




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS QUIZ 1 ECE SUNJECT-ELECTRONICS ECE COURSE-SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS YEAR-2025 PROFESOR-RAJESH.K Course Overview: This course introduces the fundamental concepts and mathematical tools used to analyze and process signals and systems. It lays the foundation for further study in areas like communications, control systems, signal processing, and electronics. Course Objectives: Understand different types of signals (continuous-time and discrete-time) and their properties. Analyze linear time-invariant (LTI) systems using convolution and system properties. Apply Fourier series, Fourier transform, Laplace transform, and Z-transform for signal and system analysis. Explore sampling theory and its implications in digital signal processing.
Typology: Quizzes
1 / 5

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




Ans:
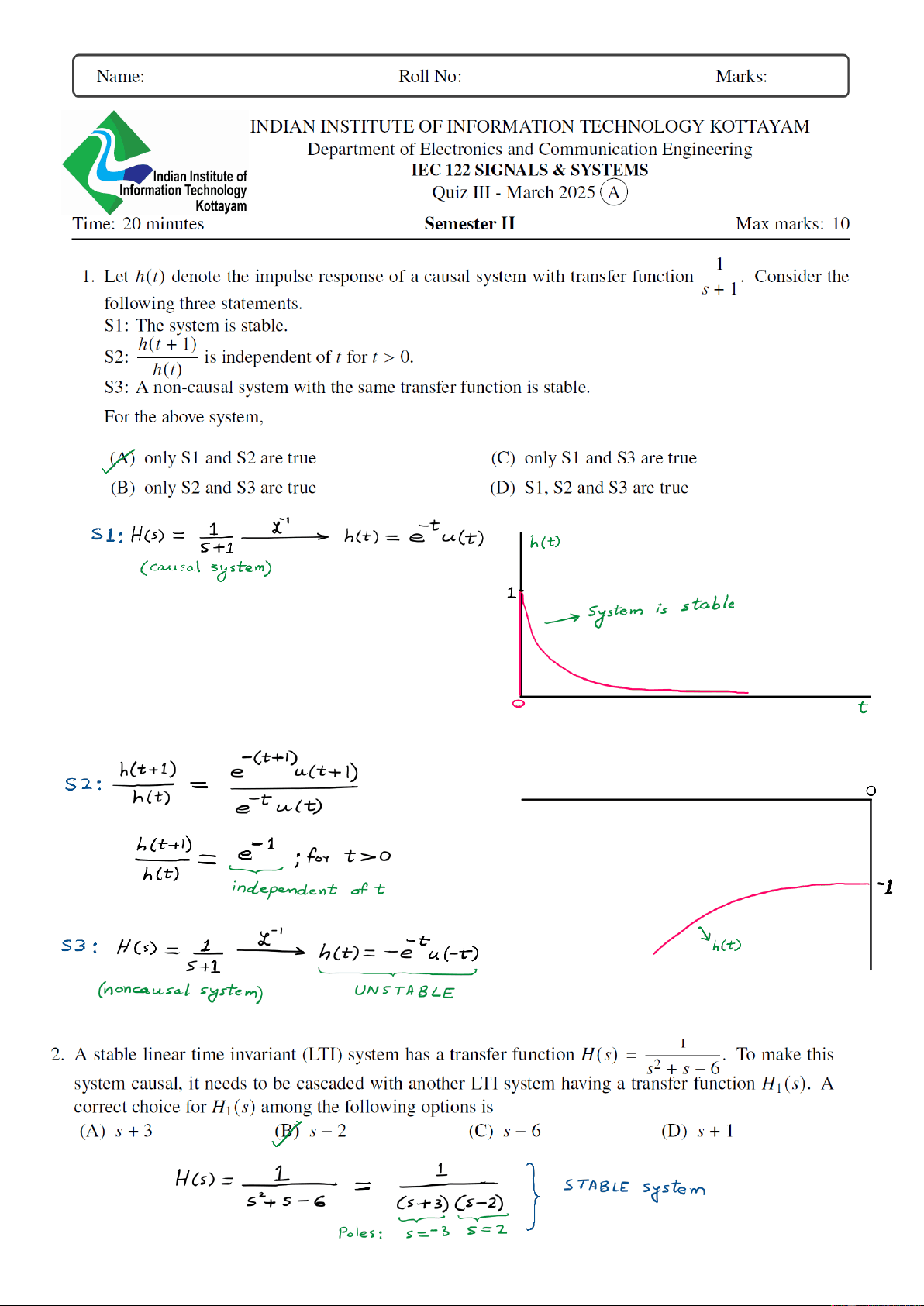
Name: Roll No: Marks: INDIAN INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY KOTTAYAM Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of TEC 122 SIGNALS & SYSTEMS Information Technology Quiz III - March 2025 (A) Kottayam ~~ Time: 20 minutes Semester IT Max marks: 1() . . . 1 . 1. Let A(t) denote the impulse response of a causal system with transfer function ——. Consider the y following three statements. S1: The system is stable. Ait+d). . 2: hl is independent of t for t > 0. $3: A non-causal system with the same transler function is stable. For the above system, VI only S1 and S2 are true (C) only SI and S3 are true (B) only $2 and $3 are true (D) S1, 82 and $3 are true Ans: A = 1 xt! _ oot Sl: He = Sq ON) = ee) Ccosssal system) h(t+1) _ oad ha) erucd bees) e! tfor THO h(t) ——~ indepemdent of t z= -1 S3: W@®= 2 4. pp Stu need S41 (honcausal sgstem) UNSTABLE 2. A stable linear time invariant (LTI) system has a transfer function H(s) = _—. To make this sets system causal, it needs to be cascaded with another LT! system having a transfer function H)(s). A correct choice for H)(s) among the following options is (A) s+3 (BS 5-2 (C) s-6 (D) s+1 Ans: 1 Hays —_1L = = STABLE system s4s-6 Cs+3) Cs—2) ee ee Poles: sard S52 To make the system both causal and stable, no poles of Hes) Shall lie on left-half of s-plane. Hence Cs-2) term in the denominator has fo be removedk using Hy €5)- H\G)=G-2) oe ) - LL. $+2 eos STABLE + CAUSAL 4 Hes Ganei Cc L 3. The transfer function of an LTI system is given by ay = var For the input r(f) = sin r, the y steady-state response c(/) is (A) 1 (B) scos t (C) S| in t+ = Ws —ssin (ft — V2 v2 ( 4 ) 4 Ans: Gwen the TF, Hos)= Sey it Res) s+i . L The. Prequency vesponse i's gen by Hy) = joi The input signal is Ct) = stn(t) wel Acjal= i > LHGw) = O-Tan (2) = —Tan() fost+4 [Hoe =tL 57 Hg) = -Ton'(/) = -Z Oo =F? ; Joost a vit)=sint DP} HGiw) p>