Partial preview of the text
Download SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS QUIZ 1 ECE and more Quizzes Signals and Systems in PDF only on Docsity!
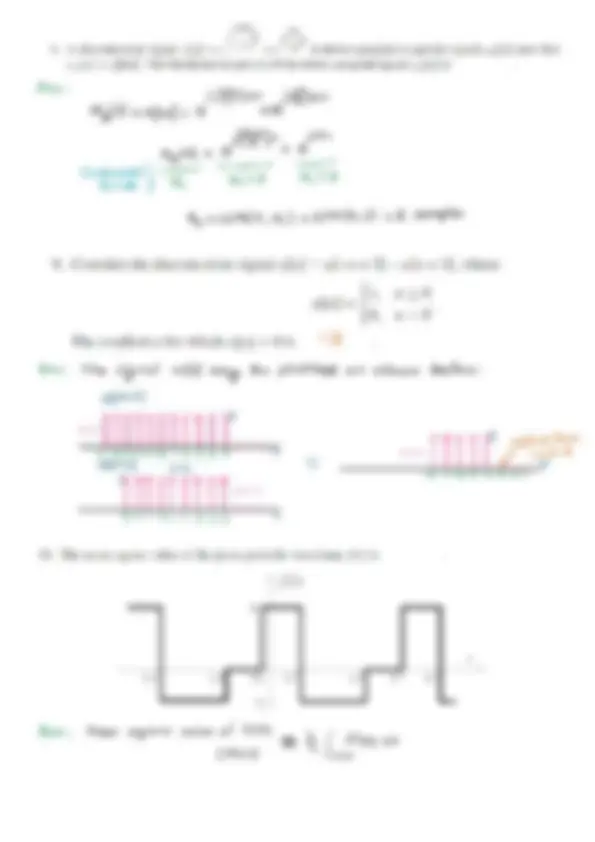
Name: Roll No: Marks: INDIAN INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY KOTTAYAM Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of IEC 122 SIGNALS & SYSTEMS Information Technology i7T- January 202 Kottayam Quiz I - January 2025 Time: 15 minutes Semester II Max marks: 10 . . 1, n=0,1.2.3.... 1. Consider the signal x[n] = sin(2zn)u[n], where u[n] = . 0, otherwise The period of this signal x[n] is (A) 4 (B) 3 (C) 2 PF! Ans; Fay n=O, ><(nJ=0 n=O : x[n) = sin(21.0) ufo] = Ox! =O xfoj n=i1 + xfn] = Sin (mt) ufi] = Ox! =O N=L! xo] = sinQam.2) uk] = Ox 1 =O . : “3-2-4 22345 2. A periodic signal x(t) of period T, is given by lL. |th Hi t Te Tr TU 7 A To Tt dic component of x(t) =4/ xe@ dt = £| at = L(t)” = 1-07) (ovevoge value) Tr en ey Tt OT Te jos 3. A system with input x(/) and output y(/) is defined by the input-output relation 2 y(t) = | x(t)dr The system will be (A) causal, time-invariant and unstable (C) non-causal, time-invariant and unstable (B) causal, time-invariant and stable er non-causal, time-variant and unstable gis future Cime Aes: Cawralty: Put t22/ a= fxcdde present = time Output signal depends on futuve values of input signal. Non-cavsat 7 Time Lavorionce + Deloyed xlt-to—y lt) = fx (t-te —D Input ' —% bout —2(t-t.) Outpe (= ylt-t) = [ xmdt —® Delceal 4: d f In QO, pet t-t,=r T— - 0% + A> ~ data=da Tn lt A Wt -t 72t-to _, © becomes y, = f xajyda —@ — 0 aro yay Time Vag ing Stability: Pat x(t)2u(t) (Bounded Input] =2t gO = fumar ~~ +00 #00 As t—-- yor = Jug@de = Jodt = 00 [Unbounded | ’ We = ° Unstable eo Total Enevgy of x,[)5 £y = Zac's 0-250-540-7574 Hors trostpo2st £y.,= 2:75 joules To tal Energy of x,[n) ; Ex, _ = |x Pell Pp 07s OS*4O.2S HO HORS Os EO-7e 4/* h=-0 &, = 3 “75 joules t a Ex, > Ex, 1 too 2 6. The integral tn in Pe /25(1 — 2t) dt is equal to 2n 1 els (B) els (C) —ne7 2 (D) 1 Nal 8V20 Av2n V2n Ans: §(t-2t) = S$ @(L-4) = 4 §G-*) [> Scat) = 450] = 1 §-t) [--&@ is an even function] <3 = fo 2 1 [ee th § (28) at = al tes $G-b)dt 6g —<& Aa Oxley §CE-Es) - Ewe _te® ~ 8\ar 7. The signal energy of the continuous-time signal x(t) = [(r- Du(t — 1)] — [@ — Dut - 2)] - [@ — 3)u(t - 3)] + [(t -— Fur - 4)] is Ans, The signal x (+) may be plotted as shown below: a(t) 1 + °° bo Energs E= [ixaldt = FO, MOO, YO _ SF joules Sa 3 3 3 Sa nt i{ =), i(—|n 8. A discrete-time signal x[”] =e ‘ BT ye ql is down-sampled to get the signal x z[m] such that a(n] =x[4n]. The fundamental period of the down-sampled signal xg[n] is Ans; j(S8)an J Zan < [>] = x(4n] =e +e J? ) n gan x, 0] = e +¢€ _—4 — Fundomental | ——— _ N, <2 Pert od No N,= 32 i f N, = LEM (N,,N,) = LOM (3,2) = 6 samples 9. Consider the discrete-time signal x[7] = u[—n + 5] — u[n + 3], where 1, n>0 my) co The smallest n for which x[n] =Qis__~3 Ans: The signal x fn] meoy be plotted as shawn below: ubars] L | | 1 etnJz 0 From “5-43-21 O12 34 5 n ose a -3 to % u(n+3] a) = n 4 < 4 -8 7-7 -G°5 “4 -32-2-1 “3-2-1 O12 345 n 10. The mean square value of the given periodic waveform f(f) is | nAC) Ans: Mean square value of £¢t) CMsv)