















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This is project presentation for Management Practices course at Dayalbagh Educational Institute. It includes: Nature, Source, Competitive, Advantage, Sustaining, Types, Cost, Differentiation, Strategic, Innovation
Typology: Slides
1 / 24

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

















OUTLINE
Competitive Advantage from Internally-
Generated Change: Strategic Innovation
Identification - Obscure superior performance
Sources of Competitive Advantage
COST ADVANTAGE
DIFFERENTIATION ADVANTAGE
COMPETITIVE
ADVANTAGE
Porter’s Generic Strategies
SOURCE OF COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE Low cost Differentiation
Industry-wide COST DIFFERENTIATION
COMPETITIVE LEADERSHIP
SCOPE
Single Segment F O C U S
OUTLINE
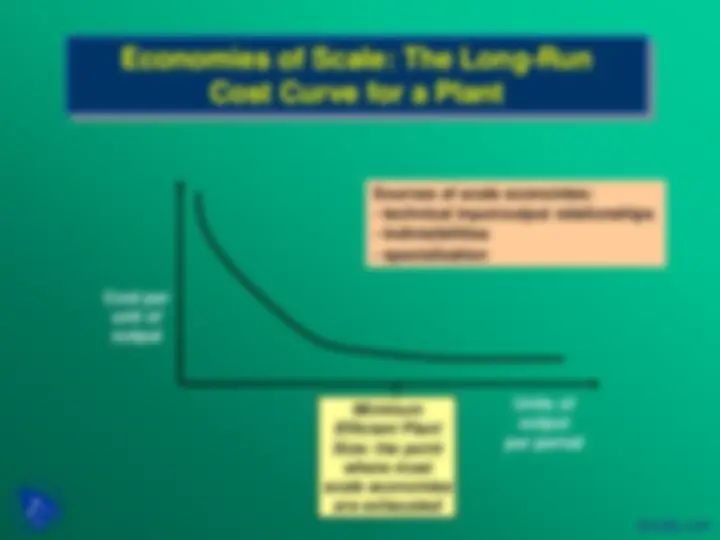
The Experience Curve
The “Law of Experience”
The unit cost value added to a standard product declines by a constant % (typically 20-30%) each time cumulative output doubles.
Cost per unit of output (in real $)
Cumulative Output
The Importance of Market Share
0-10 10-20 20-30 30-40 over 40 Market Share (%)
Drivers of Cost Advantage
The Costs Developing New Car Models
$ billion
GM Saturn 5
Ford Taurus (1996 model) 2. Ford Escort (new model 1996) 2
Renault Clio (1999 model) 1.
Chrysler Neon 1.
Honda Accord (1997 model) 0.
BMW Mini 0.
Rolls Royce Phantom (2003 model) 0.
10 20 50 100 200 500 1, Annual sales volume (millions of cases)
Advertising Expenditure ($ per case)0.
Pepsi Coke
Seven Up
Sprite^ Dr. Pepper
Diet Pepsi
Tab
Fresca
Diet Rite
Diet 7-Up
Schweppe s (^) SF Dr. Pepper
Despite the massive advertising budgets of brand leaders Coke and Pepsi, their main brands incur lower advertising costs per unit of sales than their smaller rivals.
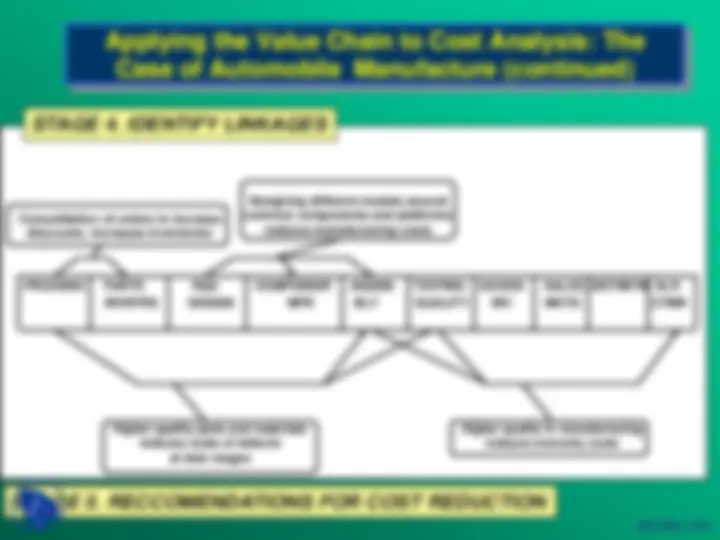
STAGE 1. IDENTIFY THE PRINCIPAL ACTIVITIES
STAGE 2. ALLOCATE TOTAL COSTS
PURCH- ASING
PARTS INVEN- TORIES
R&D DESIGN ENGNRNG
COMPONENT MFR
ASSEMBLY
TESTING, QUALITY CONTROL
GOODS INVEN- TORIES
SALES & MKITG
DISTRI- BUTION
DEALER & CUSTOMER SUPPORT
PURCH- ASING
PARTS INVEN- TORIES
R&D DESIGN ENGNRNG
COMPONENT MFR ASSEMBLY^
TESTING, QUALITY CONTROL
GOODS INVEN- TORIES
SALES & MKITG
DISTRI- BUTION
DEALER & CUSTOMER SUPPORT
--Plant scale for each -- Level of quality targets -- No. of dealers component -- Frequency of defects -- Sales / dealer -- Process technology -- Level of dealer -- Plant location support -- Run length -- Frequency of defects -- Capacity utilization under warranty
Prices paid --Size of commitment -- Plant scale --Cyclicality & depend on: --Productivity of -- Flexibility of production predictability of sales -- Order size R&D/design - - No. of models per plant --Customers’ --Purchases per --No. & frequency of new -- Degree of automation willingness to wait supplier models -- Sales / model -- Bargaining power -- Wage levels -- Supplier location -- Capacity utilization
STAGE 3. IDENTIFY COST DRIVERS