Download Urinary Incontinence in Elderly - Introduction to Geriatrics - Lecture Slides and more Slides Geriatrics in PDF only on Docsity!
Urinary Incontinence in the
Elderly:
Practical Approaches for the
Primary Care Internist
Overview
- Prevalence and clinical importance
- Transient ( or potentially reversible) causes of incontinence
- Chronic incontinence
- Clinical evaluation
- Treatments
- Some recent studies
Normal physiology
- Neural control
- Frontal lobe inhibits
- Micturition center in pons
- Detrusor under cholinergic control
- Urethra under alpha adrenergic control
- External sphincter under voluntary control
- Normal urination requires intact neural control, intact anatomic structures, mobility, and awareness of need to urinate
Case
- 80 year old man is scheduled for a TURP for nocturia and urge incontinence. He has not seen an internist for 3 years, and comes to you for “surgical clearance”. He is healthy and is on no medications. He states that he has “slowed down” over the past 2 years, and has put on 20 pounds over the past five years. ROS is otherwise unremarkable except for mild erectile difficulty over the past few years.
- What do you do?
Common Drug Causes of Incontinence
- Anticholinergics
- Alpha agonists
- Alpha antagonists
- Diuretics (including caffeine)
- Calcium channel blockers
- Sedative hypnotics and any CNS depressants, including ETOH
Case #
- 80 year old man is scheduled for a TURP for nocturia and urge incontinence.
- You do a physical exam, which is normal except for mild obesity, a slightly enlarged prostate, and mild peripheral neuropathy.
- Labs show normal renal panel, CBC, calcium, PSA 4, and glucose of 358. UA is normal except for glucose and protein in the urine.
A Bladder Diary
Time Used toilet^ Incontine nce episode (small or large?
Reason Other factors (medicin es)
Liquids and caffeine
7 - 10 10 - 1 1 - 4 4 - 7 7 - 10 Night
Observations
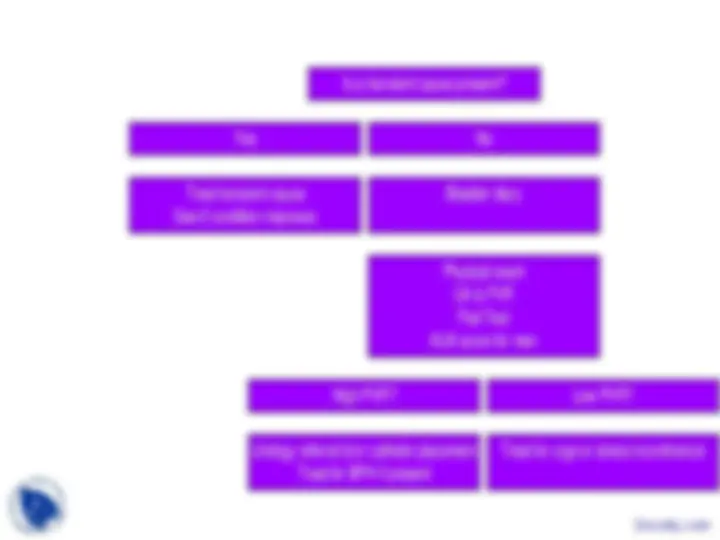
Step #3: History & Physical
- History: night-time (better or worse?), volume, stress, urgency, bladder diary
- Physical :
- Neuro exam, mental status, mobility
- Men: Prostate, AUA
- Women: Pad Test, Bimanuel with “Kegel test”
- Both men and women: PVR, UA
- Consider: glucose, calcium, electrolytes
Case #
- A 60 year old woman comes in complaining of worsening incontinence with sneezing and coughing. Her pad test is +, she has some vaginal atrophy, and her PVR is 5cc
- What do you do?
Pattern #1: “Open sphincter”
- Presentation: Stress incontinence
- Common cause in women
- Causes: Childbirth, pelvic floor laxity, radical prostatectomy, alpha antagonists
- PE: Often normal
Estrogen and Stress Incontinence
- Meta-analysis of 6 small RCTs: oral estrogen may subjectively improve UI, Fantl 1994
- Recent RCT found no improvement Fantl 1996
- More efficacy with topical estrogens
- Epidemiologic studies find increased risk of UI in women on ERT Brown JAGS 1998
- Bottom Line: Worth a trial of topical estrogen in presence of atrophy and irritative sx, otherwise questionable
Alpha agonists
- Most studies done with phenylpropanolamine
- Pseudoephedrine 15-30mg TID or prn
- Contraindications: HTN, CAD, obstruction
- Side effects: hypertension, dysrythmias, anxiety, insomnia, CVA, agitation, respiratory difficulty, sweating
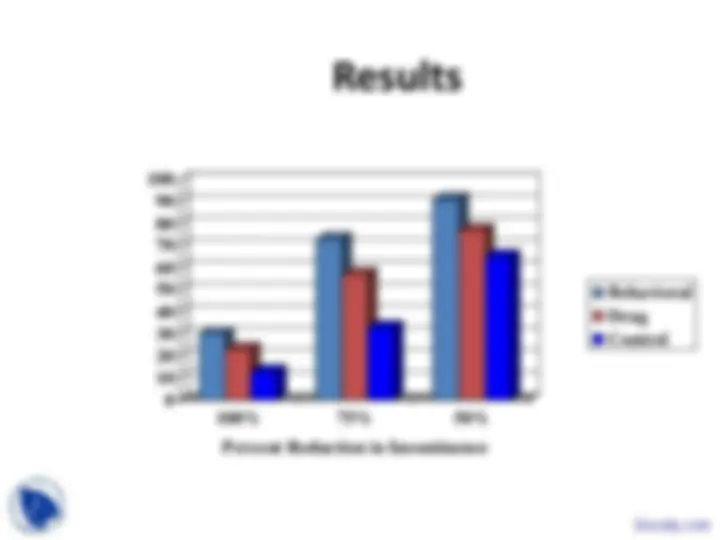
Results at 6 months
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
% Reporting "Incontinence No Longer a Problem"
Pad Leakage
Control Stimulation Kegel Cones
Bo, BMJ 1999
Case
- A 60 year old woman comes in complaining of worsening incontinence with sneezing and coughing. Her pad test is +, she has some vaginal atrophy, and her PVR is 5cc
- Patient begins topical estrogen and, Kegel exercises, and sudafed, and has marked improvement. After two years, however, her symptoms are worse, and she has developed HTN, forcing her to stop the sudafed. She undergoes bladder suspension surgery with resolution of symptoms.