







































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An introduction to simulation and modeling, explaining the concept of system imitation for understanding real-world systems. It covers the importance of models, simulation techniques, and their applications in various fields. Key topics include deterministic vs. Stochastic simulations, static vs. Dynamic models, and continuous vs. Discrete systems.
What you will learn
Typology: Study notes
1 / 49

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










































1
2
4
The term system is derive from the Greek word systema,which means an organized relationship among functioningunits or componentsunits or components.
System exists because it is designed to achieve one or moreobjectives.We come into daily contact with the transportation system
We
come into daily contact with the transportation system,
the telephone system, the accounting system, the productionsystem, and for two decades the computer system.
There are more than a hundred definitions of the word
There are more than a hundred definitions of the wordsystem, but most seem to have a common thread thatsuggests that a system is an orderly grouping ofinterdependent components linked together according to a
p
p
g
g
plan to achieve a specific objective.
5
Klir
Klir
gives a collection of 24 definitions one such
definition is “ A system is a collection ofcomponents wherein individual components are
t^
i^
d b
ti
i t
l ti
hi
h
constrained by connecting interrelationships suchthat the system as a whole fulfills some specificfunctions in response to varying demands” *Klir, George J. , an approach to general systems
theory New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Cotheory, New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co, 1969
7
It i
ll
ti
f^
titi
th t
t^
d i t
t
It
is a collection of entities that act and interact together toward the accomplishment of somelogical end (computer, network, communication
g
p
systems, queuing systems etc.)
It is an experiment in a computer where the realsystem is replaced by the execution of theprogram
It is a program that mimics (imitate) the behaviourof the real systemof the real system
t
ystem
· A system exists and operates in time and space.
Model · A model is a simplified representation of a system at
some particular point in time or space intended tosome particular point in time or space intended topromote understanding of the real system.
Simulation · A simulation is the manipulation of a model in such a
way that it operates on time or space to compress it,way that it operates on time or space to compress it,thus enabling one to perceive the interactions thatwould not otherwise be apparent because of theirseparation in time or space.
10
separation in time or space.
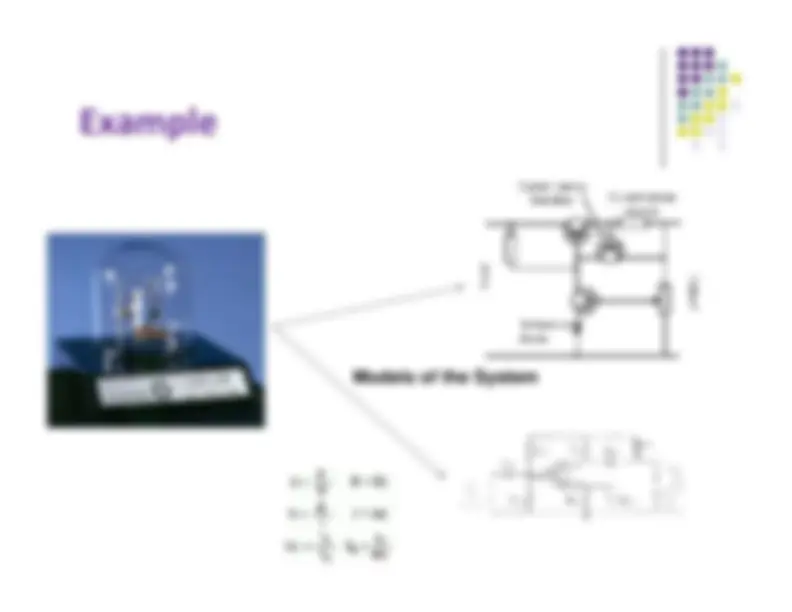
Models of the system
y
Real System (Motherboard)
Models of the System
Simulation is the representation of a real life
Simulation
is the representation of a real life
system by another system, which depicts theimportant characteristics of the real system and
ll
i^
t ti
it
allows experimentation on it.
In another word simulation is an imitation of thereality.
y
Simulation has long been used by theresearchers, analysts, designers and otherprofessionals in the physical and non physicalprofessionals in the physical and non-physicalexperimentations and investigations.
16
It may be too difficult, hazardous, or expensive to observe a real,
y
,^
,^
p
,
operational system
Parts of the system may not be observable (e.g., internals of asilicon chip or biological system) Uses of simulations
Analyze systems before they are built
Analyze systems before they are built
Reduce number of design mistakes
Optimize design
Analyze operational systems
Analyze operational systems
Create virtual environments for training, entertainment
17
S
t^
d l
S
ystem model
deterministic
stochastic
static
dynamic
static
dynamic
Monte Carlo
continuous
discrete
continuous
discrete
simulation
Discrete-event
simulation
Continuoussimulation
Discrete-event
simulation
Continuoussimulation
Simulation models can be classified as being static ordynamic, deterministic or stochastic and discrete orcontinuouscontinuous.
A static simulation model represents a system, which doesnot change with time or represents the system at a particularpoint in time.p
Dynamic simulation models represent systems as theychange over time.
Deterministic models have a known set of inputs, which
p
,
result into unique set of outputs.
In stochastic model, there are one or more random inputvariables, which lead to random outputs.
System in which the state of the system changescontinuously with time are called continuous systems whilethe systems in which the state changes abruptly at discrete
i t
i^
ti
ll d di
t^
t
20
points in time called discrete systems.