















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Mechanical Applications, Molecular Separation, Nano Solar Cells, Nanocatalysts, Nanoparticles in Medicine, Agriculture and Genomics, Nanotoxicology, Nanowire Photonics, NDR Molecular, Zinc Oxide Nanowire and many others topics are part of this course. Key points in this lecture are: Nanocatalysts, Catalyst, Equilibrium, Changes Activation Energy, Types of Catalyst, Electrocatalyst, Organocatalyst, Enzymes, Dna Polymerase, Growing Interest
Typology: Slides
1 / 24

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

















Rodrigo Benedetti Kamal Banjara Bob DeBorde John DeLeonardis
Changes the rate of a reaction
↑ rate: catalyst ↓ rate: inhibitor Does not affect equilibrium composition
Neither a product nor reactant www.pnl.gov/.../highlights/highlight.asp?id=
Changes activation energy Offers an alternative reaction pathway New pathway requires less kinetic energy in molecular collisions
Catalysts can be either heterogeneous or homogeneous, depending on whether a catalyst exists in the same phase as the substrate - Other classifications: Electrocatalyst Organocatalyst http://www.bnl.gov/bnlweb/pubaf/pr/photos/2009%5C05%5CPlatinumCatalyst ‐300.jpg
http://www.news.cornell.edu/stories/Nov08/nanocatalysts.ws.html
Definition: A Nanocatalyst is a substance or material with catalytic properties that has at least one Nanoscale dimension, either externally or in terms of internal structures 1 Generally, catalysts that are able to function at atomic scale are Nanocatalysts 1 http://www.the ‐infoshop.com/report/bc21463_nanocatalysts.html https://www.jyu.fi/fysiikka/en/research/material/compns/research/index_html/supported.jpg
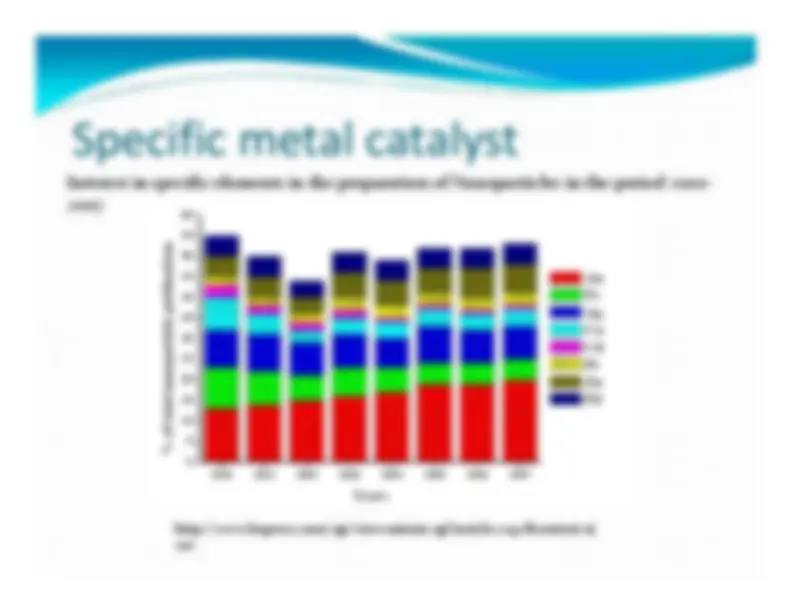
Interest in specific elements in the preparation of Nanoparticles in the period 2000 ‐ 2007 http://www.bepress.com/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2132&context=ijcre
Sizes may varies but can be controlled at less then
nm depending upon the application Particle position can be controlled increasing the reaction stability and mechanism Controllable exposed atomic structure Uniform dispersion http://www.htigrp.com/data/upfiles/pdf/Nanocatalysts0304.pdf http://news.princeton.edu/uploads/243/image/nanocatalyst_diagram.jpg
Catalytic Activity Very important factor in choosing a nanocatalyst Porous nanostructure provides high surface to volume ratio hence increase the catalytic activity 1 Example
in a Direct Formic Acid Fuel Cells,
poisoning significantly limits the catalytic activities of Pt/Ru and Pt/Pd alloys for formic acid oxidation Solution to the Poisoning
Decoding the nano particles with carbon support 2 2 References: Performance characterization of Pd/C nanocatalyst for direct formic acid fuel cells; S.HA, R. Larsen and R.I. Masel 1 Nanocatalyst fabrication and the production of hydrogen by using photon energy; ming –Tsang Lee, David J. Hwang, Ralph Greif and Costas P Gigoropoulous http://tinyurl.com/yzqps4d
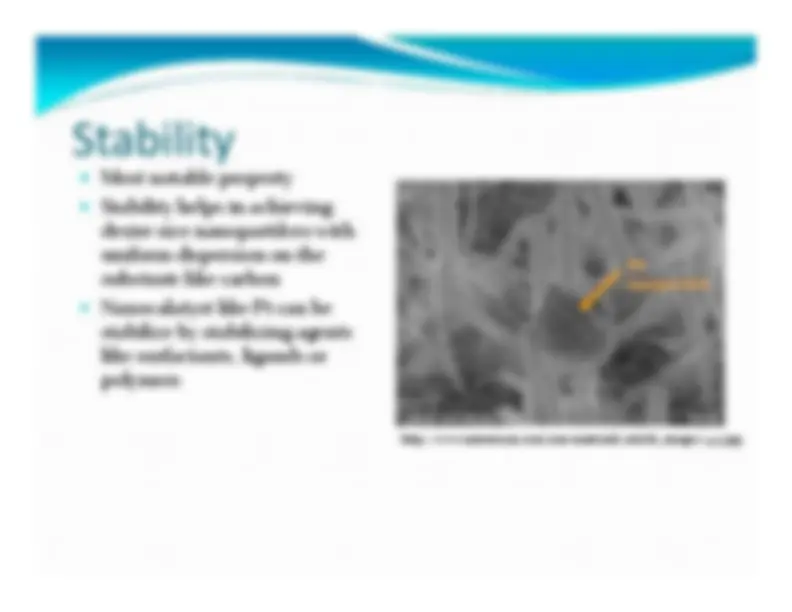
Most notable property Stability helps in achieving desire size nanopartilces with uniform dispersion on the substrate like carbon Nanocalatyst like Pt can be stabilize by stabilizing agents like surfactants, ligands or polymers http://www.natureasia.com/asia ‐materials/article_images/425.jpg
These advantages are related to the inherent properties of the material. Also to their: Size Charge Surface area http://www.inano.au.dk/research/research ‐areas/nano ‐ energy ‐materials/nanocatalysis/
Nanocatalyst can fit where many of the traditional catalyst will not. By nanocatalyst being very small in size, this property creates a very high surface to volume ratio. This increase the performance of the catalyst since there is more surface to react with the reactants chemistry.brown.edu/research/sun/research.html http://www.bnl.gov/bnlweb/pubaf/pr/photos/2002/nanoparticles ‐ w.jpg
Nano ‐ catalysts are part of tomorrow’s cutting edge technology. One example is the use of Hydrogen as a domestic fuel. As you may know, Hydrogen is as abundant as it is environmentally friendly. Companies would love to develop an efficient Hydrogen Fuel cell that is financially feasible. One major problem however, is the method of reversible storage of Hydrogen. One company, HRL Laboratories ,^ is currently working on a multi ‐ million dollar project that will increase the efficiency of current Hydrogen storage methods by utilizing the properties of Nano ‐ catalysts. The next slide shows the project overview A typical Hydrogen fuel cell
Imagine filling up your tank with a gas instead of liquid
Laboratories are working hard to meet and exceed Department of Energy standards for hydrogen storage. http://www.hydrogen.energy.gov/pdfs/review06/st_16_olson.pdf