

















































































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Visual Basic notes for Bsc Computer Science Student
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 115

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





























































































VIJAYA COLLEGE Page 1
Before we begin Visual Basic 6 programming, let us understand some basic concepts of programming. According to Webopedia, a computer program is an organized list of instructions that, when executed, causes the computer to behave in a predetermined manner. Without programs, computers are useless. Therefore, programming means designing or creating a set of instructions to ask the computer to carry out certain jobs which normally are very much faster than human beings can do.
Most people think that computer CPU is a very intelligent thing, which in actual fact it is a dumb and inanimate object that can do nothing without human assistant. The microchips of a CPU can only understand two distinct electrical states, namely, the on and off states, or 0 and 1 codes in the binary system. So, the CPU only understands combinations of 0 and 1 code, a language which we called machine language. Machine language is extremely difficult to learn and it is not for us laymen to master it easily. Fortunately, we have many smart programmers who wrote interpreters and compilers that can translate human language-like programs such as BASIC into machine language so that the computer can carry out the instructions entered by the users. Machine language is known as the primitive language while Interpreters and compilers like Visual Basic are called high-level language. Some of the high level programming languages beside Visual Basic are Fortran, Cobol, Java, C, C++, Turbo Pascal, and more
. Among the aforementioned programming languages, Visual Basic is the most popular. Not only it is easily to learn because of its English- like syntaxes, it can also be incorporated into all the Microsoft office applications such as Microsoft words, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft PowerPoint and more. Visual Basic for applications is known as VBA.
What programs can you create with Visual Basic 6?
With VB 6, you can create any program depending on your objective. For example, you can create educational programs to teach science , mathematics, language, history , geography and so on. You can also create financial and accounting programs to make you a more efficient accountant or financial controller. For those of you who like games, you can create those programs as well. Indeed, there is no limit to what program you can create!
VIJAYA COLLEGE Page 2
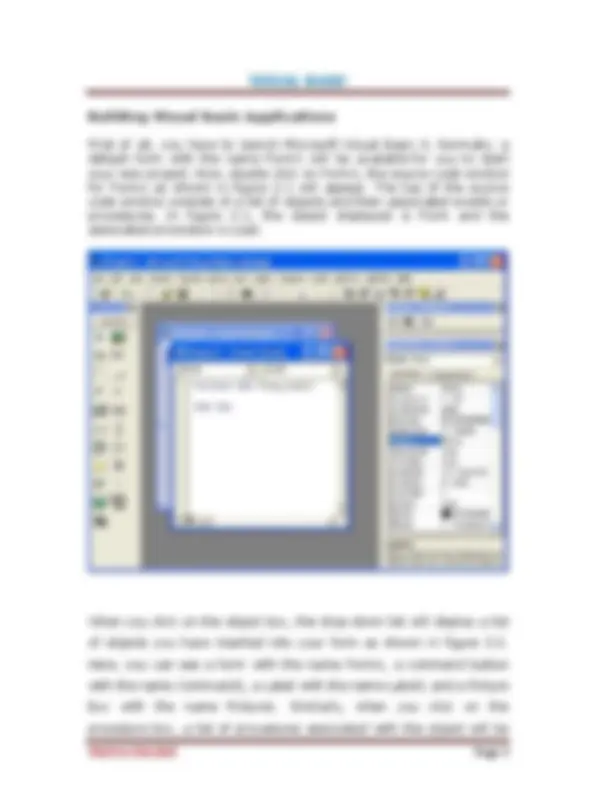
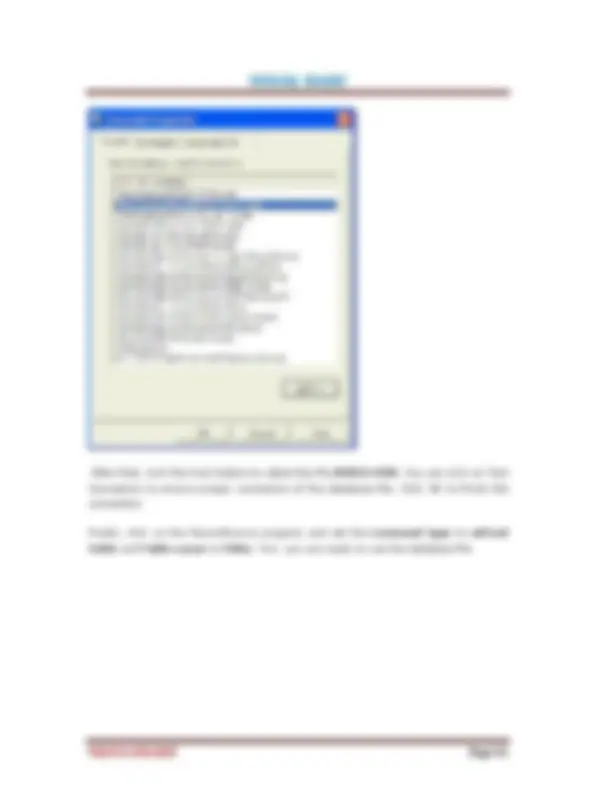
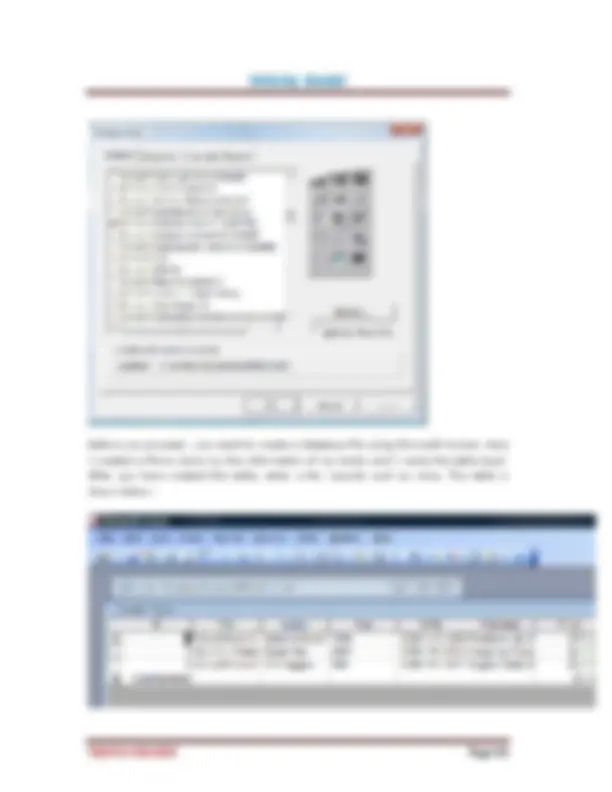
On start up, Visual Basic 6.0 will display the following dialog box as shown in Figure 1.1. You can choose to start a new project, open an existing project or select a list of recently opened programs. A project is a collection of files that make up your application. There are various types of applications that we could create, however, we shall concentrate on creating Standard EXE programs (EXE means executable program). Now, click on the Standard EXE icon to go into the actual Visual Basic 6 programming environment.
VIJAYA COLLEGE Page 4
displayed as shown in figure 2.3. Some of the procedures associated
with the object Form1 are Activate, Click, DblClick (which means
Double-Click) , DragDrop, keyPress and more. Each object has its
own set of procedures. You can always select an object and write
codes for any of its procedure in order to perform certain tasks.
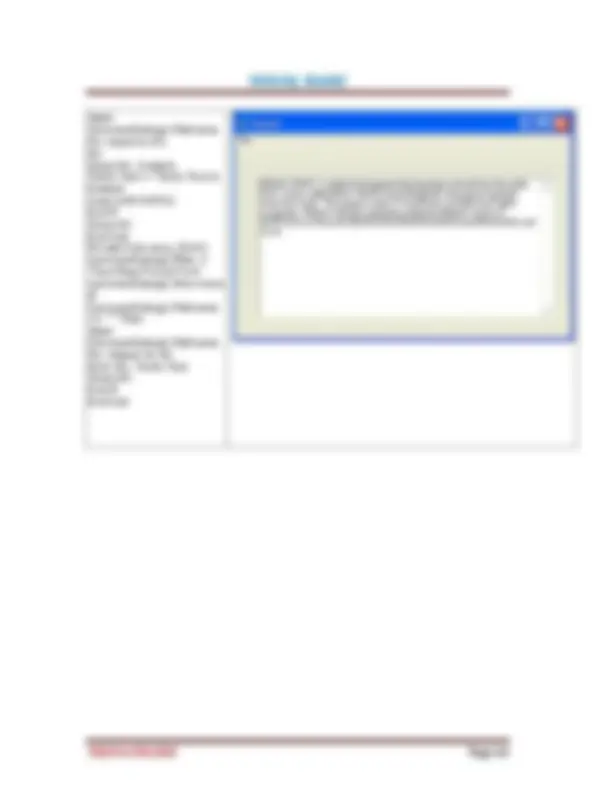
Figure 2.2: List of Object s (^) Figure 2.3: List of Procedures
You do not have to worry about the beginning and the end statements
(i.e. Private Sub Form_Load.......End Sub.); Just key in the lines in
between the above two statements exactly as are shown here. When
you press F5 to run the program, you will be surprise that nothing
shown up .In order to display the output of the program, you have to
add the Form1.show statement like in Example 2.1.1 or you can just
use Form_Activate ( ) event procedure as shown in example 2.1.2.
The command Print does not mean printing using a printer but it
means displaying the output on the computer screen. Now, press F5 or
click on the run button to run the program and you will get the output
as shown in figure 2.4.
VIJAYA COLLEGE Page 5
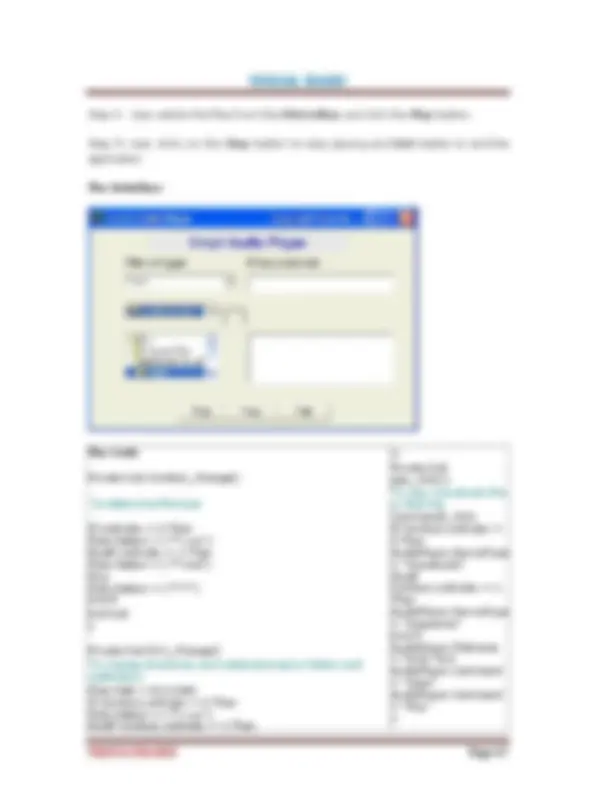
You can also perform arithmetic calculations as shown in
example 2.1.2. VB uses * to denote the multiplication operator and /
to denote the division operator. The output is shown in figure 2.3,
where the results are arranged vertically.
VIJAYA COLLEGE Page 7
Before writing an event procedure for the control to response to a user's input, you have to set certain properties for the control to determine its appearance and how it will work with the event procedure. You can set the properties of the controls in the properties window or at runtime.
VIJAYA COLLEGE Page 8
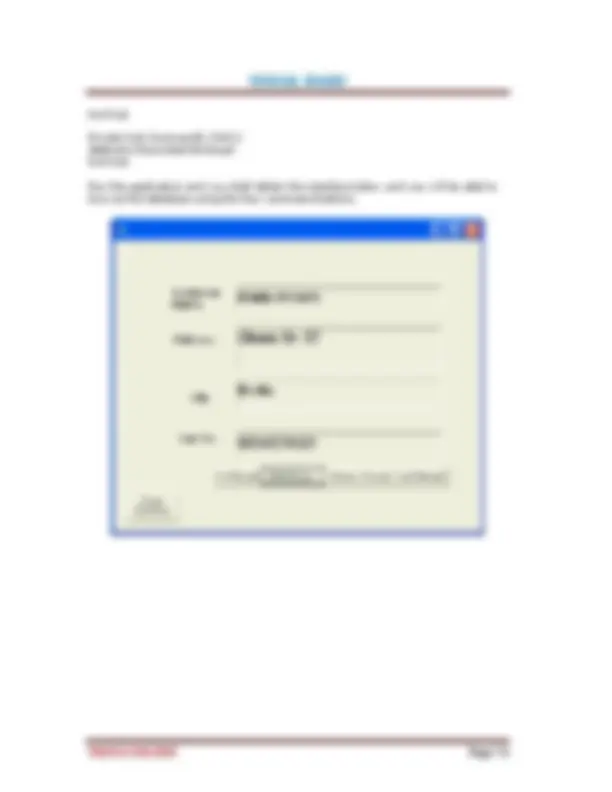
Figure 3.1 on the right is a typical properties window for a form. You can rename the form caption to any name that you like best. In the properties window, the item appears at the top part is the object currently selected (in Figure 3.1, the object selected is Form1). At the bottom part, the items listed in the left column represent the names of various properties associated with the selected object while the items listed in the right column represent the states of the properties. Properties can be set by highlighting the items in the right column then change them by typing or selecting the options
VIJAYA COLLEGE Page 10
3.2.1 The Text Box
The text box is the standard control for accepting input from the user
as well as to display the output. It can handle string (text) and
numeric data but not images or pictures. String in a text box can be
converted to a numeric data by using the function Val(text). The
following example illustrates a simple program that processes the
input from the user.
Example 3.
In this program, two text boxes are inserted into the form together
with a few labels. The two text boxes are used to accept inputs from
the user and one of the labels will be used to display the sum of two
numbers that are entered into the two text boxes. Besides, a
command button is also programmed to calculate the sum of the two
numbers using the plus operator. The program use creates a variable
sum to accept the summation of values from text box 1 and text box