











Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Machining Method used for production technology subject
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 19

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!












Saurabh Khandelwal Assistant Professor
Introduction WORKING PROCESS OF USM Main Elements of an USM OPERATIONS OF ULTRASONIC CUTTING Process Parameters Advantages Disadvantages Limitations
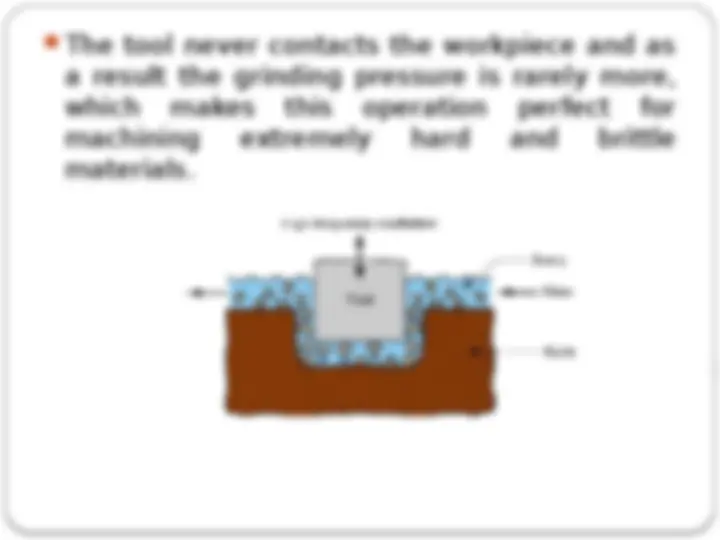
The tool never contacts the workpiece and as a result the grinding pressure is rarely more, which makes this operation perfect for machining extremely hard and brittle materials.
Generally tool is pressed down with a feed force F. Between the tool and work, machining zone is flooded with hard abrasive particles generally in the form of water based slurry. As the tool vibrates over the work piece, abrasive particles acts as indenter and indent both work and tool material. Abrasive particles, as they indent, the work material would remove the material from both tool and work piece.
Ultrasonic Machining consists of: High Power sine wave generator Transducer (^) Piezo electric transducer (^) Magneto-stricitve transducer Tool Holder Tool Abrasive slurry
These transducer generate a small electric current when they are compressed. When the current is removed, crystal attains its original size and shape. Such transducers are available up to 900 Watts
It has a high-frequency winding wound on a magnetostrictor core and a special polarizing winding around an armature. Magnetostriction is a property of ferromagnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of material's magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ. The effect was first identified in 1842 by James Joule at Manchester when observing a sample of
The tool vibrates in its downward stroke, it strikes the abrasive particles. Tools are made of relatively ductile materials like Brass, Stainless steel or Mild steel
The abrasive is carried in slurry of water with 30-60% by volume of the abrasives. It acts as an acoustic bond between the vibrating tool and the workpiece, to give efficient transfer of energy between the two. It acts as a coolant on the tool face.
OPERATIONS OF ULTRASONIC CUTTING As the tool vibrates with a specific frequency, abrasive slurry (usually a mixture of abrasive grains and water of definite proportion) is made to flow through the tool work interface. The impact force arising out of vibration of the tool end and the flow of slurry through the work tool interface actually causes thousands of microscopic abrasive grains to remove the work material by abrasion. Material removal from the hard and brittle materials will be the form of sinking, engraving or any other precision shape.
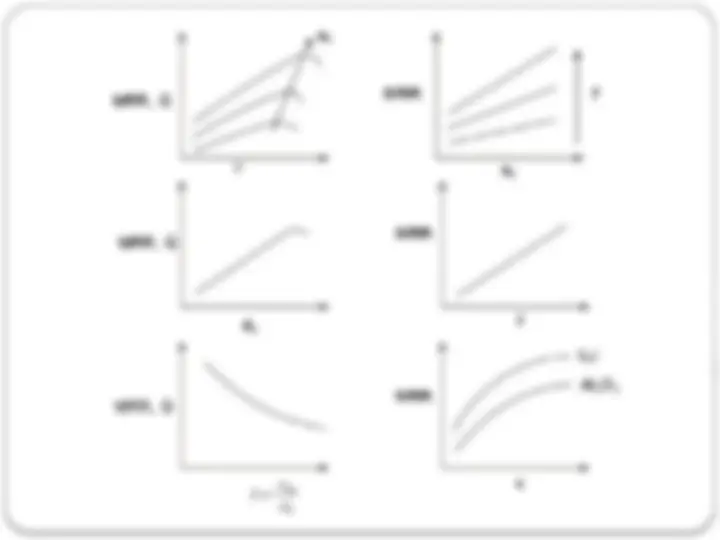
Amplitude of vibration (a0) ( 15 to 50 microns) Frequency of vibration (f) (19 to 25 kHz). Feed force (F) related to tool dimensions Feed pressure (p) Abrasive size Abrasive material: Al203, SiC, B4C, Boron silicarbide, Diamond. Flow strength of the work material Flow strength of the tool material Contact area of the tool (A) Volume concentration of abrasive in water slurry (C) Tool Material of tool Shape Amplitude of vibration Frequency of vibration Strength developed in tool Work material Material Impact strength Surface fatigue strength Slurry Abrasive – hardness, size, shape and quantity of abrasive flow Liquid – Chemical property, viscosity, flow rate Pressure Density