













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Sense organ Complete sense organ notes of human anatomy and physiology
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 35

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




























At the end of this lecture, student will be able to
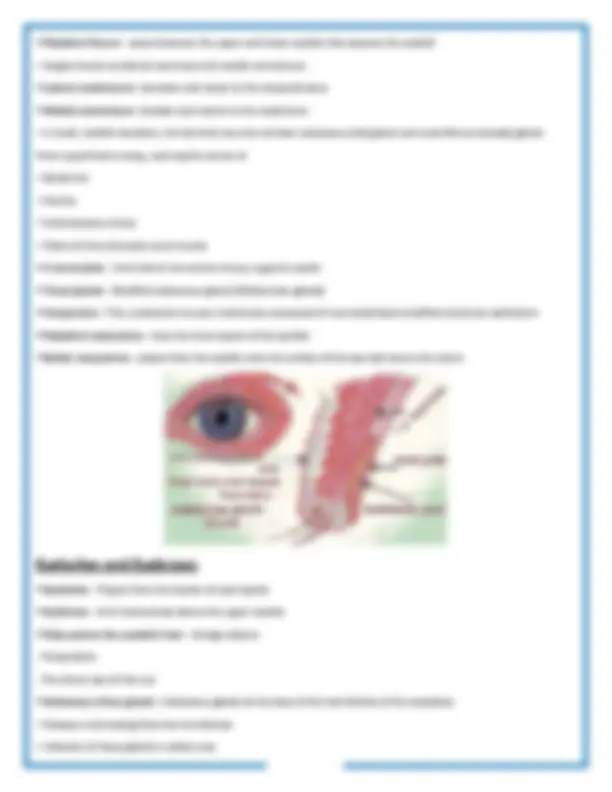
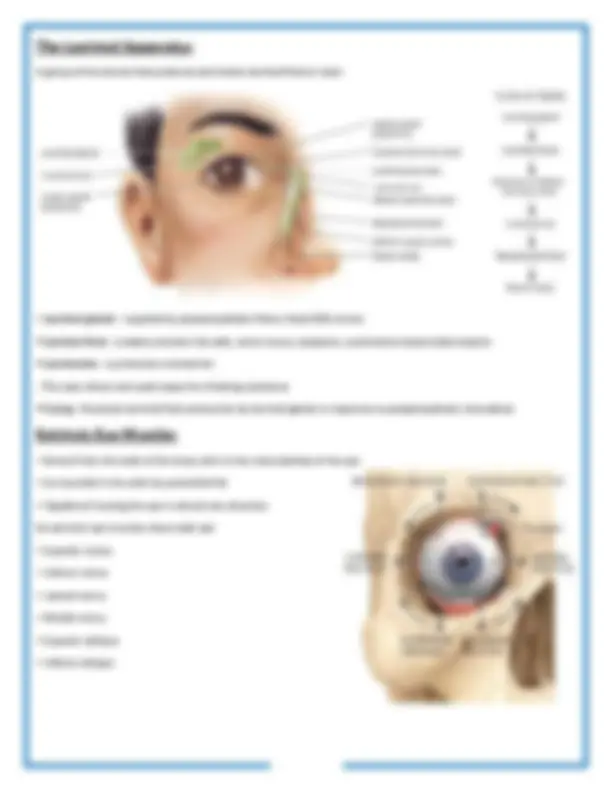
A group of structures that produces and drains lacrimal fluid or tears
Extrinsic eye muscles that move the eyeballs and upper eyelid
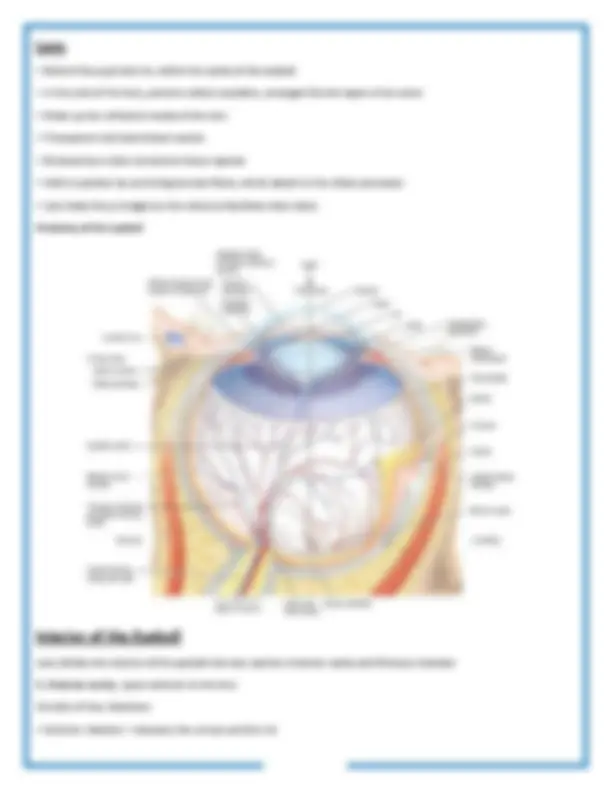
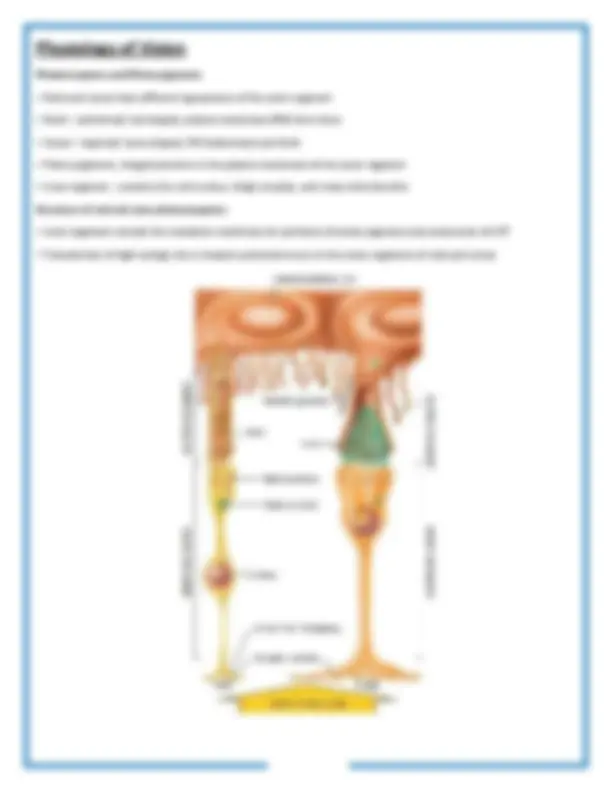
(3) Retina
Retina consists of a pigmented layer and a neural layer Pigmented layer Neural (sensory) layer
Three distinct layers of retinal neurons
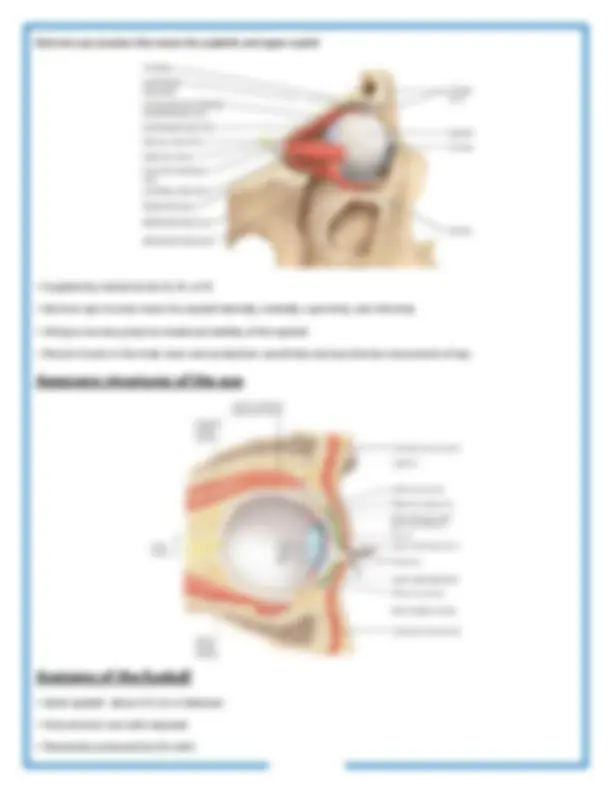
Lens divides the interior of the eyeball into two cavities: Anterior cavity and Vitreous chamber
1. Anterior cavity- space anterior to the lens Consists of two chambers
Physiology of Vision
Photoreceptors and Photo pigments
Photo pigment
Light adaptation— when emerging from a dark surrounding to sunshine
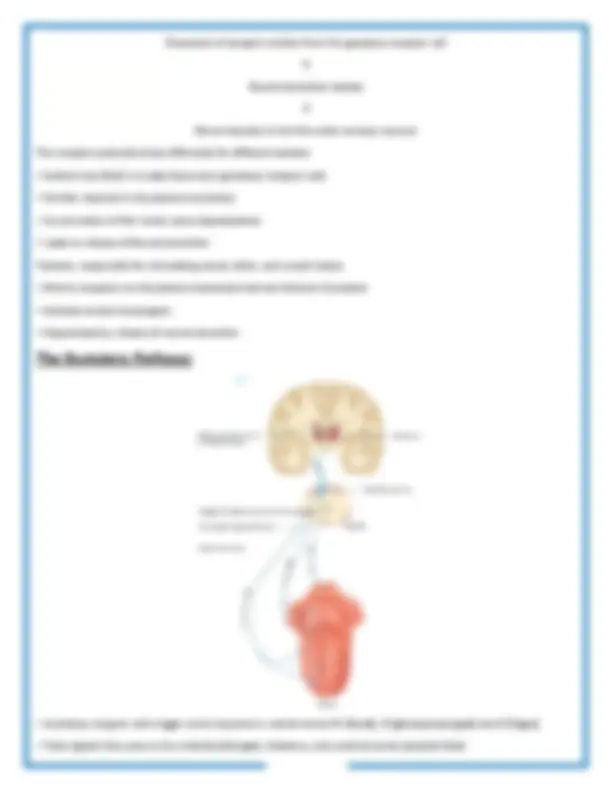
The visual pathway
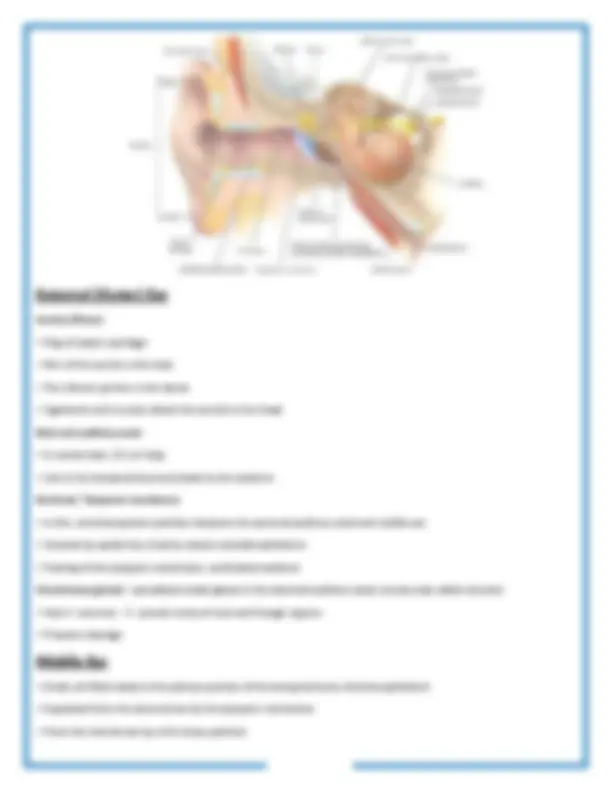
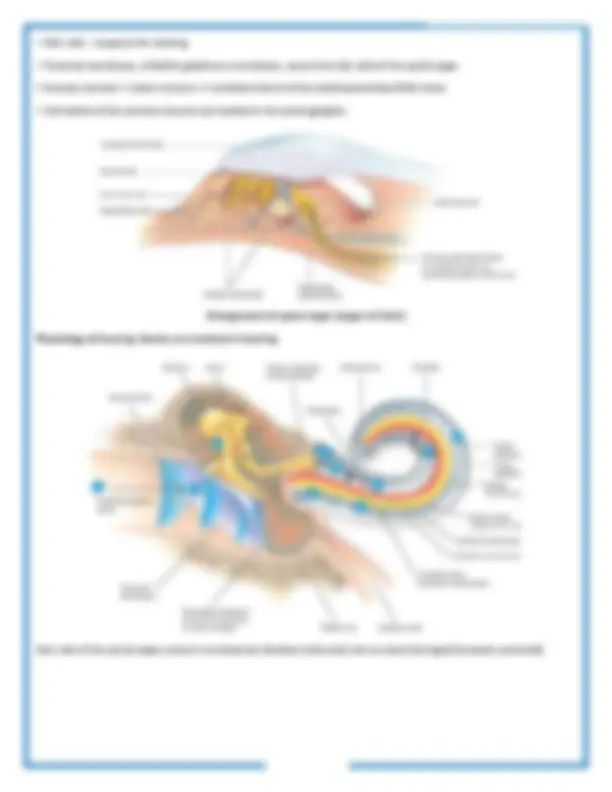
Ear is divided into three main regions
1. External (Outer) Ear - Auricle (Pinna) - Eardrum - External auditory canal 2. Middle Ear - Auditory ossicles - Auditory (eustachian) tube 3. Internal (inner) ear - Cochlea - Vestibular apparatus - Semicircular ducts
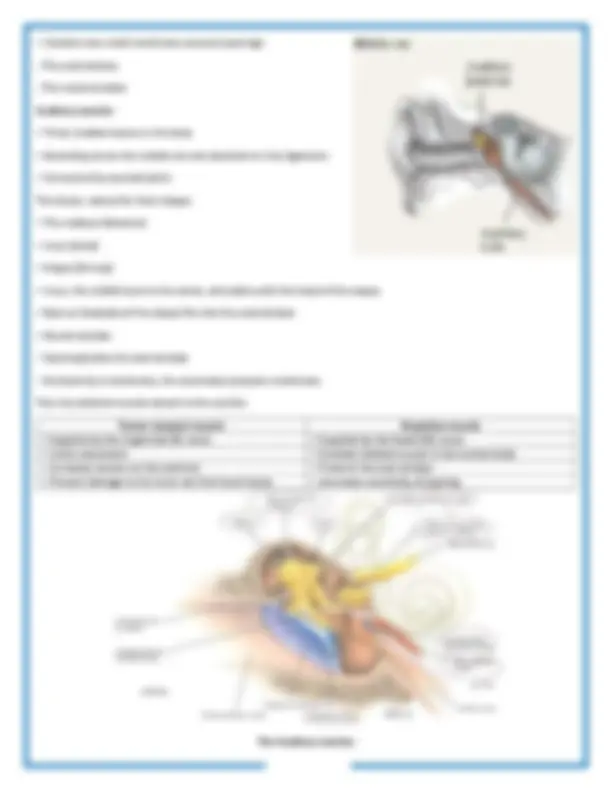
The Auditory ossicles
Auditory (eustachian) tube
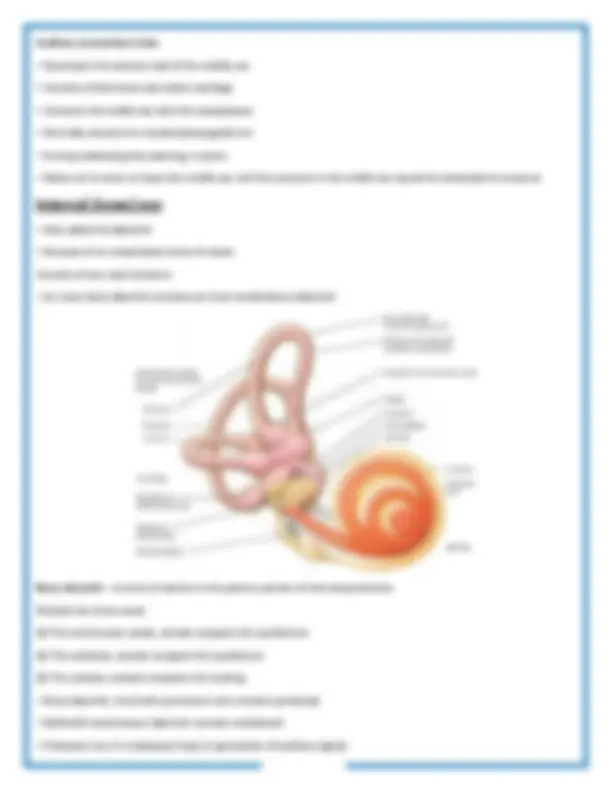
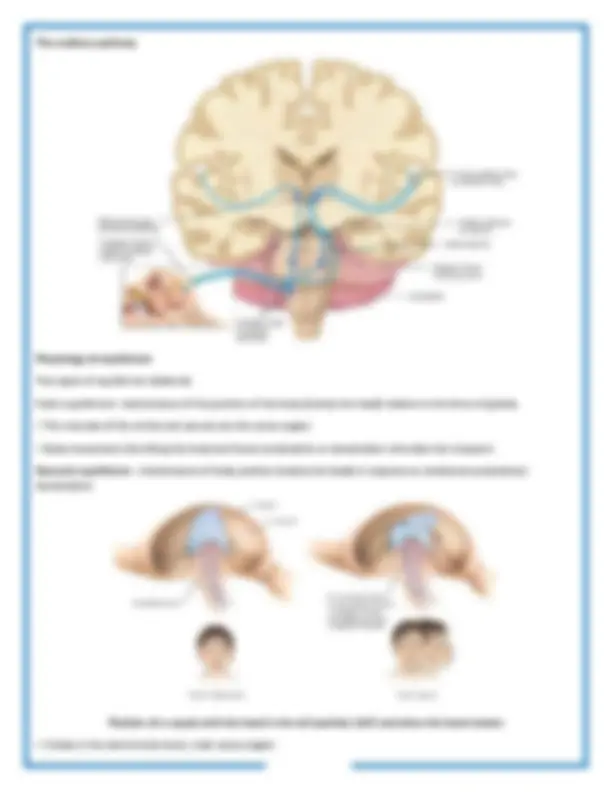
Bony labryinth - A series of cavities in the petrous portion of the temporal bone Divided into three areas: (1) The semicircular canals, contain receptors for equilibrium (2) The vestibule, contain receptors for equilibrium (3) The cochlea, contains receptors for hearing