











Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of Part II actuarial exams, which serve as a bridge between Part I and Part III exams. Part II introduces common elements of Part III, such as essay-style exams, unfamiliar context, and problem-solving methods. The document also covers the Control Cycle Framework and the importance of quantitative and qualitative skills in actuarial work.
Typology: Exams
1 / 18

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!











Part I
Part II
Part III
Professionalism Course
How does Part II fit into path to
Fellowship?
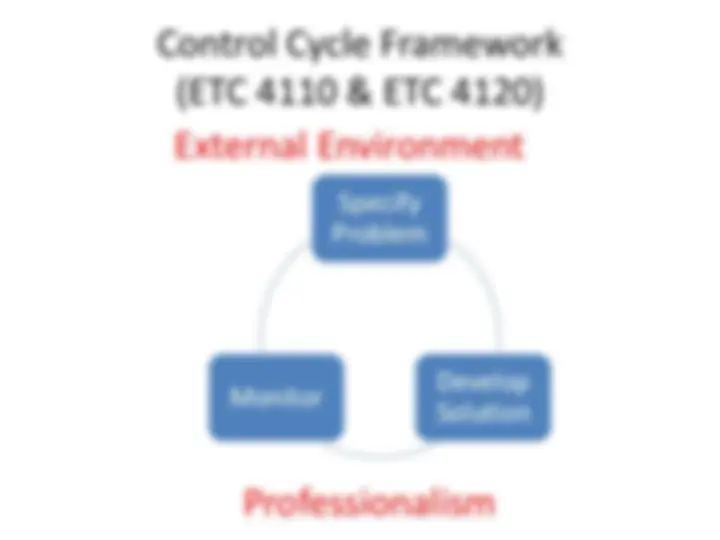
Control Cycle Framework
(ETC 4110 & ETC 4120)
Specify Problem
Develop Solution Monitor
Professionalism
External Environment
‘Part I’ (^) Part II – akin to Arts
Observations on example ACC
assignment
Core skills to practice as an Actuary:
Actuarial Capability Framework
CA1 Pass Rates and Exposure
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
40%
45%
50%
55%
Apr-12 Oct-12 Apr-13 Oct-13 Apr-
Number of Candidates
Pass Rates
Total Candidates Pass Rates