







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The concept of pass by reference in c# using ref and out parameters, and compares it to pass by value. It also covers the usage of const and readonly keywords, and introduces the concept of struct as a value type. Examples are provided to illustrate the concepts.
Typology: Slides
1 / 12

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







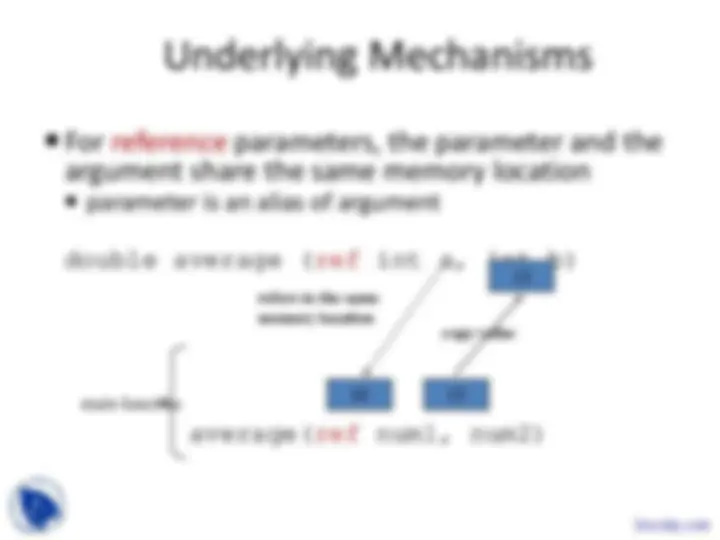
parameter is an alias of argument double average (ref int a, int b) average(ref num1, num2) 10 15 15 refers to the same memory location copy value main function
void swap(ref int a, ref int b) { int temp; temp = a; a = b; b = temp; }
public class GradeBook { private readonly string courseName = “”; public GradeBook(string name) { courseName = name; } }