


















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of c++ i/o operations, including streams, text and binary, cascading input and output operators, reading and writing characters and strings, formatted i/o, and data types such as variables and constants. Topics covered include i/o classes, functions, and flags, manipulators, rules for defining variable names, static, local, instance, and final variables, and constant declaration.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 29

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






















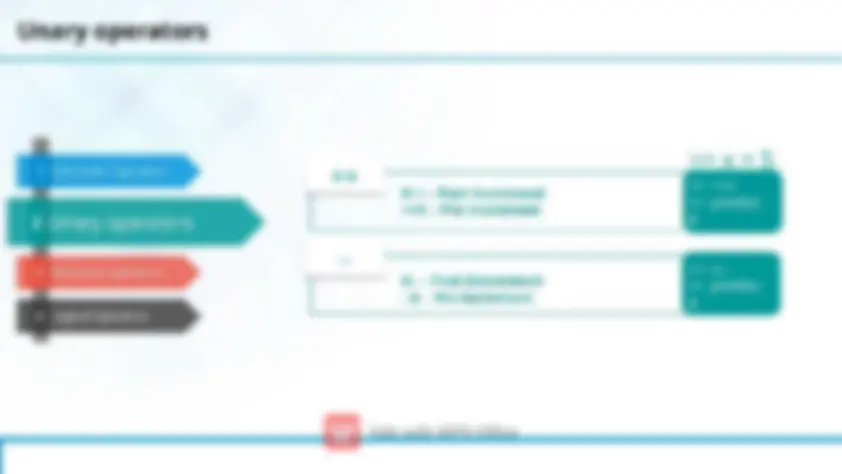
Stream in C
Text Stream (^) Binary Stream
Formatted I/O
I/O class function and flages
Manipulators
#include<iostream.h> #define PI 3. main() { cout.precision(3); cout.width(10); cout.fill(‘*’); cout<<PI; Output *****3.
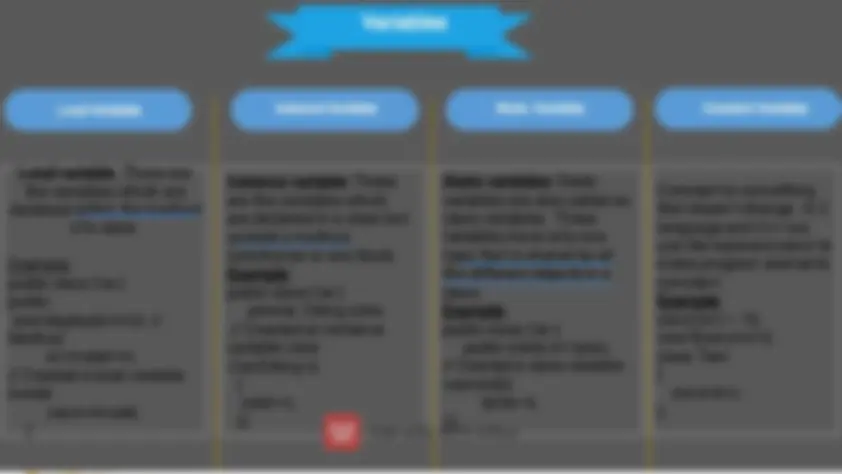
Variables
Local Variables Instance Variables^ Static Variables^ Constant Variables
Local variable: These are the variables which are declared within the method of a class.
Example: public class Car { public: void display(int m){ // Method int model=m; // Created a local variable model cout<<model; }
Static variables: Static variables are also called as class variables. These variables have only one copy that is shared by all the different objects in a class. Example: public class Car { public static int tyres; // Created a class variable void init(){ tyres=4; } }
Instance variable: These are the variables which are declared in a class but outside a method, constructor or any block. Example: public class Car { private: String color; // Created an instance variable color Car(String c) { color=c; }}
Constant is something that doesn't change. In C language and C++ we use the keyword const to make program elements constant. Example: const int i = 10; void f(const int i) class Test { const int i; };