












Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Main topics of this course are: Biocontrol Approaches, Decision Making, Disadvantages of Cultural Controls, EBPM Status, Enforced Crop Production Rules, Hybrid Sterility, IPM Evolution Continued, Regulatory Tactics, Resistance Categories. Key points of this lecture slides are: Resurgence, Pesticide, Pest Resurgence, Reduced Biological Control, Resistance, Resistant Mechanism, Resistance Process, Management Strategy, Impact of Resistance, Environmental Impact
Typology: Slides
1 / 22

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!















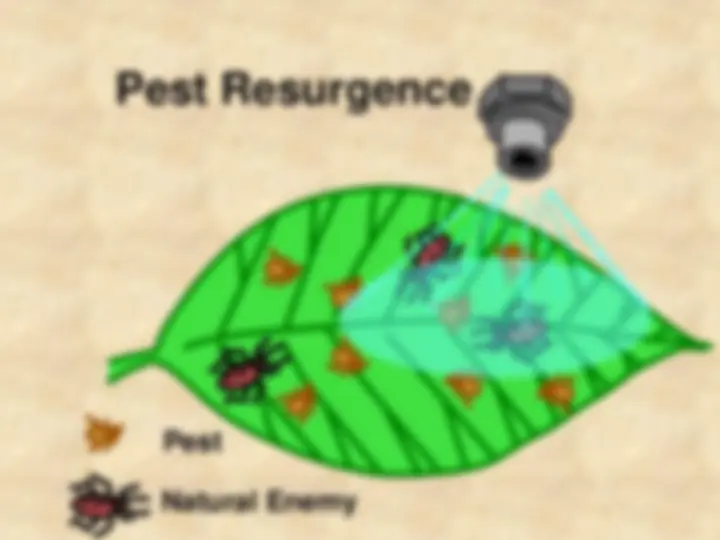
pests for several reasons.
Pest (8)
Natural Enemy
pest
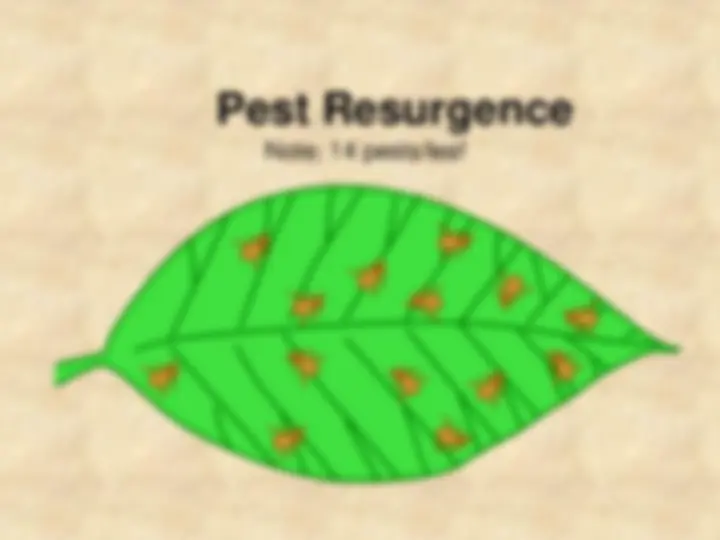
pest
Note: 14 pests/leaf
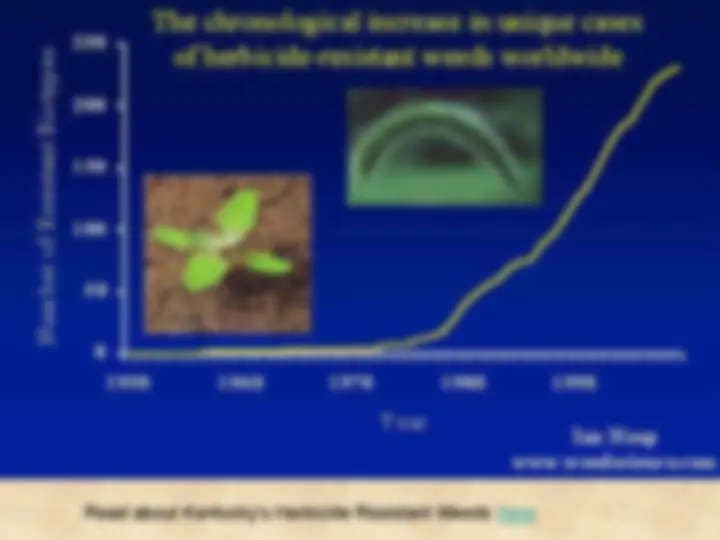
Initially, a small proportion of population has a resistant mechanism by chance.
These individuals survive at a higher rate than others
Eventually, the pesticide or other management tactic causes too little control to be effective.
Prevention
Abandon Pesticide/Management Tactic
Need to monitor resistance
Independent of Pesticide
of susceptibles survive to reproduce
coverage
reduces selective pressure