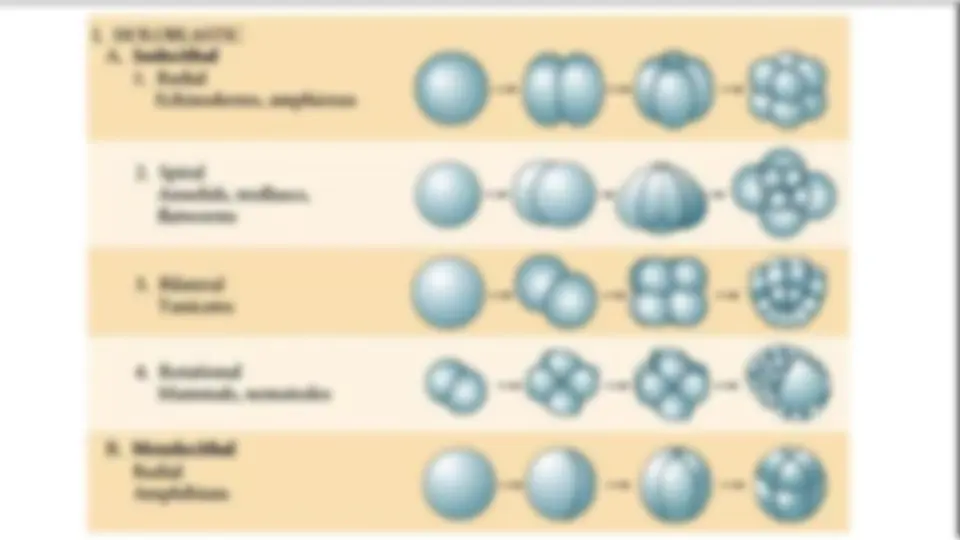
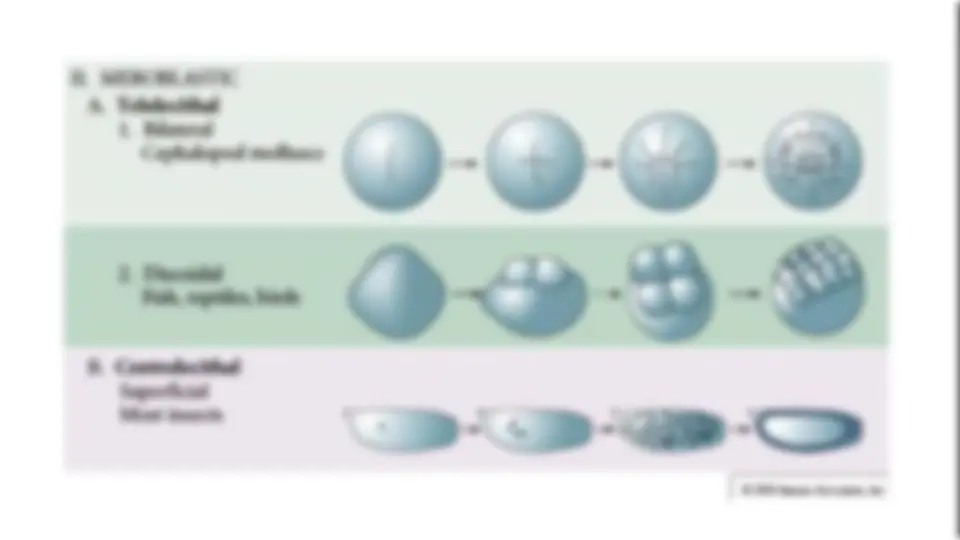
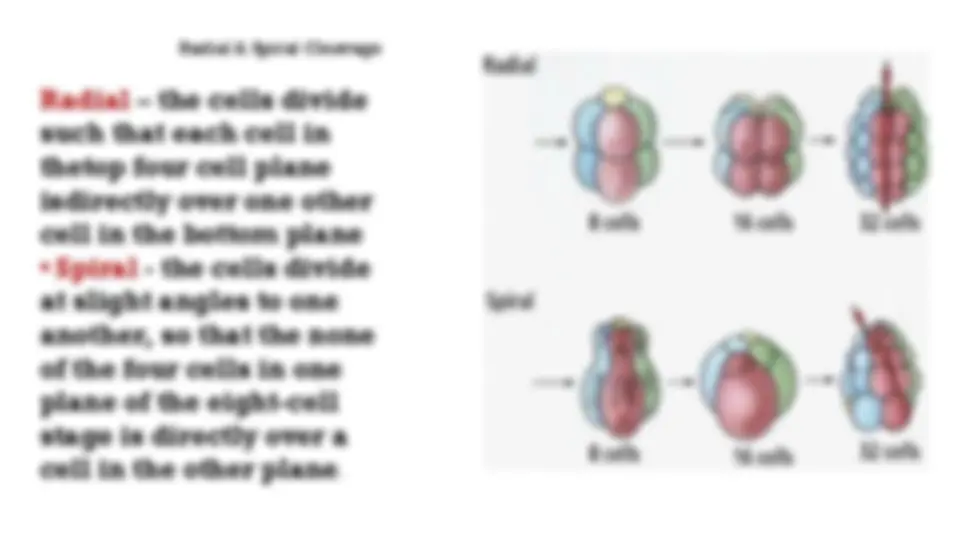
Download UNIT 3: DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY and more Study Guides, Projects, Research Developmental biology in PDF only on Docsity!
UNIT 3: DEVELOPMENTAL
BIOLOGY
BY; DR. LUNA PHUKAN
TH
SEM GENERAL
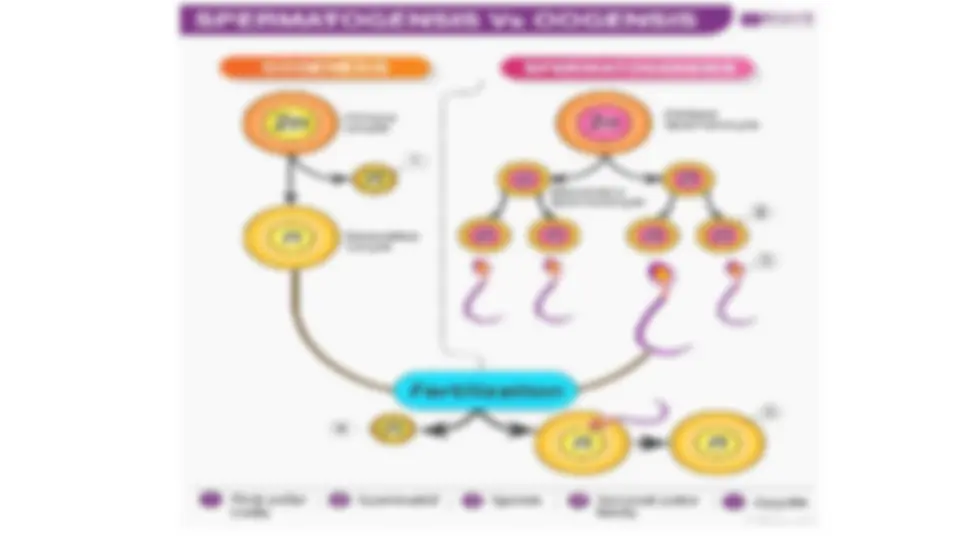
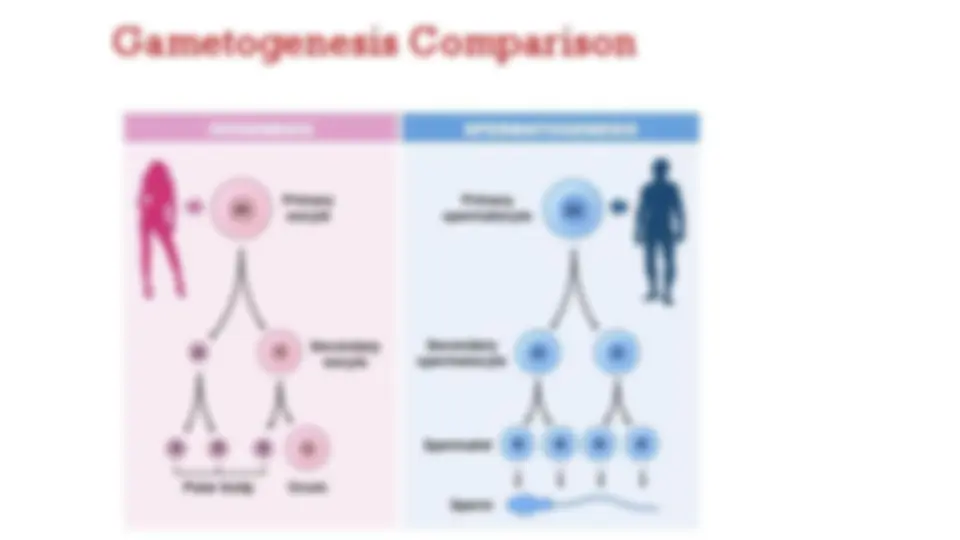
GAMETOGENESIS: SPERMATOGENESIS
AND OOGENESIS
Gametogenesis occurs when a haploid cell (n) is
formed from a diploid cell (2n) through meiosis.
We call gametogenesis in the male
spermatogenesis and it produces spermatozoa.
In the female, we call it oogenesis. It results in
the formation of ova.
An organism undergoes a series of changes
throughout its life cycle. Gametogenesis
(spermatogenesis and oogenesis), plays a crucial
role in humans to support the continuance of
generations.
Gametogenesis is the process of division of diploid
cells to produce new haploid cells. In humans, two
different types of gametes are present. Male
gametes are called sperm and female gametes are
called the ovum.
Spermatogenesis: Sperm formation
Oogenesis: Ovum formation
The process of gametogenesis occurs in the
gonads and involves the following steps:
Multiple mitotic divisions and cell growth of
precursor germ cells
- Two meiotic divisions (meiosis I and II) to
produce haploid daughter cells
- Differentiation of the haploid daughter cells to
produce functional gametes
Oogenesis
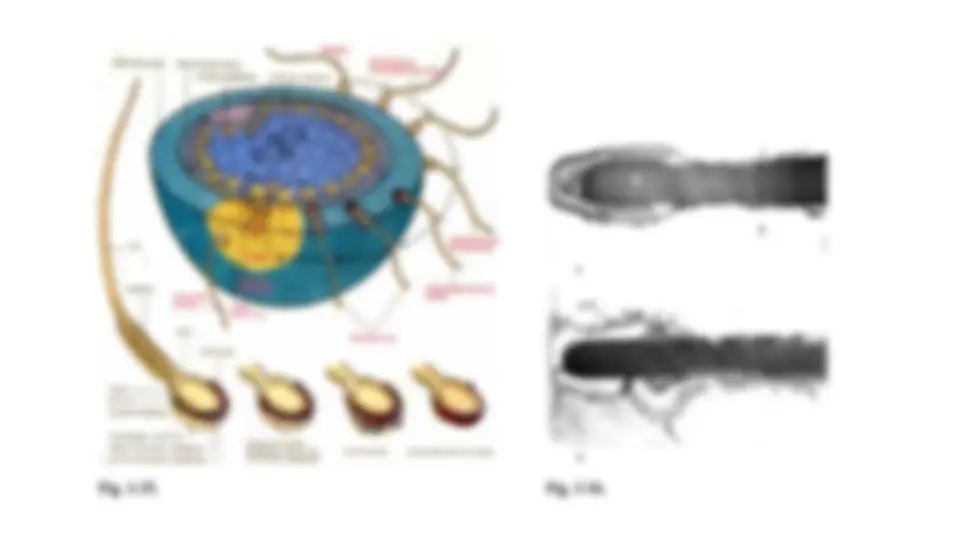
- Oogenesis describes the production of female gametes (ova) within the ovaries (and, to a lesser extent, the oviduct)
- The process begins during foetal development, when a large number of primordial cells are formed by mitosis (~40,000)
- These cells (oogonia) undergo cell growth until they are large enough to undergo meiosis (becoming primary oocytes)
- The primary oocytes begin meiosis but are arrested in prophase I when granulosa cells surround them to form follicles
- The secondary oocyte is released from the ovary (ovulation) and enters into the oviduct (or fallopian tube)
- The follicular cells surrounding the oocyte form a corona radiata and function to nourish the secondary oocyte
- If the oocyte is fertilised by a sperm, chemical changes will trigger the completion of meiosis II and the formation of another polar body (the first polar body may also undergo a second division to form a third polar body)
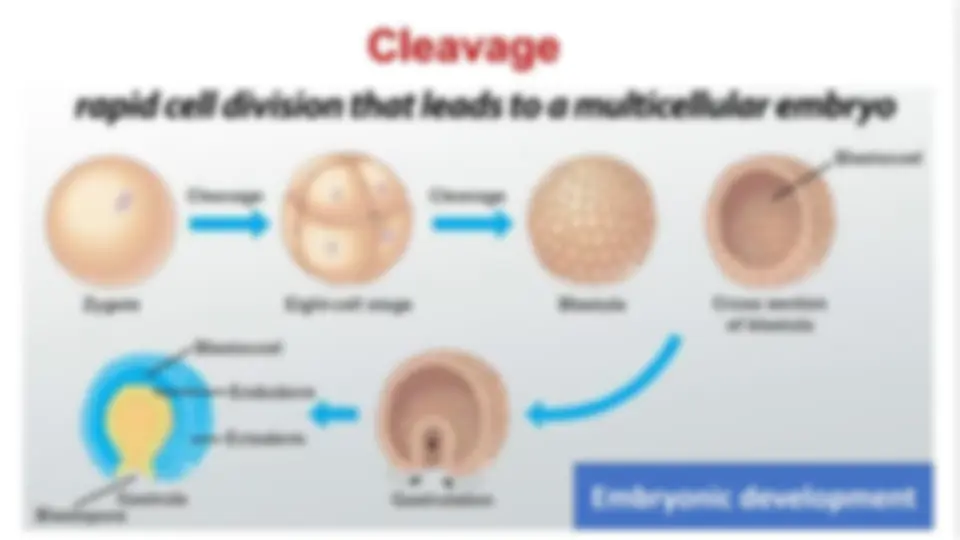
- Once meiosis II is complete the mature egg forms a ovum, before fusing its nucleus with the sperm nucleus to form a zygote
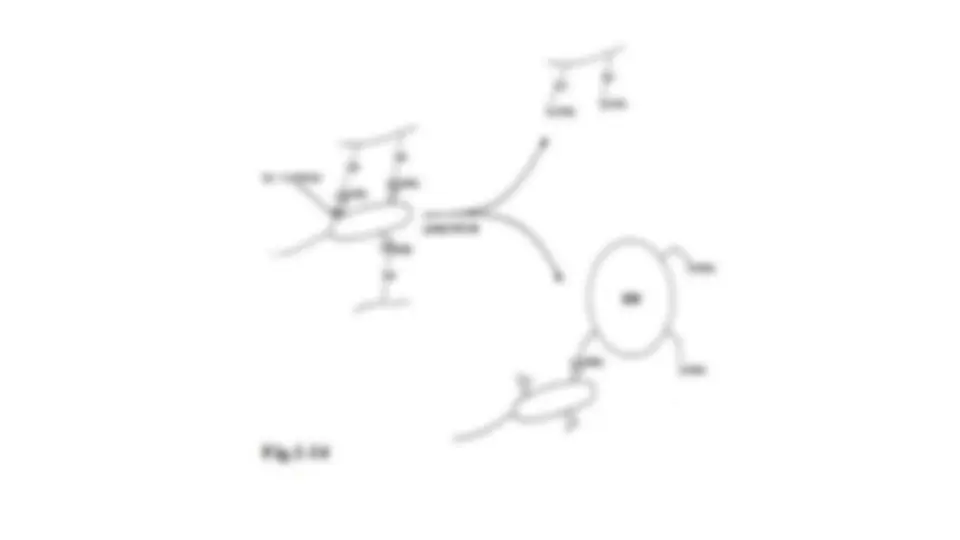
Formation of Polar Bodie
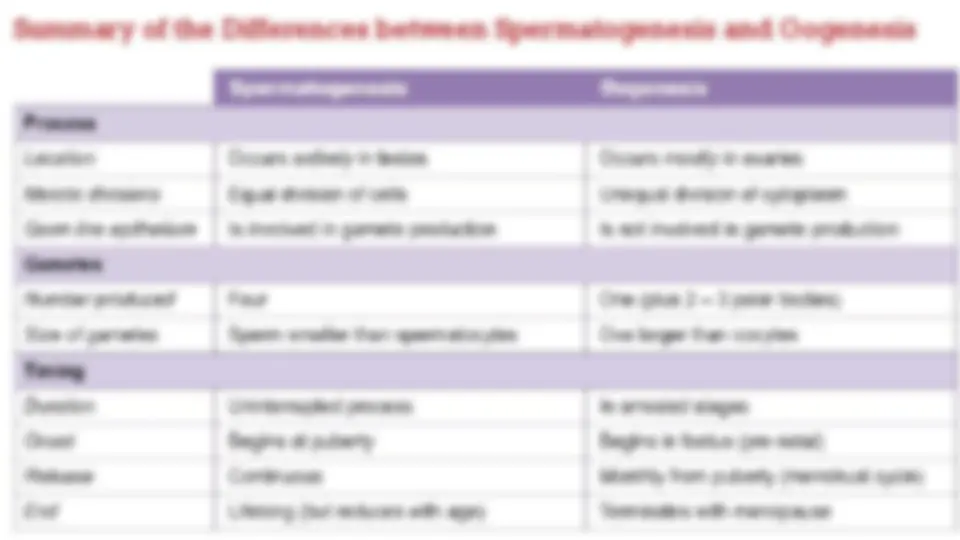
Timing of the process In spermatogenesis, the production of gametes is a continuous process that begins at puberty and continues until death In oogenesis, the production of gametes is a staggered and finite process: It begins before birth (prenatally) with the formation of a fixed number of primary oocytes (~40,000) It continues with the onset of puberty according to a monthly menstrual cycle It ends when hormonal changes prevent the further continuance of the menstrual cycle (menopause)
Summary of the Differences between Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis
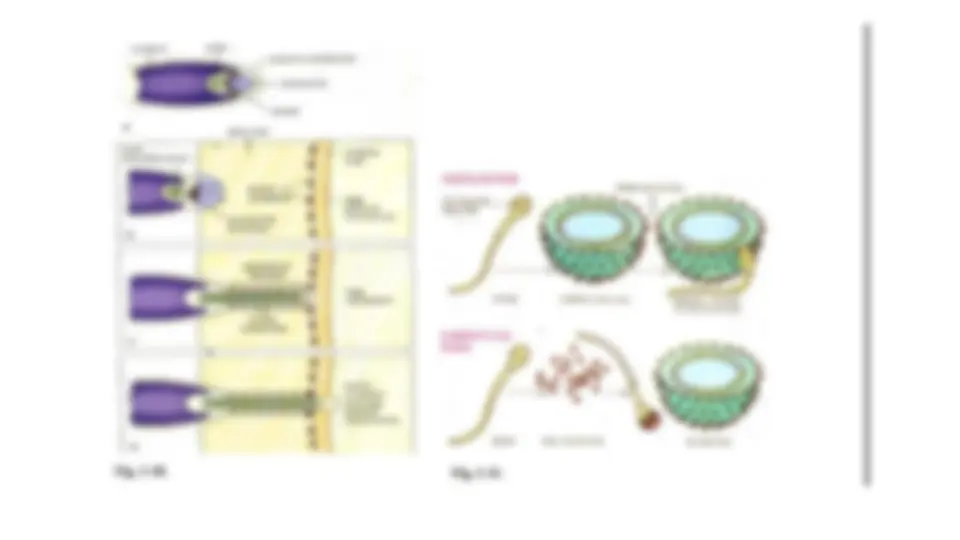
FERTILIZATION : SPERM EGG
INTERACTION : ACTIVATION OF EGG:
GAMETE FUSION IN SEA URCHIN
Fertilization is a multi-step process that involves
the interaction of a mature, capacitated
spermatozoon and ovulated egg. ... Sperm and egg
plasma membranes bind and fuse, resulting in
incorporation of sperm contents into the egg
cytoplasm. Fusion triggers egg activation and
establishment of a block to polyspermy.
SUMMARY: Fertilization is a cell-cell
recognition process that occurs between two
distinct cells: a small
asymmetric and motile sperm cell and a large
and nonmotile egg. The stages of fertilization
can be divided intofour processes:
1 ) sperm preparation, 2) sperm-egg
recognition and binding, 3) sperm-egg fusion
and 4) fusion
of sperm and egg pronuclei and activation of
the zygote.
Discuss the sequential nature of fertilization in which
ordered changes in the gametes “drive”
the process of fertilization toward completion.
2. Explain the role of specialized sperm and egg surface
structures in fertilization.
3. Describe how egg and sperm receptors were
identified.
4. Explain the current state of knowledge about sperm-
egg membrane fusion and how sperm
components are incorporated into the egg.
5. Describe how polyspermy is prevented and the
fertilized egg is activated for development.
GLOSSARY:
Capacitation: The process by which the sperm
becomes capable of fertilizing an egg.
Acrosome Reaction: A regulated exocytotic event in
which an apical vesicle in the sperm head fuses with
the sperm plasma membrane. The acrosome
reaction is triggered in response to egg factors.
Acrosin: A serine protease released during the
acrosome reaction.
Cortical Reaction: A regulated exocytosis in which
apically localized vesicles (cortical granules) in the
egg fuse with plasma membrane after fertilization.