven)
Create a model web application that utilizes multiple security techniques and practices to protect against the most common threats.
Components
Our Project consists of the following: Security Concerns SQL Injection Prevention Role Based Access Control (RBAC) N-Tier Technique (3 Layers) SQL Encryption (symmetrical & asymmetrical)
Technology ASP.NET SQL Server 2008
N-Tier – What is it?
Multi-Tier applications distribute processing across multiple layers
4 Different Layers:
Source: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms973829.aspx Docsity.com
N-Tier – (1) User Interface Layer
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Users can interact with the application, input data, and view the results of requests.
Manages the manipulation and formatting of data.
Input validation occurs both on client and server side.
Validation on this layer is performed using javascript and asp vailidator.
N-Tier – (3) Data Access Layer
The layer that actually accesses the database.
Receives request for data from BLL.
Based on request it queries database & calls stored procedures.
Provides data to the Business Logic Layer.
N-Tier – (4) SQL Server
Holds all application data.
Query database.
Write procedures & functions.
Perform encryption.
Encryption – Why use it?
Occasionally information in a database is stolen or accessed inappropriately. Encryption ensures that data retrieved in this manner will be unreadable and unusable.
Safeguards from databases being physically removed or stolen.
Encryption - Hierarchy
Source: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms189586%28SQL.90%29.aspx Docsity.com
Source: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc278098.aspx Docsity.com
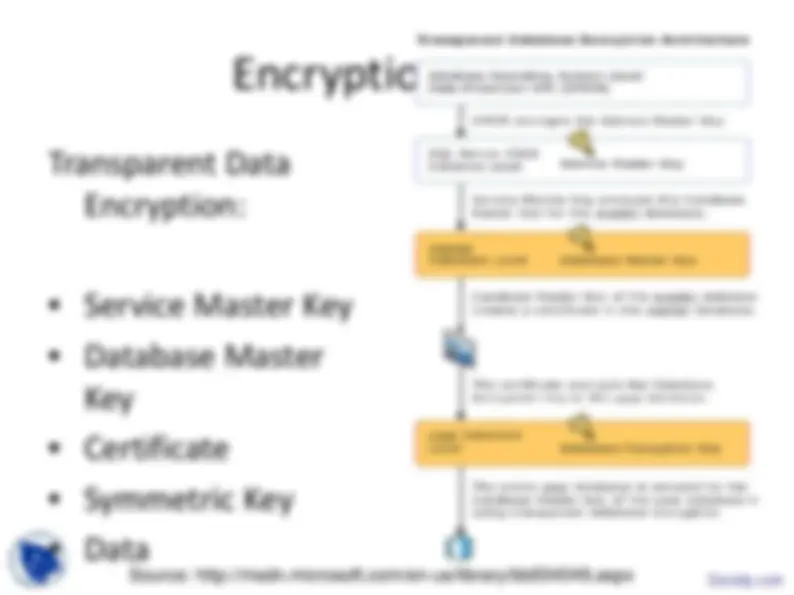
Encryption - TDE
Why use Transparent Data Encryption?
Ability to comply with many regulations and requirements
It is completely transparent, meaning no changes to the application are necessary.
Strong method for securing data.
No need to manage keys storage
Minimal performance impact (3-5%)
Future Work