Download Understanding Stock Positions: Going Long vs. Short Selling and Sale Process and more Slides Finance in PDF only on Docsity!
Short and Long Positions
Going Long in A Stock
• This is a phrase used to describe buying a stock.
• It is also called a positive investment in the stock because
the buyer is optimistic that the price of the share will go
up…hence she is positive about the prospects for the
stock.
• Once the stock has risen in price, the buyer will sell the
stock (close out the position) in order to realize and lock
in their capital gain returns.
Street name
• Usually investors keep their shares in ‘street name’
- This means that they instruct their broker not to register the shares in
their name…but in the name of the brokerage firm.
- The shares usually stay in the brokerage firms inventory.
- The brokerage firm accounts show the investor that they own the
stock, but the issuing firm for the stock will have records that show the
brokerage firm as the owner.
- Shareholder information such as the annual reports, forms of proxy
and information circulars will all be sent to the brokerage firm. If the
investor wants that information passed along to them, they will have
to leave instructions with the brokerage firm to do so.
- Street name shares can be used to allow other brokerage clients to sell
short.
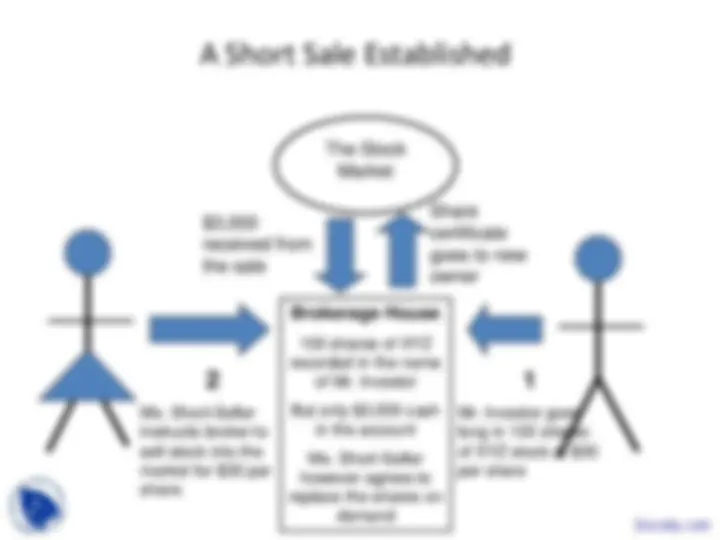
A Short Sale Established
Brokerage House
100 shares of XYZ recorded in the name of Mr. Investor
But only $3,000 cash in the account
Ms. Short-Seller however agrees to replace the shares on demand
2
Ms. Short-Seller instructs broker to sell stock into the market for $30 per share.
1
Mr. Investor goes long in 100 shares of XYZ stock at $ per share
The Stock
Market
received from
the sale
Share
certificate
goes to new
owner
The short sale details
- Since the shares are borrowed through the brokerage house from an investor who has a long position in the stock, the short seller risks that the borrowed stock will be sold by its owner; in this case, the short seller must repurchase and close the position at current (and potentially unfavourable market prices from the short-sellers point of view) unless further stock can be borrowed.
- Hence, the short seller’s strategy is at the mercy of the lender’s own investment decision.
- Short sellers must not only return the shares but also give the lender any dividends paid on the shares during the period of the short sale.
- Exchange rules permit short sales only after an UPTICK, that is, only when the last recorded change in the stock price is positive. - This rule is meant to stop waves of speculation against the stock
- Proceeds from a short sale must be kept on account with the broker…the short seller therefore cannot invest these funds to generate income.
- In addition, short sellers are required to post margin (which is essentially collateral) with the broker to ensure that the trader can cover any losses sustained should the stock price rise during the period of the short sale.
- The minimum margin requirement is 30 percent.