




























































































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Defination Of Contract, Essentials Of Contract, Consideration, Capacity,
Typology: Slides
1 / 122

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





























































































CONTRA CONTRA CT CT
person made a proposal, when he signifies to another his willingness to do or to abstain from doing something. AGREEMENT = OFFER + ACCEPTANCE
According to Sec.13, meeting of minds or identity of minds or receiving the same thing in same sense at same time.
Agreement Legal Obligation Contract
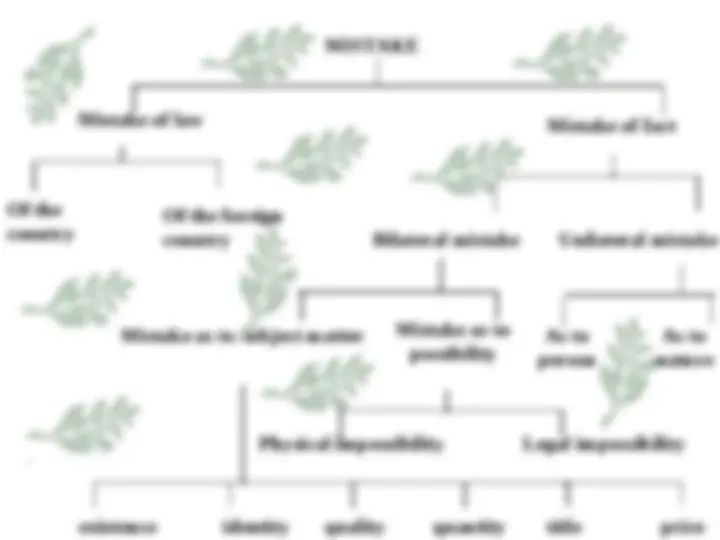
TYPES OF CONTRACTS TYPES OF CONTRACTS VALID CONTRACTS Absolute contract Contingent contract(Sec. 31-36) Express contract Implied/Quasi contract(Sec.68- 72)
Valid contract - If all the condition are fulfilled it is called as a valid contract. Contingent contract - In a contract to do or not to do something, if an event is collateral, does or doesn't happen. Express contract - When contracts are either in writing or in oral. Implied contract - When contracts are neither in writing nor in oral. Absolute contract - A contract which is not dependent on fulfillment of any condition.
Executed contract - In a contract where both the parties have performed their obligation, there is remaining nothing to perform. Executory contract - In a contract where both the parties are yet to perform their obligation. Unilateral contract - In a contract one party has performed his obligation and other person is yet to perform his obligation. Bilateral contract - In a contract where both the parties have performed their
TYPES OF OFFER
Express offer - When offer is given to another person either in writing or in oral. Implied offer - When offer is given to another person neither in writing nor in oral. Specific offer - When offer is given to a specific person. General offer - When offer is given to entire world at a large.(Carlill Vs. Carbolic smoke ball Co.,)
LEGAL RULES FOR OFFER Offer must be given with an intention to create a legal relationship.(Balfour Vs. Balfour, 1919) Offer must be definite.(Taylor Vs. Portington : Terms of the contract were vague , Took house 285 per annum) There is a clear cut difference between offer, invitation to offer, invitation to sale. (Harris Vs. Nickerson)
Offer must be communicated. (Fitch Vs. Snedkar) Mere statement of price of price is not an offer.(Harvey Vs. Facey)