Download Motivation Theories in Management: A Comprehensive Overview and more Essays (university) Geochemistry in PDF only on Docsity!
Motivation
Let’s Ponder…
What is motivation?
What are the different types of individual needs?
What are the challenges of motivation in the new
workplace?
Question 1: What is motivation?
Basic motivational concepts
- (^) Motivation—the forces within the individual that account for the level, direction, and persistence of effort expended at work.
- (^) Reward—a work outcome of positive value to the individual
- (^) Extrinsic rewards—valued outcomes given to someone by another person.
- (^) Intrinsic rewards—valued outcomes that occur naturally as a person works on a task.
Management - Chapter 14 5
Question 2: What are the different types of
individual needs?
Needs
- (^) Unfulfilled physiological and psychological desires of an individual.
- (^) Explain workplace behavior and attitudes.
- (^) Create tensions that influence attitudes and behavior.
- (^) Good managers and leaders facilitate employee need satisfaction.
Types of content theories:
- (^) Hierarchy of needs theory
- (^) ERG theory
- (^) Two-factor theory
- (^) Acquired needs theory
Maslow’s Theory
Hierarchy of needs theory
- (^) Developed by Abraham Maslow.
- (^) Lower-order and higher-order needs affect workplace behavior and attitudes.
- (^) Lower-order needs:
- (^) Physiological, safety, and social needs.
- (^) Desires for physical and social well being.
- (^) Higher-order needs:
- (^) Esteem and self-actualization needs.
- (^) Desire for psychological growth and development.
Hierarchy of needs theory
- (^) Deficit principle
- (^) A satisfied need is not a motivator of behavior.
- (^) Progression principle
- (^) A need at one level does not become activated until the next lower-level need is satisfied.
ERG theory
- (^) Developed by Clayton Alderfer.
- (^) Three need levels:
- (^) Existence needs — desires for physiological and material well-being.
- (^) Relatedness needs — desires for satisfying interpersonal relationships.
- (^) Growth needs — desires for continued psychological growth and development.
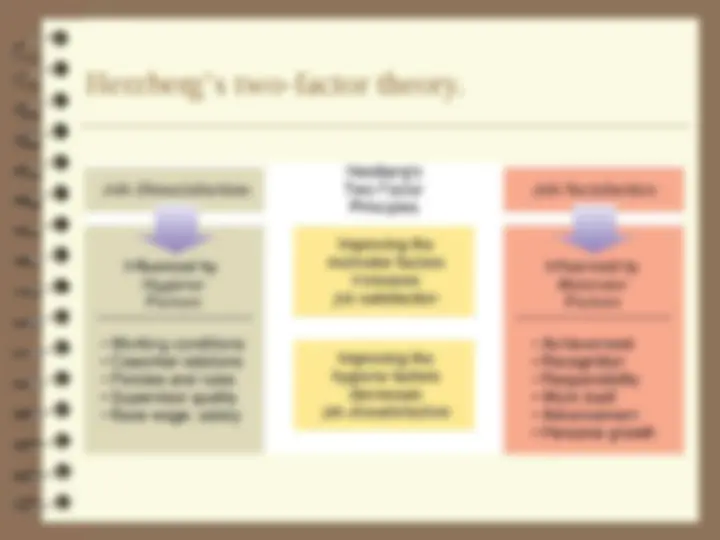
Herzberg’s Two-factor theory
- (^) Developed by Frederick Herzberg.
- (^) Hygiene factors:
- (^) Elements of the job context.
- (^) Sources of job dissatisfaction.
- (^) Satisfier factors:
- (^) Elements of the job content.
- (^) Sources of job satisfaction and motivation.
Herzberg’s two-factor theory.
Acquired needs theory
- (^) Need for Achievement (nAch)
- (^) Desire to do something better or more efficiently, to solve problems, or to master complex tasks.
- (^) People high in (nAch) prefer work that:
- (^) Involves individual responsibility for results.
- (^) Involves achievable but challenging goals.
- (^) Provides feedback on performance.
Acquired needs theory
- (^) Need for Power (nPower)
- (^) Desire to control other persons, to influence their behavior, or to be responsible for other people.
- (^) Personal power versus social power.
- (^) People high in (nPower) prefer work that:
- (^) Involves control over other persons.
- (^) Has an impact on people and events.
- (^) Brings public recognition and attention.
Questions for summarizing the content
theories of motivation:
- (^) How many different individual needs are there?
- (^) Can a work outcome or reward satisfy more
than one need?
- (^) Is there a hierarchy of needs?
- (^) How important are the various needs?
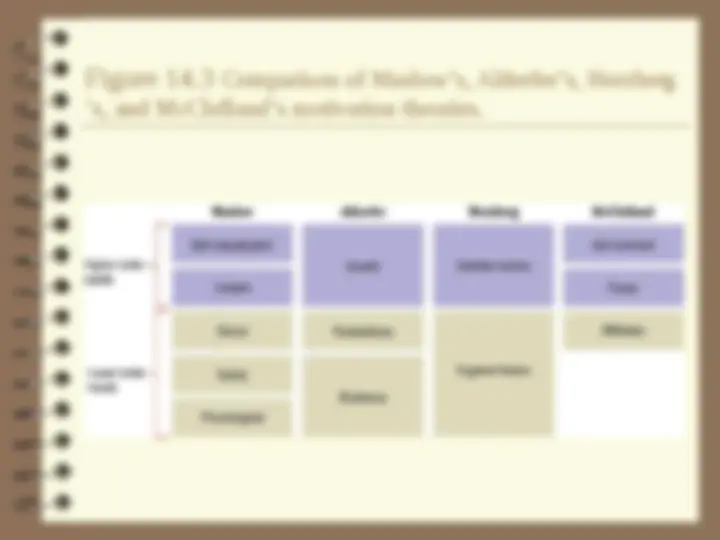
Figure 14.3 Comparison of Maslow’s, Alderfer’s, Herzberg
’s, and McClelland’s motivation theories.