
























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An introduction to the physical layer of lan/wan, discussing the purpose, theoretical basis, and transmission of data. It also covers the maximum data rates of channels using nyquist's theorem and shannon's theorem. Topics include harmonics, signal-to-noise ratio, and various transmission media such as magnetic media, twisted pair, coaxial cable, fiber optics, and wireless transmission.
Typology: Slides
1 / 32

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

























)
)
)
)
)
)
ex -
)
)
)
attenuate
(weaken)
distortion
unevenly
spectrum
(cutoff)
)
)
)
Thermal noise
from agitation of electrons in a
conductor. Uniform. “White noise.”
Intermodulation noise
different frequencies share the
same medium
Crosstalk noise
results from coupling signal paths
Ex: Other conversation (faintly) on a telephone
Impulse noise
from sharp, short-lived disturbances
Ex: from lightning
)
)
10
decibels, dB
)
)
)
directed manner)
)
)
)
tapes hurtling down the highway
)
)
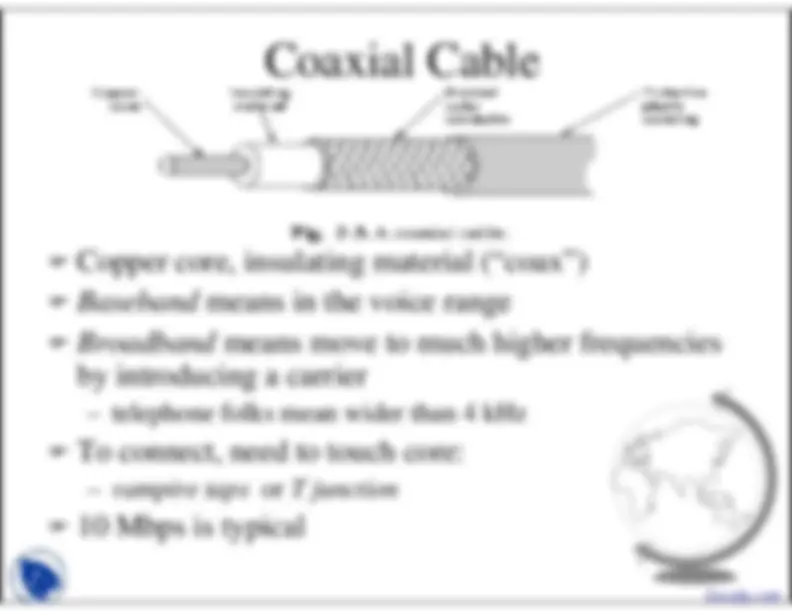
Copper core, insulating material (“coax”) )
Baseband
means in the voice range
)
Broadband
means move to much higher frequencies
by introducing a carrier– telephone folks mean wider than 4 kHz )
To connect, need to touch core:
vampire taps
or
T junction
)
10 Mbps is typical
)
)
)
)
Three components required:
current generates a pulse of light
signals
)
Wide fiber = many diff. Wavelengths of light(multimode fiber) )
Narrow fiber = only 1 wavelength (single mode,better)
)
)
training or expensive tools or parts are required
Two fibers needed for
full duplex
communication
)
frequency
and
wavelength
)
)
Easy to generate, travel far, through walls )
Low bandwidth )
Low radio freqs follow earth )
High freqs travel in straight lines, bounce off obstacles )
Restricted use by regulation