

















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Main points of Local and Wide Area Networks are: Physical Layer Two, Amplitude-Shift, Modulation Modes, Frequency-Shift, Phase-Shift Modulation, Degree, Interval, Valid Symbols, Speedup, Symbols
Typology: Slides
1 / 25

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


















Physical Layer (contd)
)
amplitude-shift
)
frequency-shift
)
phase-shift modulation
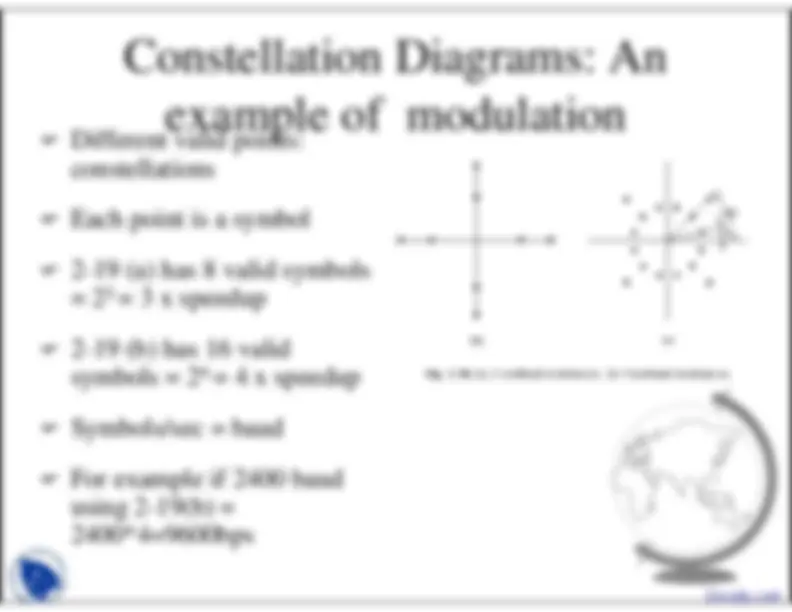
225, 315 degree(2bits/interval).
(a) QPSK.(b) QAM-16.(c) QAM-64.
)
Analog circuits require amplifiers, and eachamplifier adds distortion and noise to thesignal.
)
Digital amplifiers regenerate an exact signal
)
Integrate all traffic
)
Although most local loops are analog, endoffices increasingly use digital circuits forinter-trunk lines. A codec (coder/decoder) isa device that converts an analog signal intoa digital signal.
)
To convert analog signals to digital signals,many systems use Pulse Code Modulation(PCM)
)
Convert analog to digital (done by codec)
Uses sampling (snapshots of waveform)
PCM samples the 4kHz signal 8,000 times persecond. (Nyquist theorem)
Each sample measures the amplitude of the signal,converting it into an n-digit integer value.
The digital channel carries these n-digit encodings.
Architecture of an LMDS system.
IEEE 802.
)
Problem: Given a channel of large capacity, howdoes one subdivide the channel into smaller logicalchannels for individual users? Multiplex manyconversations over same channel.
)
Three flavors of solution: 1.Frequency division multiplexing (FDM)2.Time division multiplexing (TDM)3.Statistical multiplexing
(a) The original bandwidths.(b) The bandwidths raised in frequency.(b) The multiplexed channel.
)
Use time slicing to give each user the fullbandwidth, but for only a fraction of asecond at a time (analogous to time sharingin operating systems).
)
Problem?if the user doesn't have data to sent duringhis time slice, the bandwidth is not used(e.g., wasted).
)
Allocate bandwidth to arriving packets ondemand.
)
Advantage:leads to the most efficient use of channelbandwidth because it only carries usefuldata. Channel bandwidth is allocated topackets that are waiting for transmission,and a user generating no packets doesn't useany of the channel resources.
)
Circuit SwitchingUsed in current telephone system
)
Message Switching
)
Packet SwitchingUsed in the next generation telephonesystem--broadband ISDN system
(Fig2-35)
)
1.Once a call setup has been completed, the user sees a setof virtual wires between communicating endpoints.
)
2.The user sends a continuous stream of data, which the channel guarantees to deliver at a known rate.
)
3.Data transmission handled elegantly using TDM or FDM.
)
4.Call setup required before any data can be sent.
)
5.Call termination required when parties complete call.
)
No physical copper path is established in advancebetween communicating endpoint.
)
Entire message stored at each node. Each message isreceived in its entirety,inspected for errors and thenforwarded.
)
A network using this technique is called a store-and-forward network.
)
Memory requirements at intermediate nodes