Download Lecture 39: Turbulence Modeling & 3D Flow Prediction in Turbomachinery with Case Studies and more Slides Turbomachinery in PDF only on Docsity!
1
In this lecture...
- Computational Fluid Dynamics for turbomachinery - Turbulence modelling - Prediction of 3D flows: case studies - Computing requirement - Errors and uncertainties
Turbulence Models
- Zero equation or algebraic eddy viscosity model - Use an algebraic form for the turbulent stresses - Valid for simple 2D shear flows - Mild pressure gradient - 3D boundary layers with small cross flows - Not accurate for flows with pressure or turbulence driven secondary flows - Cannot predict shock-induced separated flows
Turbulence Models
- One equation model: Spalart Allmaras
- Employ an additional PDE for a
turbulence velocity scale
- Usually used in design-iteration type
simulations
- Popular in recent times due to
inherent problems with more refined
models
- Very robust models, rarely produce
completely unphysical results
Turbulence Models
- Near wall treatment
- On-design flows without large separated regions, wall function model close to the wall
- Off-design, low Re model, over production of turbulent KE must be checked
- Menter’s SST Κ-ω and Durbin’s v2f
- Works well for adverse pressure gradients and separating flows
Turbulence Models
- Reynolds stress models
- Use seven different PDEs for all the
components of the turbulence
stresses.
- Reasonably better in cases where
two-equation models were not
satisfactory
- More realistic physical simulation of
turbulent flows
Case studies
- Types of shear flows
- Tip leakage flow
- Scraping vortex
- Corner separation
- Passage vortex
- Secondary flows
- Shock boundary layer interaction
- Inflow distortion
Tip leakage flows
- Several papers on simulation of tip leakage flows
- Steady computations reasonably good
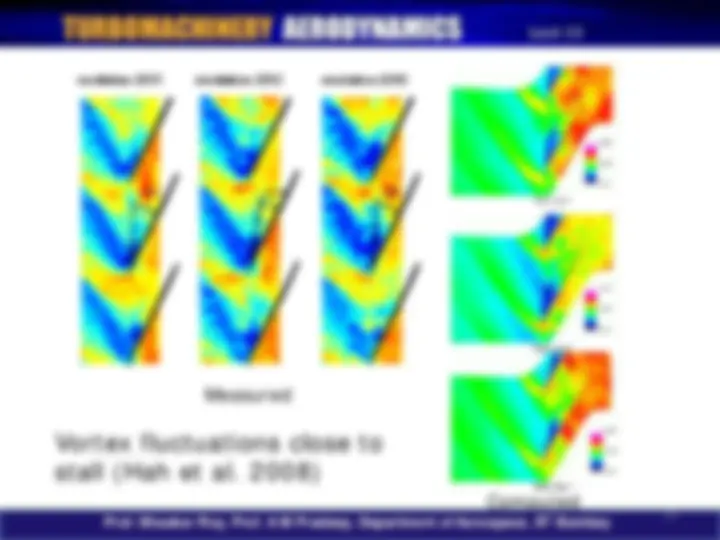
- Vortex fluctuations close to compressor stall for eg. not predicted well.
- Case: Hah et al. 2008
- Full annulus flow simulation
- LES of Darmstadt transonic rotor
- 25 million grid points
- 60 CPU hours on 124 CPU NASA’s Columbia!
- Results compared with experimental data from TU Darmstadt
Vortex fluctuations close to stall (Hah et al. 2008)
Measured
Computed
Passage vortex
• Strength of secondary flows, passage
vortices depend upon the blade
loading
• Case: Hjarne et al. , 2007
• Secondary flow studies on turbine
OGV cascade
• Different turbulence models
• Realizable Κ-ε, SST Κ-ω and RSM
• Simulations compared with
experimental data
Passage vortex
W-velocity at downstream location of 0.5C of the blade (Hjarne et al. , 2007)
Transonic rotor: shocks, tip flow
unsteadiness
- Tip flow
- Significant effect on flow stability, pressure rise, and efficiency
- Self induced unsteadiness related to spike initiated stall?
- Role of shock wave in the flow physics
- Experimentally capturing the tip flow dynamics very challenging
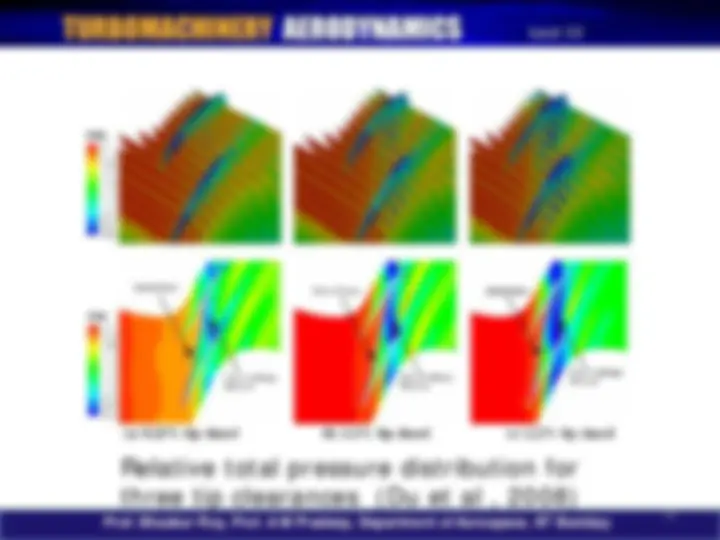
Shock positions at two operating points (Du et al , 2008)
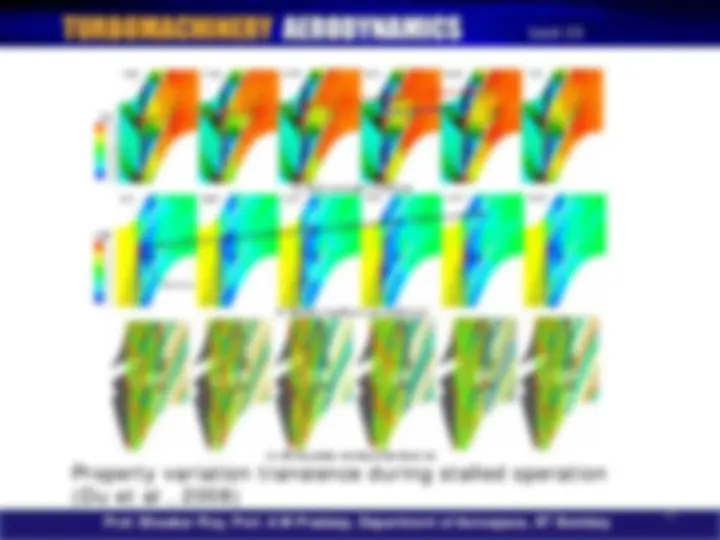
Property variation transience during stalled operation (Du et al , 2008)