













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This presentation is part of Solid State Physics course requirement at Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology. It includes: Zinc, Blende, FCC, Lattice, Crystal, Structure, Formation, Tetrahedrally, Cordinated, Closest-packed
Typology: Slides
1 / 21

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!














Observed by the French chemist Théodore Sidot in 1866.
Presented by the renowned chemist A. E. Becquerel.
It was used by Ernest Rutherford in the early years of Nuclear Physics.
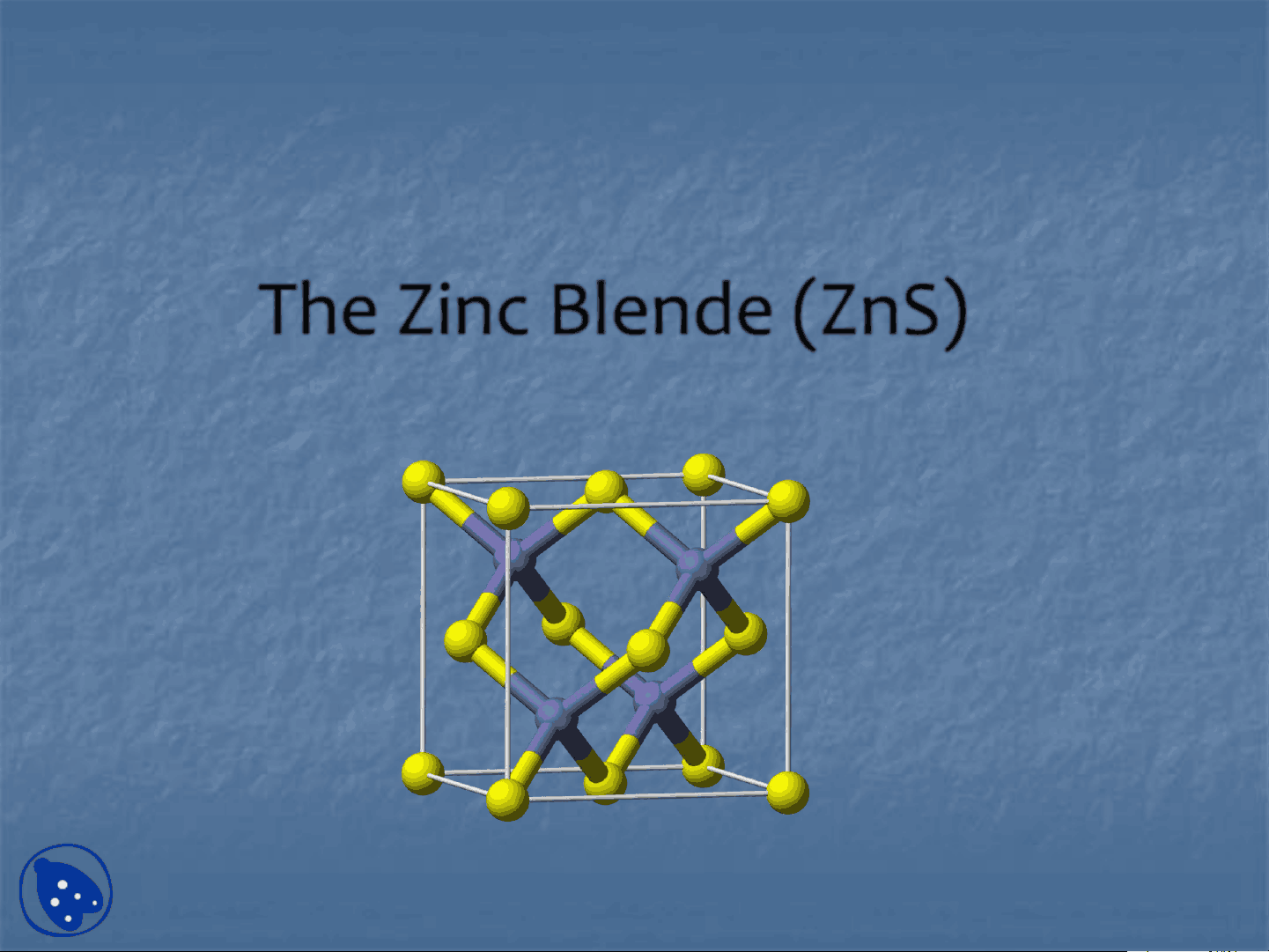
Zinc Blende (ZnS)
Calamine or Zinc Spar ( ZnCO3)
Zincite ( ZnO)
Name: Zinc Symbol: Zn Atomic number: 30 Atomic weight: 65. Standard state: solid at 298 K Group in periodic table: 12 Block in periodic table: d- block Colour: bluish pale grey Classification: Metallic
Name: Sulfur Symbol: S Atomic number: 16 Atomic weight: 32. Standard state: solid at 298 K Group in periodic table: 16 Group name: Chalcogen Period in periodic table: 3 Block in periodic table: p-block Colour: lemon yellow Classification: Non-metallic
Yellow colored powder
It is in the form of sphalerite having a cubic structure
If the sulfide ions originally adopt a hexagonal closest-packed structure , the ZnS crystal is wurtzite. If the sulfide ions originally adopt a cubic closest-packed structure , the ZnS crystal is zinc blende.
Both sphalerite and wurtzite are intrinsic, wide- bandgap semiconductors. The cubic form has a band gap of 3.54 eV at 300 K whereas the hexagonal form has a band gap of 3.91 eV. The transition from the sphalerite to the wurtzite form occurs at around 1020 °C.
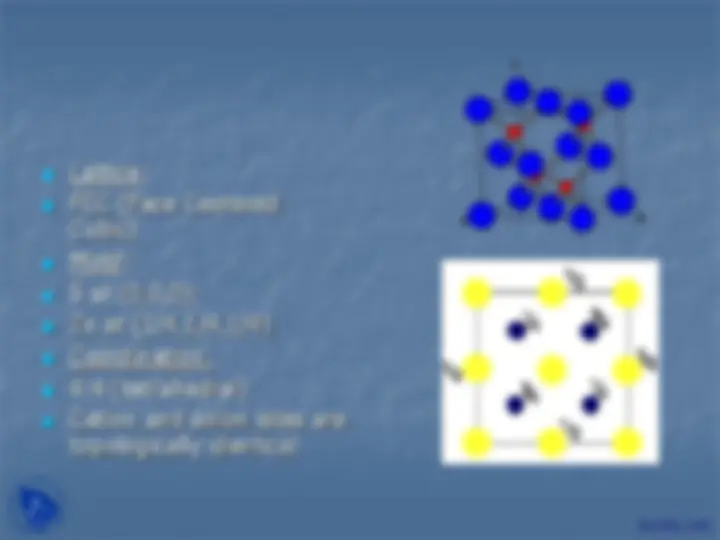
Lattice: FCC (Face Centered Cubic) Motif: S at (0,0,0); Zn at (1/4,1/4,1/4) Coordination: 4:4 (tetrahedral) Cation and anion sites are topologically identical
The two most important sources are the Chivera mine, Cananea, Sonora, Mexico ; and the Picos de Europa, Cordillera Cantabrica , near Santander on Spain's northern coast.
Used in Nuclear Physics.
Used in Cathode Ray tubes.
It also exhibits phosphorescence due to impurities on illumination with blue or ultraviolet light.
Zinc sulfide is also used as an infrared optical material
It can be used planar as an optical window
It is made as microcrystalline sheets
It can be doped as both n-type semiconductor and p-type semiconductor