

















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
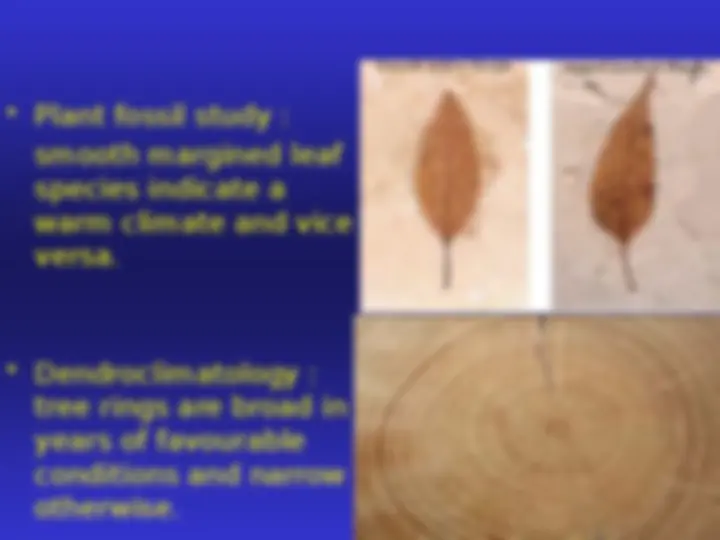
A seminar on the palaeomap and climate of different ages and the reconstruction of past climates. It discusses the maps of different ages and their climates, major ice ages, and the reconstruction of past climates. The document also covers the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras and the Triassic, Jurassic, and Permian periods. It also talks about the variation in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. The document concludes with the reconstruction of past climates through drilling ice cores, palaeosol, plant fossil study, and dendroclimatology.
Typology: Study Guides, Projects, Research
1 / 26

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



















Hadean : harsh
terresterial environment,
low oxygen(1%), high
Archean : no free oxygen,
reducing condition,
composed of methane,
CO2 and H. like the
present day Venus and
Jupiter
Proterozoic : oxygen rich
i.e from reducing to
oxygenated. Warm
conditions replaced by an
Ice Age, might have
covered the whole earth
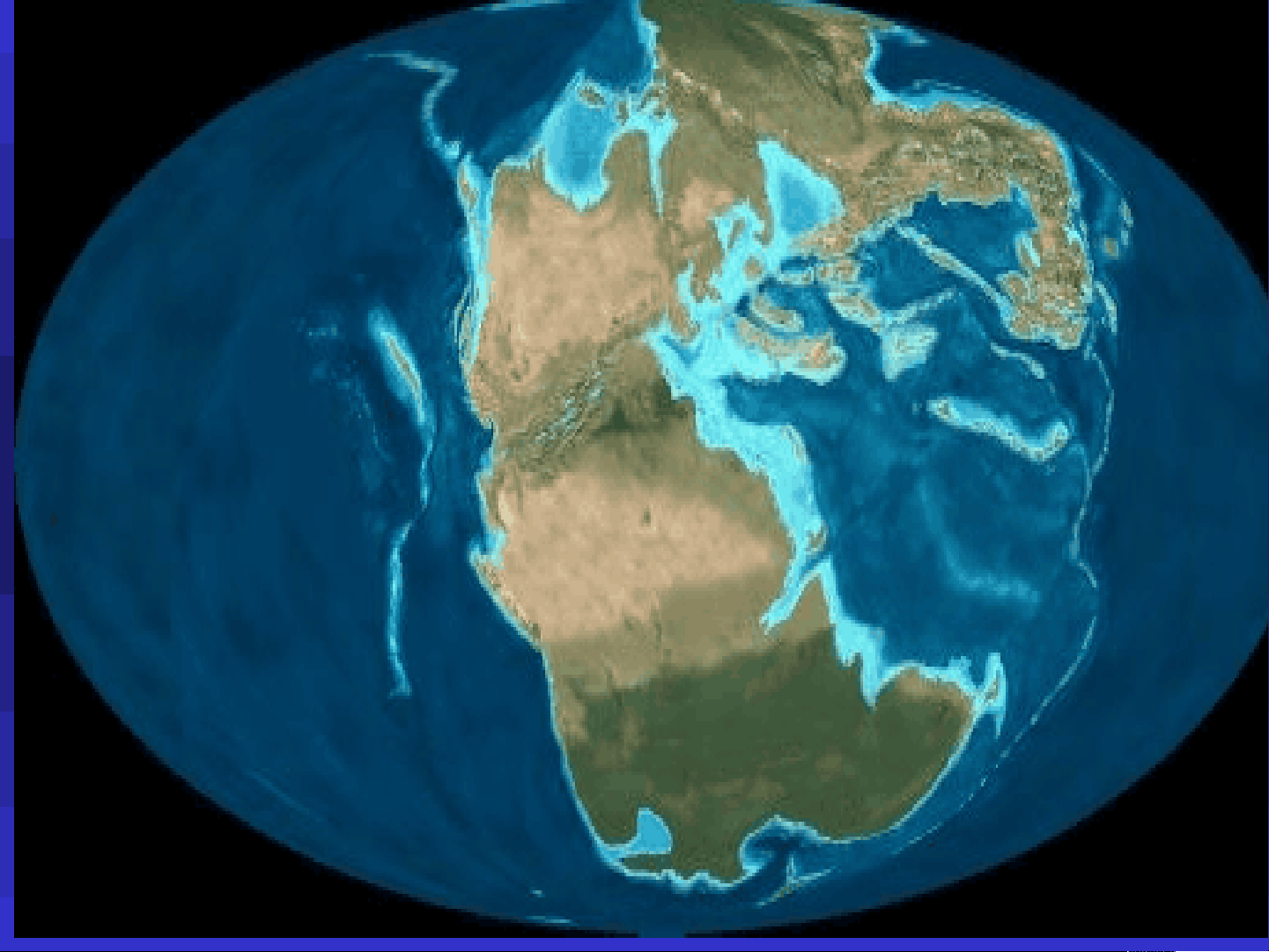
Gondwanaland;
Located near the
south pole, covered
by glaciers
North America,
Europe, Siberia and
Asia were all
separate.
Warm and arid in early
part.
Atmospheric oxygen
attains the present
levels, generating an
ozone shield.
Evidence of arid
climate: cambrian of
North America and
Europe joined by the
end of the Silurian.
The Siberian/Asian
continent was
converging on Europe.
The North
America/Europe
continent began to
approach
Gondwanaland.
Generally warm and
possible dry climate.
Aridity evident by halite
pseudomorphs and salt
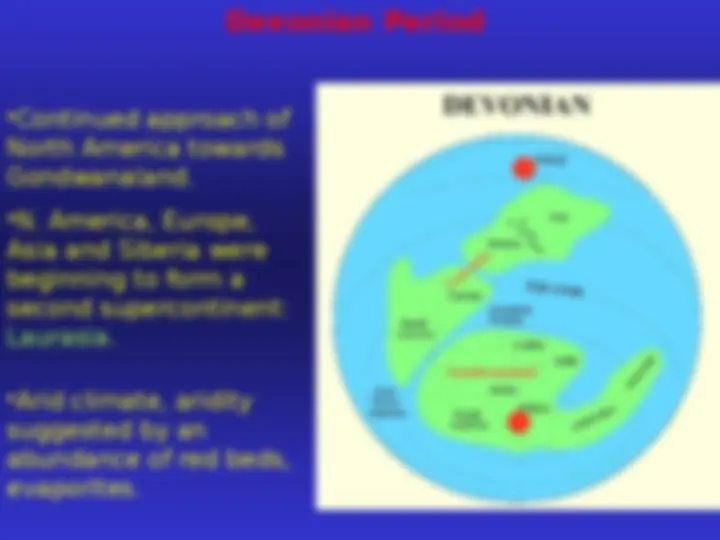
Continued approach of
North America towards
Gondwanaland.
N. America, Europe,
Asia and Siberia were
beginning to form a
second supercontinent:
Laurasia.
Arid climate, aridity
suggested by an
abundance of red beds,
evaporites.
Asia collides with
Europe to form the Ural
Mountains.
One large
supercontinent (called
Pangea) forms with the
merging of Laurasia
and Gondwanaland.
mass extinction
possibly due to ocean
cooling or fluctuating
due to ice sheet.,
reduced aquatic
environments due to
Pangaea forming, ash
from large volcanic
Small land masses on
the subducting Pacific
Plate collided with
North America.
Warm climate, mean
global temperature
may have been 6 to 8
degrees higher then
today.
North & South
America, Australia
and Antarctica
spread away from
Pangea, further
opening the Atlantic
Ocean.
Africa collided with
Europe; India collided
with Asia.
The early Cenozoic
was another period
of mountain building
in the Rocky
Mountains.
Over all this time there were other changes taking place:
Variation in O2 levels in the atmosphere