




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Main points of this past exam are: Sums Notation, Little Trickier, Sums Notation, Sequence Detector, State Machine, Finite State, Moore Machine, State Diagram, Karnaugh Maps, Flipflop Counter
Typology: Exams
1 / 5

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




Midterm 10/5/ Professor Pister
Note: problem 1 and 2 are a little trickier than last semester! Read carefully!
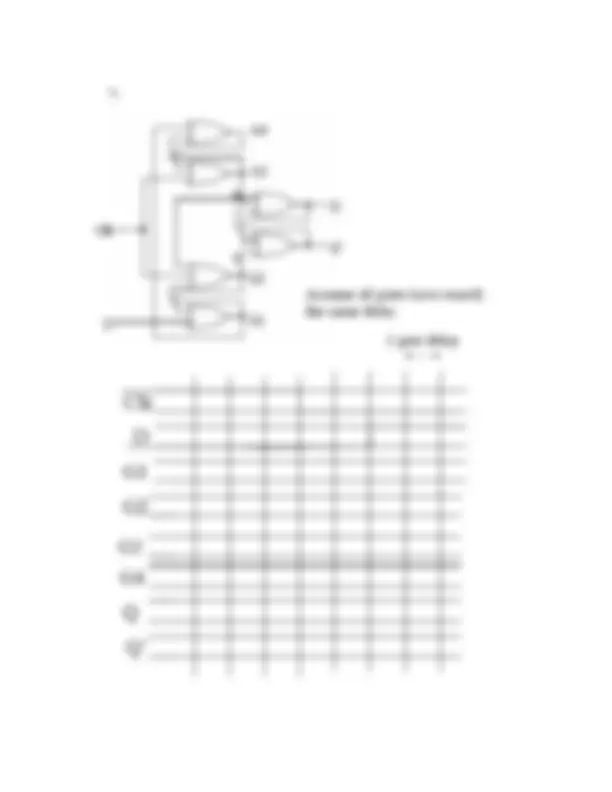
b. Implement F using as few 2 input NOR gates as possible. Assume that only the true literals (A,B,C,D) are available, not their complements(A’, B’, C’, D’).
b. Implement G using as few 2 input NAND gates as possible. Assume that only the true literals are available, not their complements.
b. Write a verilog module which would implement this FSM for input variable “In” and output variable “Out.” Use the same standard format as was presented in the Lab 3 lecture and used in Lab 3. (Define your states; use one always block for next state and output; use one always block for state transitions.
Mo 0
Ray 1
Star 0
Reset
a. Draw the state diagram and state transition table b. Draw the Karnaugh maps, clearly indicating the implicants that you use in your covers of the next-state functions. c. Implement the counter using D flip flops and whatever gates you like. d. Is your counter self starting? If yes, show the transitions of the unused states. If no, change it to make it self starting, and show the transitions of the unused states.