































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This lecture was delivered by Pooja Rathore at Anand Agricultural University for Training and Development course. It includes: Special, Issues, Training, Employee, Development, Trainers, Instructional, System, Legal, External, Environment
Typology: Slides
1 / 38

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!































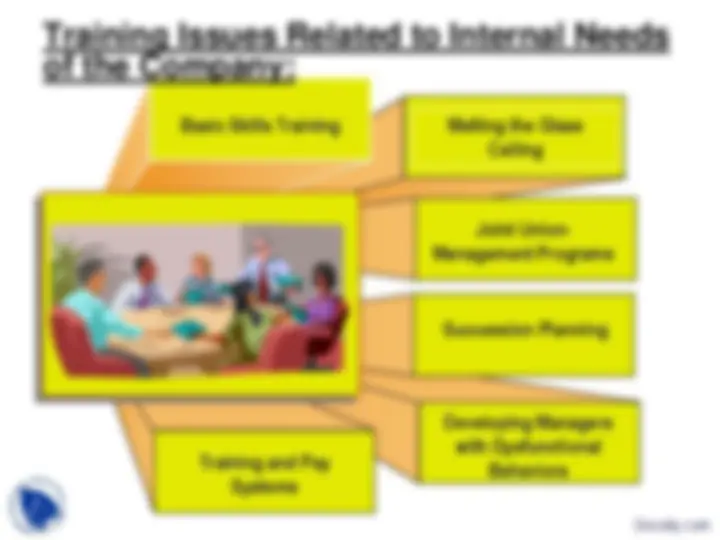
Trainers are often forced to deal with a
wide variety of important issues that fall
outside the traditional discussion of the
components of instructional system
design.
Time Orientation
To prepare employees
for cross-cultural
assignments,
companies need to
provide cross-cultural
training.
phases:
parent company and country from the foreign assignment
experience high levels of stress and anxiety when they return because of the changes that have occurred since their departure
company because the assignment they are given upon return has less responsibility, challenges, and status than the foreign assignment
manage the repatriation process
Implications of Cultural Dimensions for Training Design:
Cultural Dimension
Implications
Power Distance Culture high in power distance expects trainer to be expert. Trainers expected to be authoritarian and controlling of session.
Time Orientation Culture with long-term orientation will have trainees who are likely to accept development plans and assignments.
environment that allows all employees to contribute to organizational goals and experience personal growth
The goals of diversity training are:
managerial practices that inhibit employees’ personal development.
organizational goals regardless of their race, age, physical condition, sexual orientation, gender, family status, religious orientation, or cultural background.
How Managing Cultural Diversity Can Provide Competitive Advantage
Argument Rationale