

































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The issue of sturgeon depletion in the caspian sea and the policies available to mitigate the losses of sturgeon stocks. Topics include the regulation of fishing and reduction in pollution, the use of hatcheries, and the management of transboundary fish stocks under external effects. The document also includes a numerical model for modelling fish population dynamics and harvesting.
Typology: Slides
1 / 42

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



































Habitat destruction: Loss of spawning grounds due to
dams, and possibilities of circumventing these
sturgeon
significant factor in decline of stocks Volgograd dam reduced the available grounds to 12% - lost all of Beluga grounds. Only on the Ural do sturgeon still reproduce naturally – but spawning population may have been destroyed by poaching and pollution
Water Pollution/ Oil spills
major ecological imbalance, especially in North severe effect on human health and both water and land quality. Effects on fish reproduction.
international cooperation is essential.
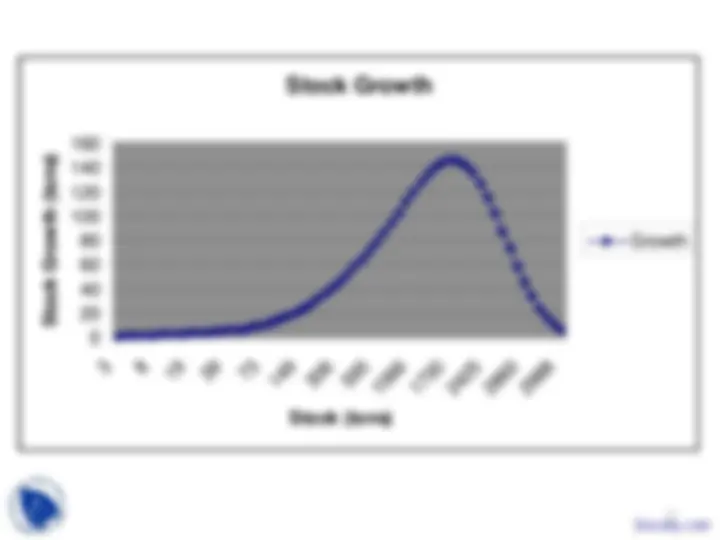
Modelling fish population
dynamics
10
(^) − C
S rS 1
11
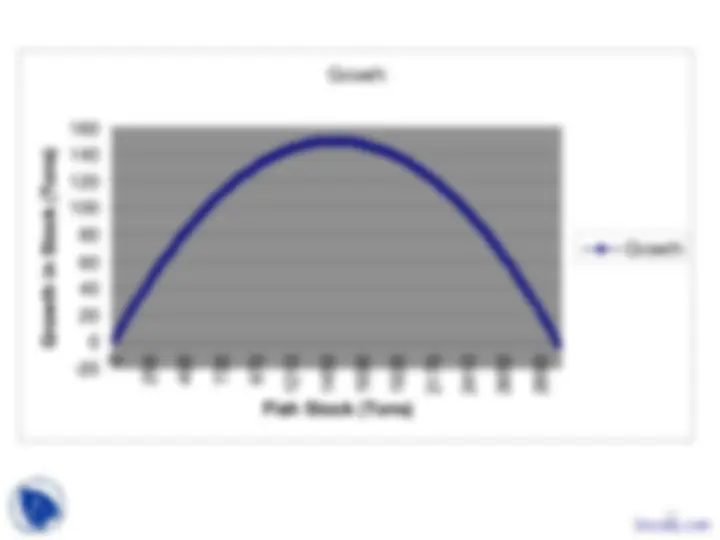
Growth
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
2 (^25049073097012101450169019302170241026502890) Fish Stock (Tons)
Growth in Stock (Tons)
Growth
The Optimal Effort Level
Converting levels of effort into the implied levels of total revenue^13
G
S
H 1 SS
H 4 SS (^) H 3 SS H 5 SS H 2 SS
$
E 1 E 2 E 3 E 4 E 5 E (^6)
H 6 SS
- Steady State Revenue
14
Identifying the profit maximising level of fishing effort
Effort E 1 E 2 E 3 E 4 E 5 E (^6)
- Total
π (^) max.
Total Revenue
External effects and the
management of transboundary fish
17
The socially optimal use of an environmentally polluting input
MEC
MEB
Q
$
Q * Q P
19
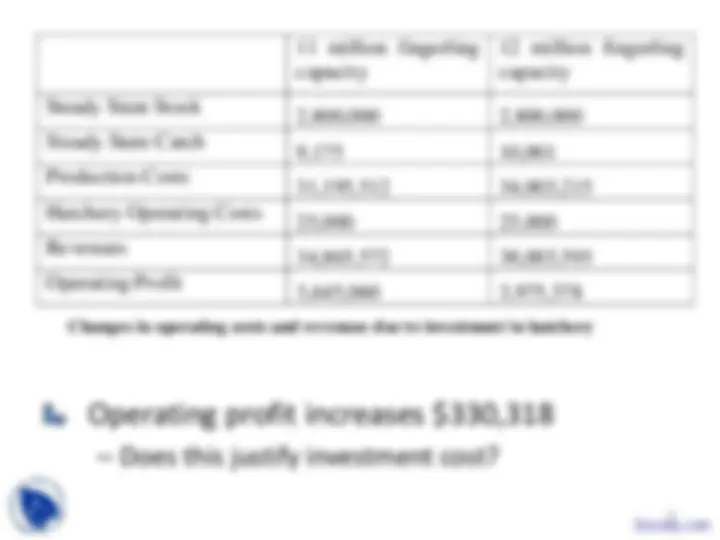
Privately optimal and socially optimal levels of investment in hatchery provision
External effects: implications for the management of Caspian Sturgeon