















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An introduction to java programming, covering the basics of types, variables, operators, and assignments. It includes examples of cpu instructions, programming languages, compiling java, and writing simple java programs. Students will learn how to declare variables, perform assignments, and use operators for simple computations.
Typology: Slides
1 / 23

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
















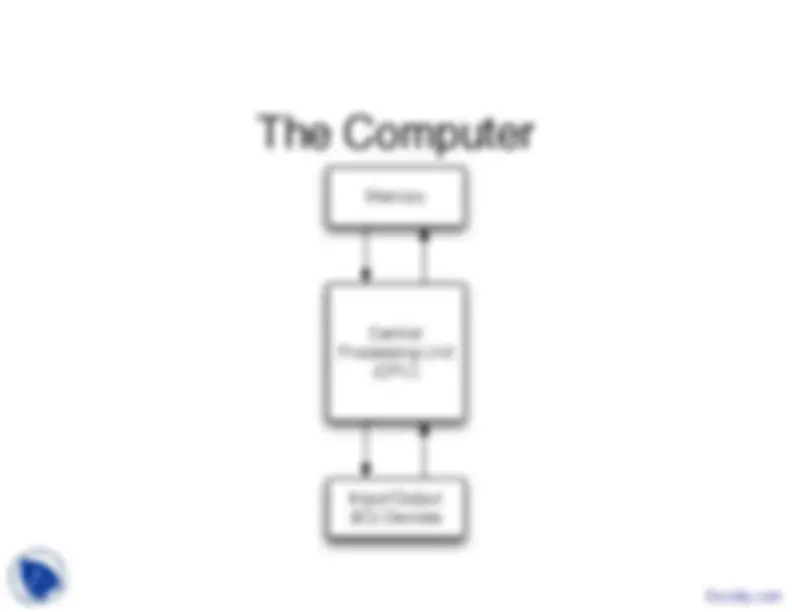
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Input/Output (IO) Devices
Memory
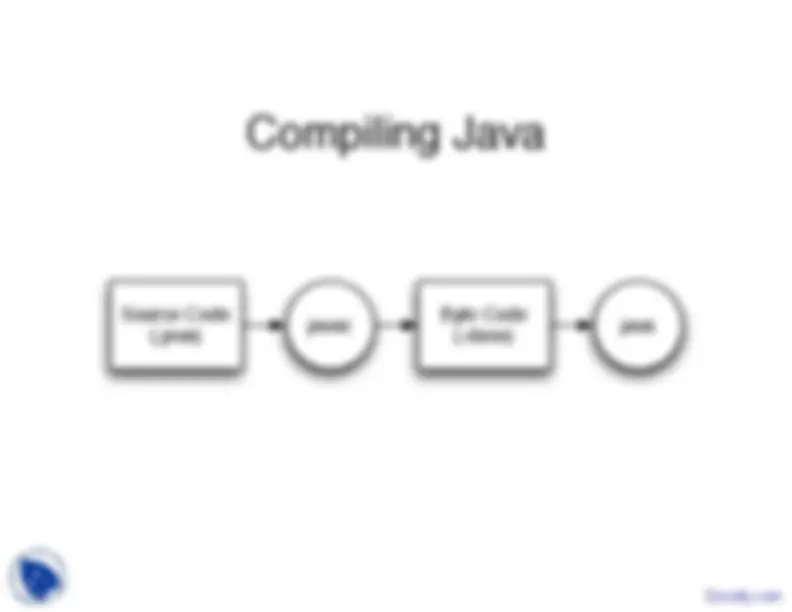
Source Code (.java)
Byte Code javac (^) (.class) java
class CLASSNAME {
public static void main ( String [] arguments ) { STATEMENTS }
}
class Hello3 {
public static void main ( String [] arguments ) { String foo = "IAP 6.092" ; System. out. println ( foo ); foo = "Something else" ; System. out. println ( foo ); }
}
Follows standard math rules: