






Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
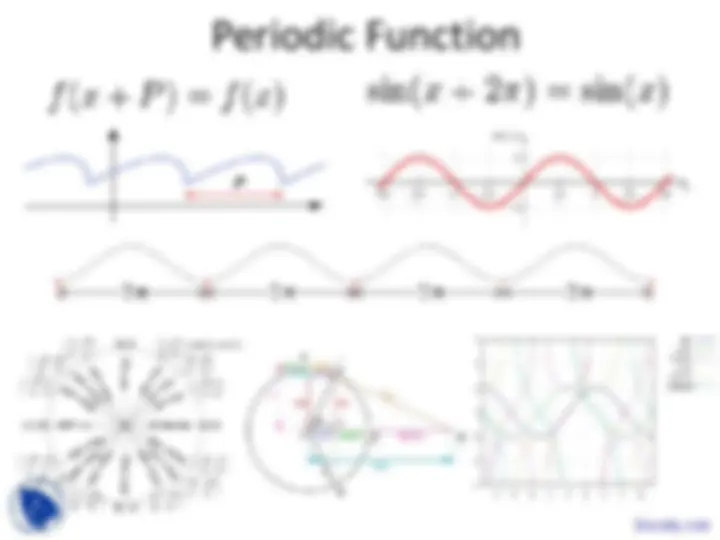
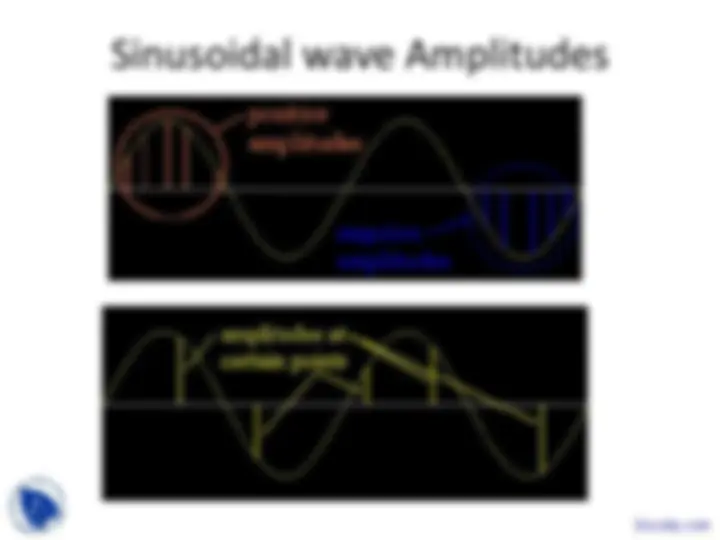
In the course of introduction to geophysics, The key points are:Sine and Cosine, Rim, Rotating Wheel, Components, Degree and Radians, Unit Circle, Arclength, Sinusoidal Wave Amplitudes, Points, One Cycle Apart
Typology: Slides
1 / 21

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!














θ θ θ θ θ θ θ θ
° ° ° ° ° °
Equivalence relation
r
for unit circle r
π
π
°
°
s (m) = r (m) * θ (radians) arclength = radius * radians
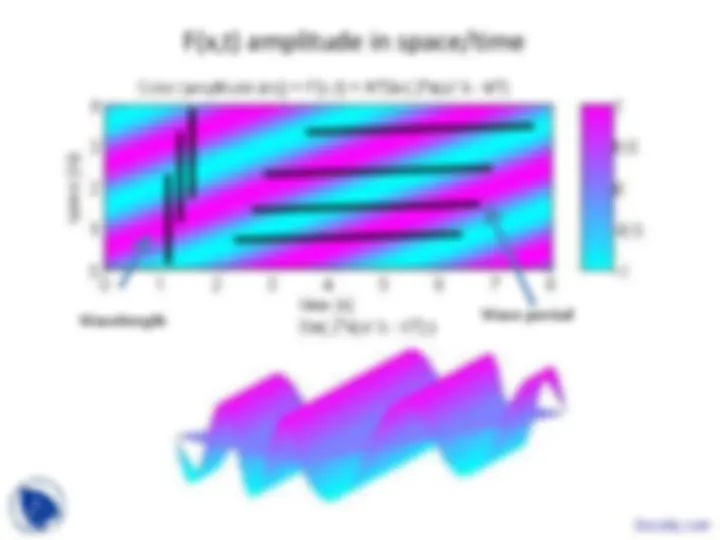
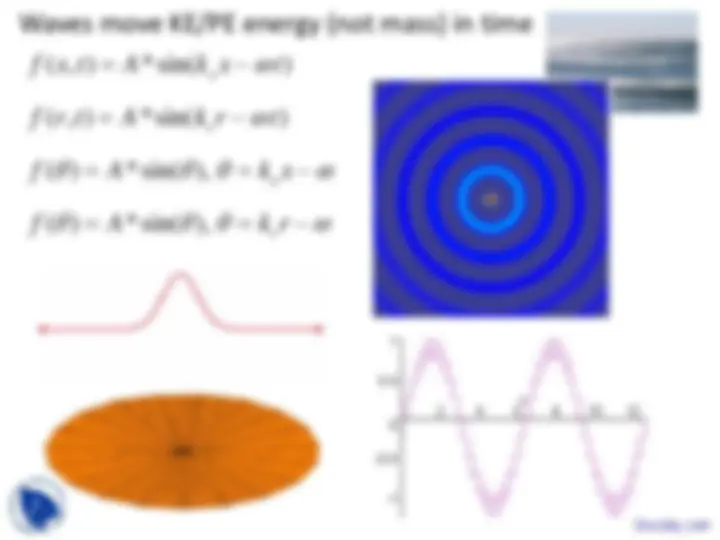
Wavelength (meters)
Wavelength defined between any two points on wave that are one cycle apart (2*pi radians).
e.g.,
Wavelength of a sine wave, λ, can be measured between any two points with the same phase, such as between crests, or troughs, or corresponding zero crossings as shown.
Wavelength Wave period
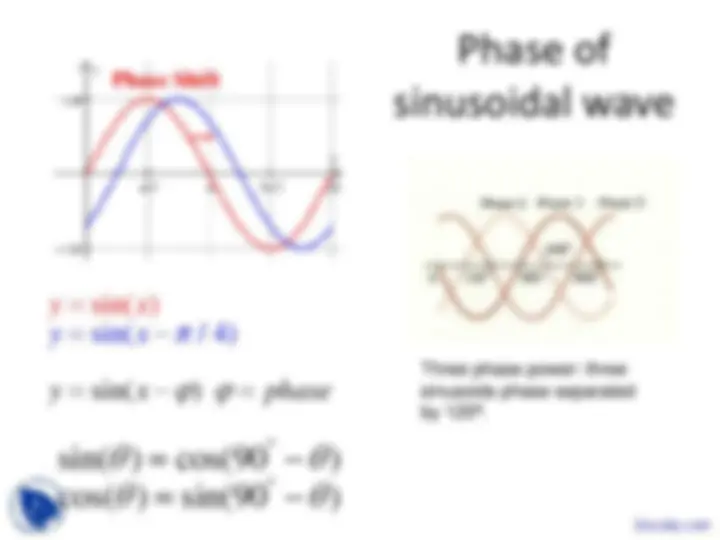
Three phase power: three sinusoids phase separated by 120⁰.
Phase advance/delay and Unit circle
( ) *sin( ( ))
:
f A f
initial phase
θ θ ψ
ψ
= − Note minus sign in phase argument.
The red sine phase is behind (negative) the blue line phase; hence, red sin function leads the blue sin function.
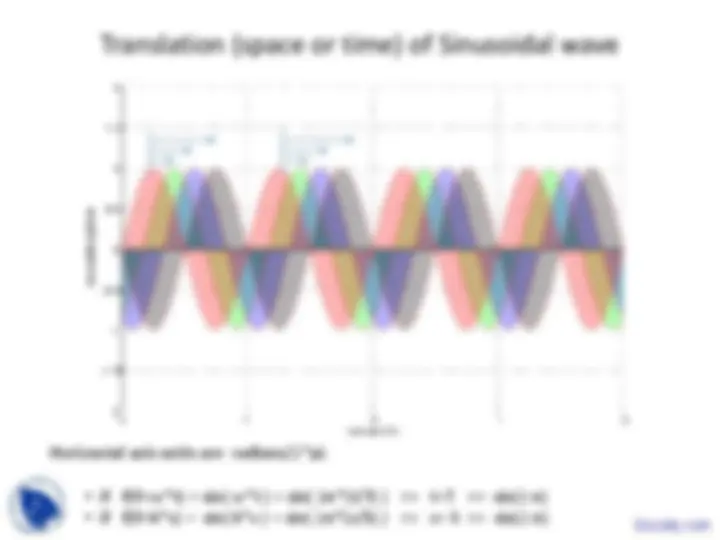
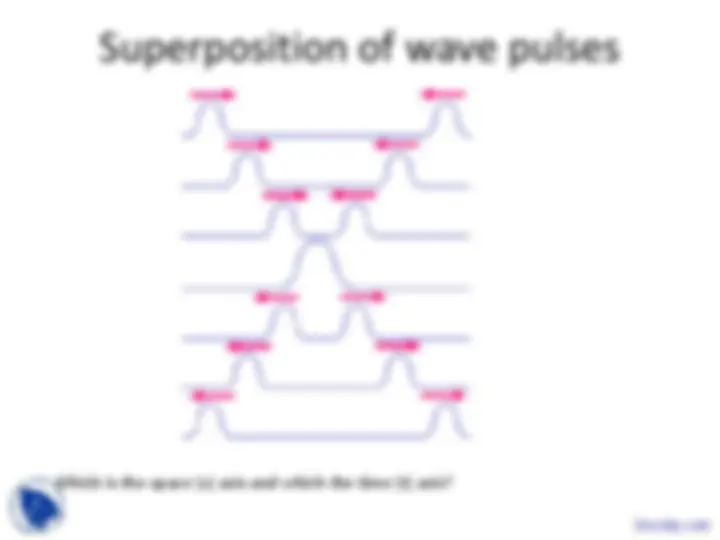
A pulse is a compact disturbance in space/time.
A sinusoidal wave is NOT compact, it is everywhere in space/time.
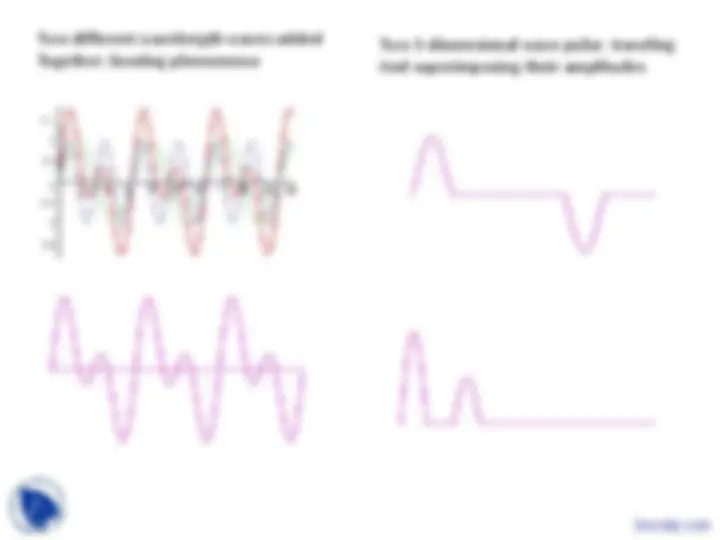
A pulse can be ‘built’ up mathematically as a sum of sinusoidal waves.
Which is the space (x) axis and which the time (t) axis?
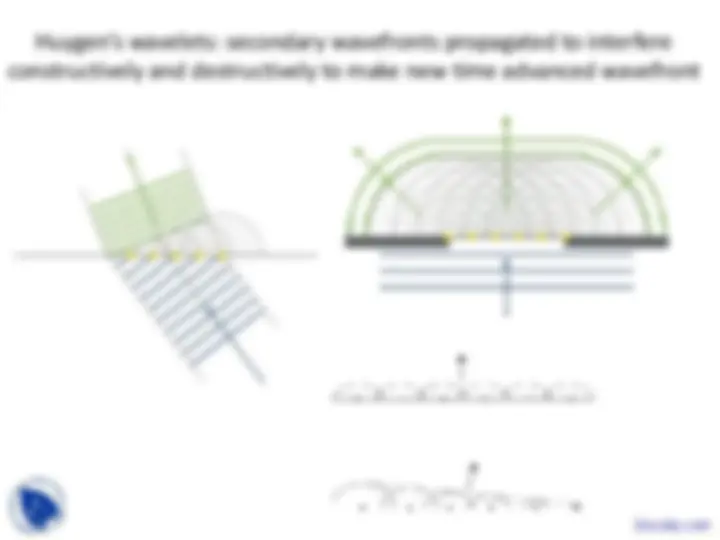
Huygen’s wavelets: secondary wavefronts propagated to interfere
constructively and destructively to make new time advanced wavefront
Standing waves on a string.
Fixed endpoint don’t move; wave is trapped.