








































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Selection Models, Models for Counts, Hazard Models, Dynamic Models, Canonical Sample Selection Model, Marginal Effects, Extensions of the Poisson Model, Overdispersion are points which describes this lecture importance in Econometric Analysis of Panel Data course.
Typology: Slides
1 / 47

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!








































Canonical Sample Selection Model
Two Step Estimation
i i i i
i
Step 1: Estimate the probit model
d *= +u ; d =1[d * > 0] (probit).
Estimation of by. Now compute
Step 2: Estimate the regression model with estimated re
φ
λ =
φ
i
i
i
z γ
z γ
γ γ
z γ
i i
i i i
i i i i i i
i
i i i
gressor
y *= +
y = y * if d = 1; not observed otherwise
E[y *|x ,d =1] = +E[ | x , d 1]
Linearly regress y on x ,.
Step2a. Fix standard errors (Murphy
ε
ε =
λ
i
i
i
x β
x β
x β
and Topel). Estimate
and using and /n
ρ
σ θ e'e
The “LAMBDA”
i
d 0
2
i i i
2 d 1
2
i i
2
d 0
2
2
i i i
d
logL log
log exp
y
Let
logL log
log exp y ( 1 ) ( y )
=
=
=
=
= Φ − γ
−ε γ + ρε σ
σ
σ π
− ρ
ε = −
ρ
θ = σ δ β σ τ
ρ
= Φ − γ
θ
π
i
i
i i
z
z
x β
z
x δ z x δ
1
Note : no inverse Mills ratio appears anywhere in the model.
Panel Data Extensions
Mundlak Treatment: Zabel, Economics Letters, 1992
Two step treatments: Wooldridge, 1995, etc. (See text)
Both Fixed Effects: Greene, 2002- ‘Brute force’ (WIP)
Random Parameters: Greene, 2003- (WIP), classical
simulation based
Interesting survey: Jensen, Rosholm, Verner, CIM/CLS,
Models for Counts
German Health Care Usage Data , 7,293 Individuals, Varying Numbers of Periods
Variables in the file are
Data downloaded from Journal of Applied Econometrics Archive. This is an unbalanced panel with 7,
individuals. They can be used for regression, count models, binary choice, ordered choice, and bivariate binary
choice. This is a large data set. There are altogether 27,326 observations. The number of observations ranges
from 1 to 7. (Frequencies are: 1=1525, 2=2158, 3=825, 4=926, 5=1051, 6=1000, 7=987). Note, the variable
NUMOBS below tells how many observations there are for each person. This variable is repeated in each row of
the data for the person. (Downlo0aded from the JAE Archive)
DOCTOR = 1(Number of doctor visits > 0)
HSAT = health satisfaction, coded 0 (low) - 10 (high)
DOCVIS = number of doctor visits in last three months
HOSPVIS = number of hospital visits in last calendar year
PUBLIC = insured in public health insurance = 1; otherwise = 0
ADDON = insured by add-on insurance = 1; otherswise = 0
HHNINC = household nominal monthly net income in German marks / 10000.
(4 observations with income=0 were dropped)
HHKIDS = children under age 16 in the household = 1; otherwise = 0
EDUC = years of schooling
AGE = age in years
MARRIED = marital status
EDUC = years of education
Hospital Visits
Histogram for Variable HOSPITAL
Frequency
HOSPITAL
0
694
1388
2082
2776
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Choice Based Sample: Censored at Y=10, then 90% of the zeros were deleted.
Hospital Visits
+---------------------------------------------+
| Poisson Regression |
| Number of observations 4916 |
| Iterations completed 7 |
| Log likelihood function -5967.059 |
| Restricted log likelihood -5995.100 |
| Chi squared 56.08026 |
| Degrees of freedom 5 |
| Prob[ChiSqd > value] = .0000000 |
| Chi- squared = 10292.78230 RsqP= .0144 |
| G - squared = 6704.29865 RsqD= .0083 |
| Overdispersion tests: g=mu(i) : 7.283 |
| Overdispersion tests: g=mu(i)^2: 7.358 |
+---------------------------------------------+
+---------+--------------+----------------+--------+---------+----------+
|Variable | Coefficient | Standard Error |b/St.Er.|P[|Z|>z] | Mean of X|
+---------+--------------+----------------+--------+---------+----------+
Constant -.01097644 .12877669 -.085.
AGE .00492571 .00168005 2.932 .0034 44.
HHNINC .18287767 .09558999 1.913 .0557.
HHKIDS .01073511 .04023519 .267 .7896.
EDUC -.05292805 .00860326 -6.152 .0000 11.
MARRIED -.04487271 .04372825 -1.026 .3048.
Extensions of the Poisson Model
Overdispersion
2
2
NonPoissonness
Omitted Heterogeneity
j
u
1
α α−
∫
Testing for Overdispersion
| Overdispersion tests: g=mu(i) : 7.283 |
| Overdispersion tests: g=mu(i)^2: 7.358 |
Dispersion parameter for count data model
Alpha .63363306 .03061167 20.699.
Sample Selection
2
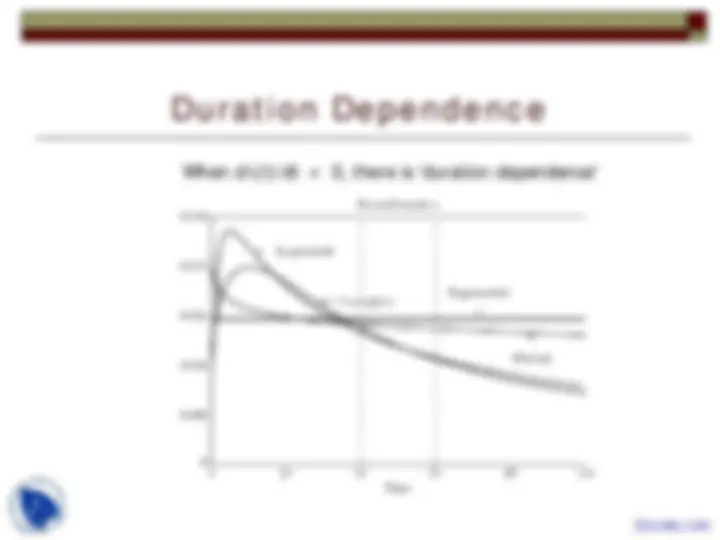
Modeling Duration
Hazard Models for Duration