Download Understanding the Cash Flow Cycle and Working Capital Management and more Slides Finance in PDF only on Docsity!
The Cash Flow Cycle
Cash and Net Working Capital
• The cash flow cycle – where cash comes from…how it is used to
finance the operations of the firm…and how it is recovered and
how it grows over time is a crucially-important part of
understanding how a business functions.
Cash and Net Working Capital
Activities that Decrease Cash
• Decreasing long-term debt
• Decreasing equity
• Decreasing current liabilities
• Increasing current assets other than cash
• Increasing fixed assets
• Paying dividends
Operating Cycle
Operating cycle is the time period
between the acquisition of inventory and
when cash is collected from receivables.
Example of Exhaustion of the Liquid Resources of a
New Firm
A simple example of a $1.0 million equity investment in
a business levering additional financial resources
and the need to finance the growth of the
business leaving it exhausted of cash resources.
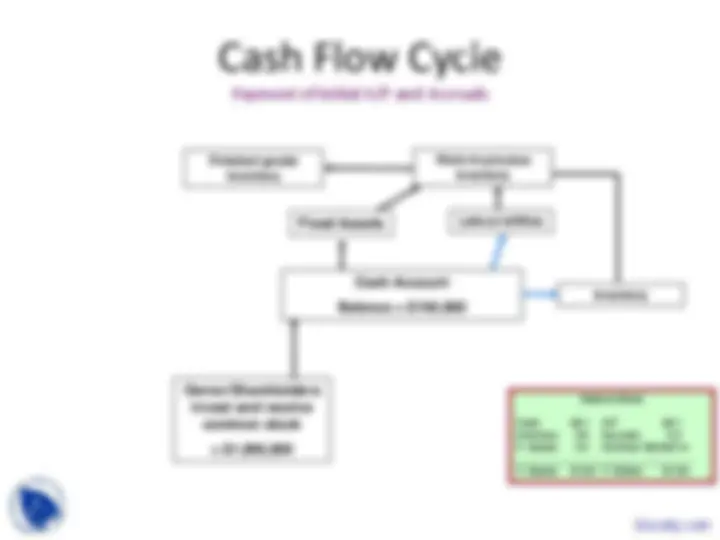
Cash Flow Cycle
Start
Cash Account
Balance = $
The entrepreneur opens a
current account in the name of
the business. Step 1
Cash Flow Cycle
Purchase of $500,000 Fixed Assets
Balance Sheet
Cash $0. F. Assets 0.5 Common Stock $1 m
T. Assets $1m T. Claims $1m
Cash Account
Balance = $500,
Owner/Shareholders
invest and receive
common stock
Fixed Assets
The firm purchases fixed
assets.
Step 3
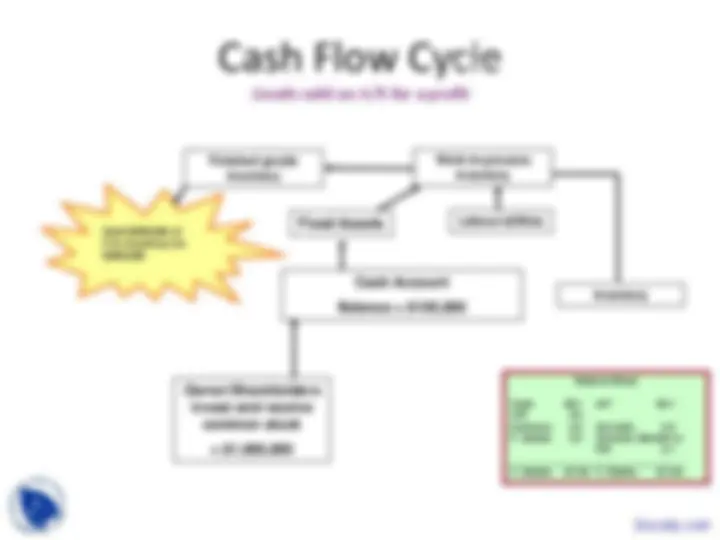
Cash Flow Cycle
Buy $300,000 of inventory on trade credit
Balance Sheet
Cash $0.5 A/P $0. Inventory 0. F. Assets 0.5 Common Stock $1 m
T. Assets $1.3m T. Claims $1.3m
Cash Account
Balance = $500,
Owner/Shareholders
invest and receive
common stock
Fixed Assets
Inventory
The firm purchases
$300,000 inventory from
suppliers. Step 4
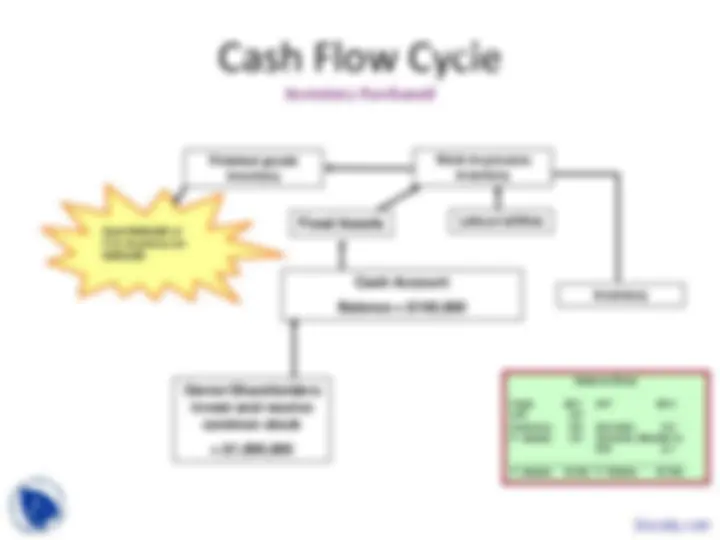
Cash Flow Cycle
Payment of initial A/P and Accruals
Balance Sheet
Cash $0.1 A/P $0. Inventory 0.8 Accruals 0. F. Assets 0.4 Common Stock$1 m
T. Assets $1.3m T. Claims $1.3m
Cash Account
Balance = $100,
Owner/Shareholders
invest and receive
common stock
Fixed Assets
Inventory
Work-in-process
inventory
Labour/utilities
Depreciation
Finished goods
inventory
Labour and suppliers are
paid.
Step 6
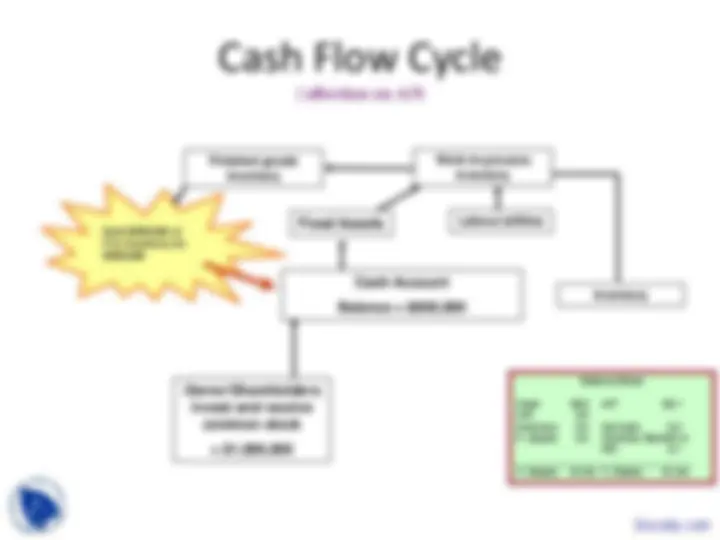
Cash Flow Cycle
Goods sold on A/R for a profit
Balance Sheet
Cash $0.1 A/P $0. A/R 0. Inventory 0.4 Accruals 0. F. Assets 0.4 Common Stock$1 m R/E 0.
T. Assets $1.4m T. Claims $1.4m
Cash Account
Balance = $100,
Owner/Shareholders
invest and receive
common stock
Fixed Assets
Inventory
Work-in-process
inventory
Labour/utilities
Depreciation
Finished goods
inventory
Sold $400,000 of F.G. Inventory for $500,
Sale of inventory occurs.
Accounts receivable
created. Cash resources
near exhausted. 30 days
till A/R collected.
Step 7
Cash Flow Cycle
Value Added to W.I.P. Inventory
Balance Sheet
Cash $0.1 A/P $0. A/R 0. Inventory 1.2 Accruals 0. F. Assets 0.4 Common Stock$1 m R/E 0.
T. Assets $2.2m T. Claims $2.2m
Cash Account
Balance = $100,
Owner/Shareholders
invest and receive
common stock
Fixed Assets
Inventory
Work-in-process
inventory
Labour/utilities
Depreciation
Finished goods
inventory
Sold $400,000 of F.G. Inventory for $500,
Value is added to inventory
through labour ($300,000)
and equipment ($100,000). Step 9
Cash Flow Cycle
Suppliers and Employees Paid
Balance Sheet
Cash $0.1 A/P $0. A/R 0. Inventory 0.4 Accruals 0. F. Assets 0.4 Common Stock$1 m R/E 0.
T. Assets $1.4m T. Claims $1.4m
Cash Account
Balance = -$
Owner/Shareholders
invest and receive
common stock
Fixed Assets
Inventory
Work-in-process
inventory
Labour/utilities
Depreciation
Finished goods
inventory
Sold $400,000 of F.G. Inventory for $500,
Firm pays suppliers and
employees.
Step 10
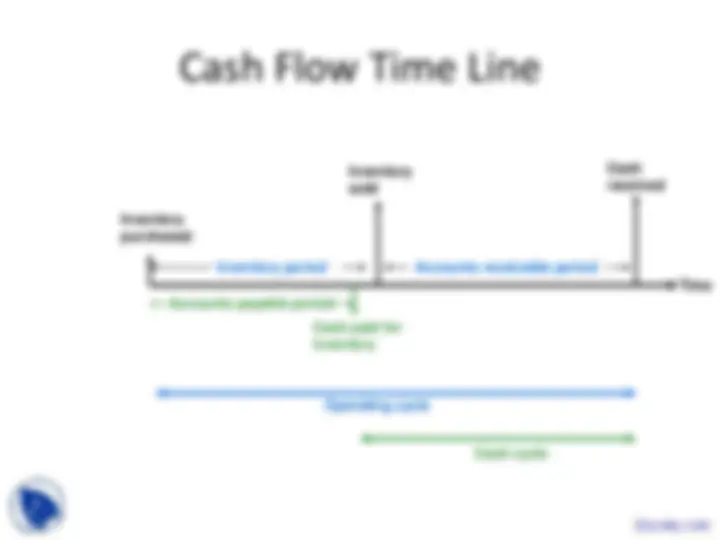
Cash Conversion Cycle
Cash Conversion Cycle = Inventory conversion period +
Receivables conversion period -
Payables deferral period
Management of the cash cycle can make an important difference in the
amount of financing required, assets employed to generate a given level
of sales...and therefore, can affect ROA and ROE.
Cash Flow Time Line
Inventory period
Inventory
sold
Cash
received
Inventory
purchased
Accounts receivable period
Operating cycle
Cash cycle
Cash paid for
inventory
Accounts payable period
Time