







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Probability, Classical Probability, Classical Sample spaces, Complement, Mutually Exclusive, Rules of Probability, Multiplication rules, Fundamental rule of Counting are learning points available in this lecture notes.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 11

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
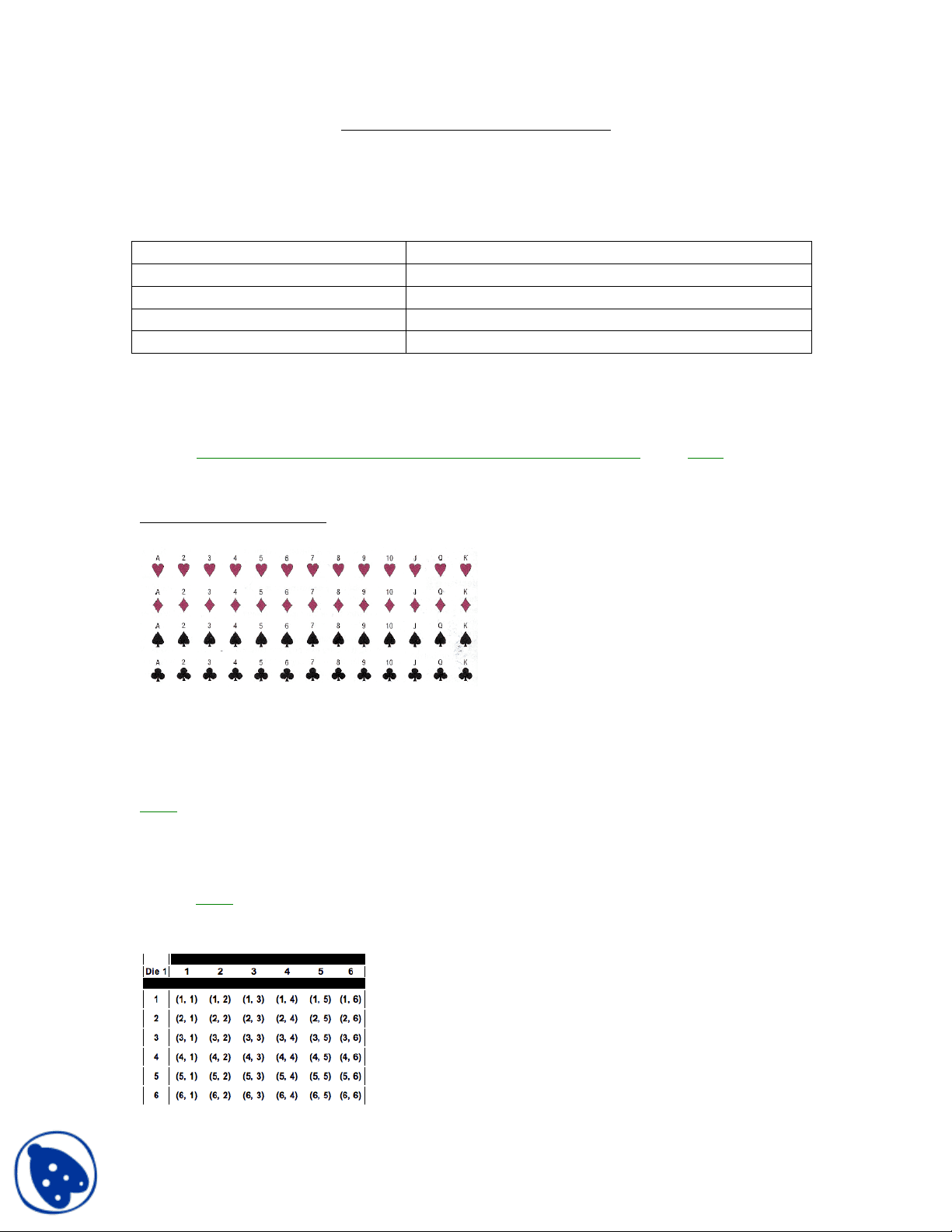






Classical & Empirical Probability A probability experiment is a chance process that leads to well-defined outcomes. A sample space is the set of all possible outcomes. Classical Probability : is applied when you can assume each event is equally likely. Experiment Sample space Coin toss Head, Tail Die roll 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 True-false question True, False Double coin toss HH, HT, TH, TT An Event E is a set of outcomes Ex: flipping 2 heads in 2 tosses, rolling a 2 or a 5, etc. P(E) = Number of ways “E” can occur _ = n(E) Total number of outcomes in the sample space n(S) Classical Sample spaces: Draw a card Ex: Find the following: P(A heart) P(An ace or a two) Rule : 0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1
P(Total value 13) = P(Total value 7) = P (A 2 and a 1) = Ex: Genetic Probablity A couple has three children, all are healthy boys or girls. P(2 girls) = P(At least 1 girl) = P(No girls) = P(All Boys) =
In a sample of 50 people, 21 had type O blood, 22 had type A blood, 5 had type B blood, and 2 had type AB blood. Set up the frequency distribution and and find the following: P(O), P(A or B), P(neither A nor O), P(not AB). Mutually Exclusive events are two events that cannot occur at the same time. Mutually Exclusive Not
**Rules of Probability
So Permutations are the possible number of arrangements of objects (when order matters).