







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
These are the Lecture Slides of Thin Film Materials Processing which includes Vaporization, Vapor Pressure Curves, Thermal Desorption, Molecular Binding Energy, First Order Desorption, Desorption Rate, Real Surfaces, Diffusion of Gas Particles etc. Key important points are: Step Coverage of Cvd Films, Chemical Vapor Deposition, Flow Ofphospho-Silicate Glass, Contact Openings, Epitaxial Growth, Polycrystalline Silicon, Types of Cvd, Equipment Components, Wafer Heating System
Typology: Slides
1 / 12

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







Docsity.com
High Surface Migration rate
Conformal coating
Low Surface Migration Rate
Arrival Angle θ = 180° θ = 270°
θ = 90°
Docsity.com
Reflow - Allows the surface tension of the glass to draw back the edges of the contact openings
Surface tension of the film at high temperatures causes the edges to draw back, lowering the side wall angle.
Θ - reflow angle
a b
(a) SEM of dry-etched contact window before reflow, (b) Reflowed BPSG film with 4 wt.% P and 4 wt.% B. Reflow was 930°C in N 2 for 25 minutes
Reference: Silicon Processing for the VLSI Era Vol. 1 by Wolf and Tauber, page 191
Docsity.com
Literally means “arranged upon”
A continuation of the single crystal substrate which acts as the seed
Vapor Phase Epitaxy will be discussed here, as opposed to liquid or solid phase epitaxy
Allows lightly doped layers to be grown on top of heavily doped material, which is impossible through diffusion.
Thickness Range
Fast digital devices (3.3V) Power Analog, 100’s of Volts
Doping Range
Docsity.com
Polycrystalline silicon - Deposition from Silane at 610°C, amorphous silicon occurs if the temperature is reduced to ~550°C. The use of disilane would allow the deposition temperature to be reduced even further. No insitu doping of the polysilicon. Good uniformity
Silicon Nitride - Deposition from ammonia and dichlorosilane at ~800°C. Good uniformity
Oxide - Deposition from silane and oxygen at ~400°C. No insitu doping of the oxide films, i.e. no PSG. Poor Uniformity, extremely large gas depletion effect.
Docsity.com
Epitaxy - “Arranged Upon”
APCVD - Atmospheric Pressure CVD
LPCVD - Low Pressure CVD
PECVD - Plasma Enhanced CVD
MOCVD - Metal Organic CVD
Process Advantages Disadvantages
APCVD Simple Reactor Poor Step Coverage Fast Deposition Particle Contamination Low Temperature
LPCVD Excellent Purity High Temperatures Excellent Uniformity Low Deposition Rate Conformal Step Complex Reactor Coverage Large Wafer Capacity
PECVD Low Temperature Chemical and Particulate
Fast Deposition Contamitation Good Step Coverage Complex Reactor
Docsity.com
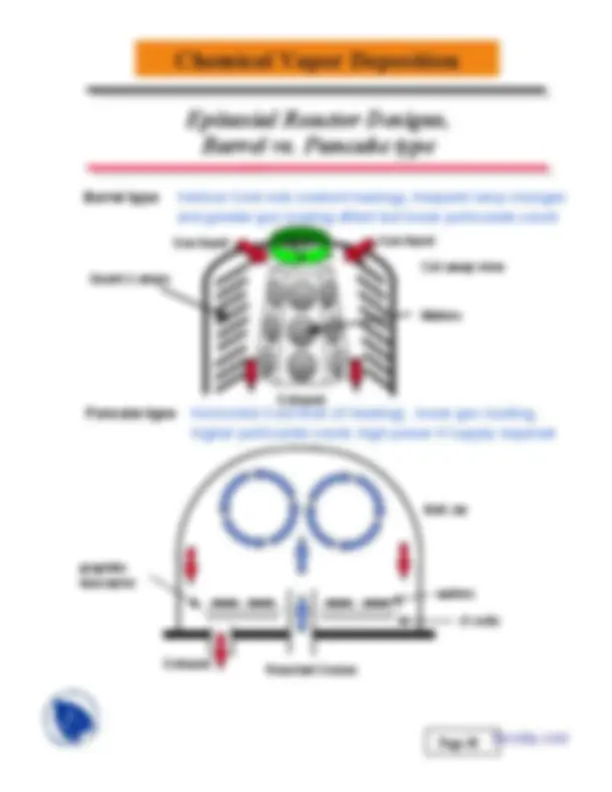
Horizontal Cold Wall (rf heating), lower gas loading, higher particulate count, high power rf supply required
Pancake type
Vertical Cold wall (radiant heating), frequent lamp changes and greater gas loading effect but lower particulate count
Barrel type
wafers
rf coils
graphite susceptor
Bell Jar
Quartz Lamps
Gas Input
Wafers
Cut-away view
Gas Input
Exhaust
Exhaust (^) Reactant Gases
Docsity.com
Vacuum Pump
Burn Box
~ 200 mTorr
gas monitor “sniffer”
Building Exhaust
Docsity.com