













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An introduction to Virtual LANs (VLANs), explaining how they logically segment switched networks based on workgroups or applications, and the benefits of using VLANs for scalability, security, and network management. It covers the operation of VLANs, different VLAN membership types, and the role of routers in VLAN topologies.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 21

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!














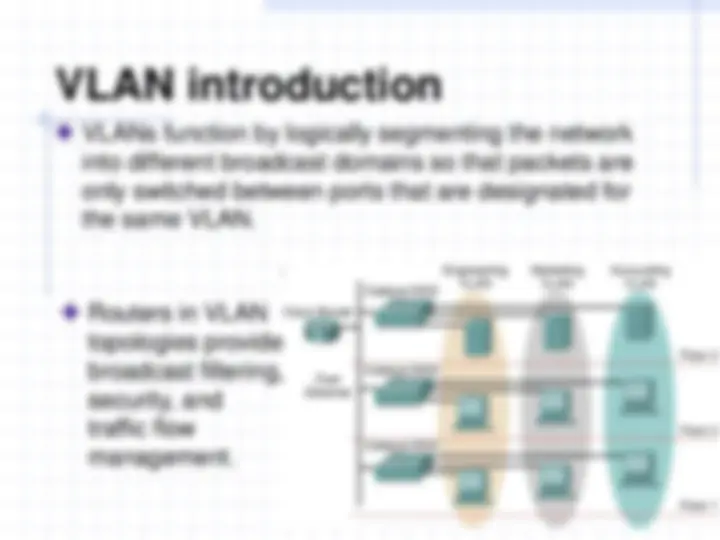
VLANs logically segment switched networks based on the functions, project teams, or applications of the organization regardless of the physical location or connections to the network. All workstations and servers used by a particular workgroup share the same VLAN, regardless of the physical connection or location.
VLANs function by logically segmenting the network into different broadcast domains so that packets are only switched between ports that are designated for the same VLAN. Routers in VLAN topologies provide broadcast filtering, security, and traffic flow management.
VLANs address scalability, security, and network management. Switches may not bridge any traffic between VLANs, as this would violate the integrity of the VLAN broadcast domain. Traffic should only be routed between VLANs.
Layer 3 routing allows the router to send packets to the three different broadcast domains.
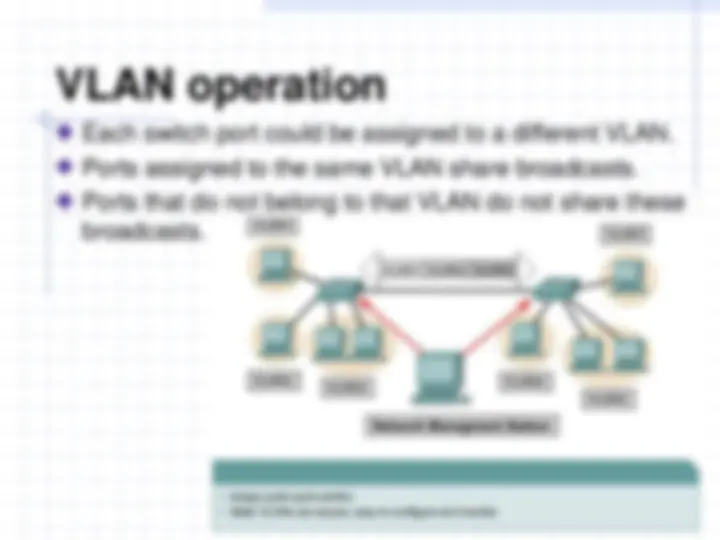
Implementing VLANs on a switch causes the following to occur: The switch maintains a separate bridging table for each VLAN. If the frame comes in on a port in VLAN 1 , the switch searches the bridging table for VLAN 1. When the frame is received, the switch adds the source address to the bridging table if it is currently unknown. The destination is checked so a forwarding decision can be made. For learning and forwarding the search is made against the address table for that VLAN only.
Users attached to the same shared segment, share the bandwidth of that segment. Each additional user attached to the shared medium means less bandwidth and deterioration of network performance. VLANs offer more bandwidth to users than a shared network. The default VLAN for every port in the switch is the management VLAN. The management VLAN is always VLAN 1 and may not be deleted. All other ports on the switch may be reassigned to alternate VLANs.
Dynamic VLANs allow for membership based on the MAC address of the device connected to the switch port. As a device enters the network, it queries a database within the switch for a VLAN membership.
Network administrators are responsible for configuring VLANs both manually and statically.
The key benefit of VLANs is that they permit the network administrator to organize the LAN logically instead of physically.
Port-based VLANs MAC address based VLANs Protocol based VLANs
The number of VLANs in a switch vary depending on several factors: Traffic patterns Types of applications Network management needs Group commonality
An important consideration in defining the size of the switch and the number of VLANs is the IP addressing scheme. Because a one-to-one correspondence between VLANs and IP subnets is strongly recommended, there can be no more than 254 devices in any one VLAN. It is further recommended that VLANs should not extend outside of the Layer 2 domain of the distribution switch.