


Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Applications of Biology is most interesting course. Its specialty is, its interesting fro everyone. This lecture also describes some applications. It includes: Nervous Systems, Brain Development, Sympathetic, Arousal, Energy Production, Fight or Flight, Parasympathetic, Back to Maintenance, Autonomic, Somatic
Typology: Slides
1 / 20

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!













Sympathetic arousal & energy production “fight or flight” Parasympathetic calming & back to maintenance “rest & digest”
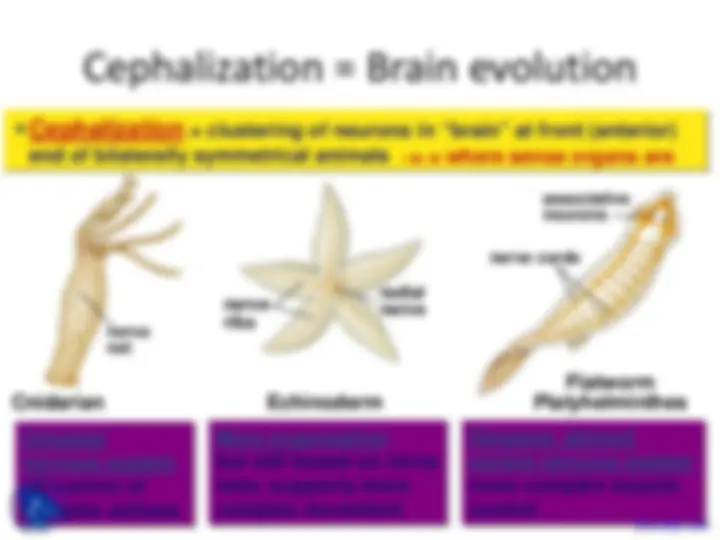
Cnidarian
nerve net
Simplest nervous system no control of complex actions
More organization but still based on nerve nets; supports more complex movement
Cephalization = clustering of neurons in “brain” at front (anterior) end of bilaterally symmetrical animals
Flatworm Platyhelminthes
nerve cords
associative neurons
Simplest, defined central nervous system more complex muscle control
Echinoderm
radial nerve nerve ribs
→→ where sense organs are
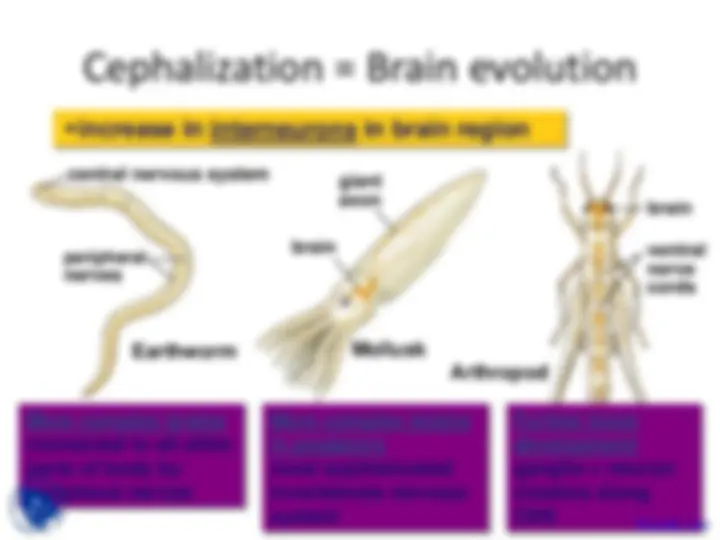
Mollusk
brain
giant axon (^) brain
ventral nerve cords
Arthropod
Further brain development ganglia = neuron clusters along CNS
increase in interneurons in brain region
Earthworm
central nervous system
peripheral nerves
More complex brains connected to all other parts of body by peripheral nerves
More complex brains in predators most sophisticated invertebrate nervous system
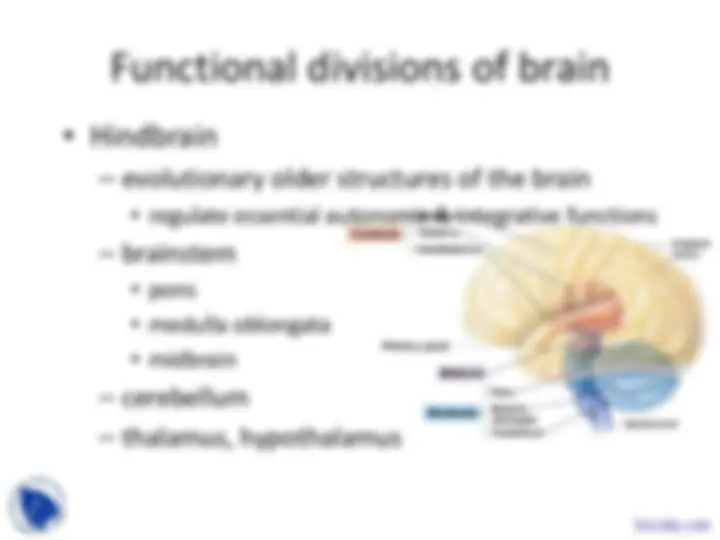
Mediates basic emotions (fear, anger), involved in emotional bonding, establishes emotional memory
Amygdala involved in recognizing emotional content of facial expression Docsity.com
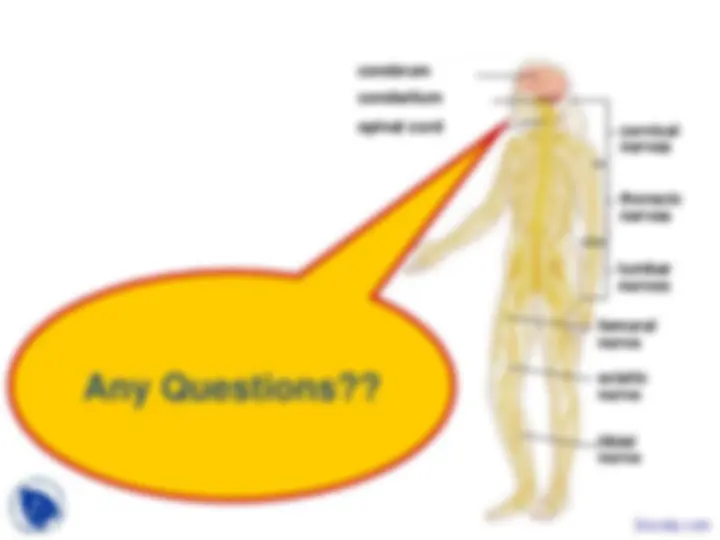
cerebrum cerebellum spinal cord (^) cervical nerves
thoracic nerves
lumbar nerves
femoral nerve sciatic nerve
tibial nerve
Any Questions??