




















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
These are the Lecture Slides of Wind Engineering which includes Governing Equations for Flow, Preliminary Remarks, Conservation of Mass, Continuity Equation, Area of Boundary, Speed Incompressible Flow, Angular Velocity of Fluid etc. Key imporatnt points are: Momentum Theory, Simple Performance, Prediction Methods, Equations of Motion, Conservation of Mass, Conservation of Momentum, Conservation of Energy, Continuity, Compressible Flow
Typology: Slides
1 / 28

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





















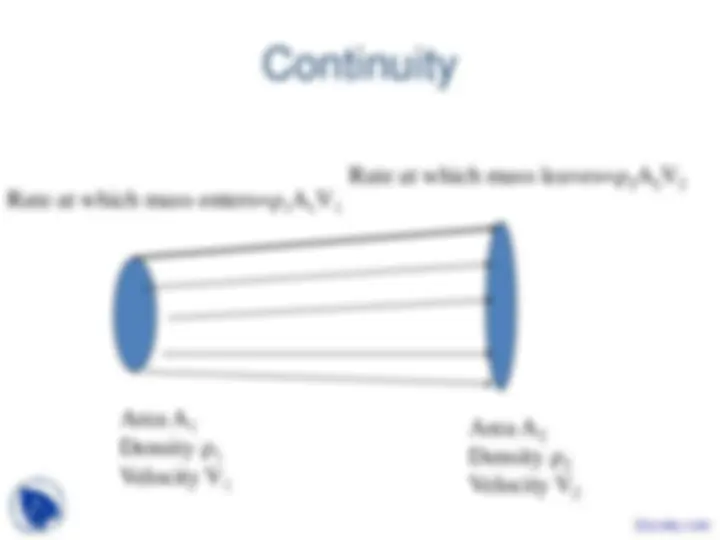
In compressible flow through a “tube”
ρAV= constant
In incompressible flow, ρ does not change. Thus,
AV = constant
AV = constant
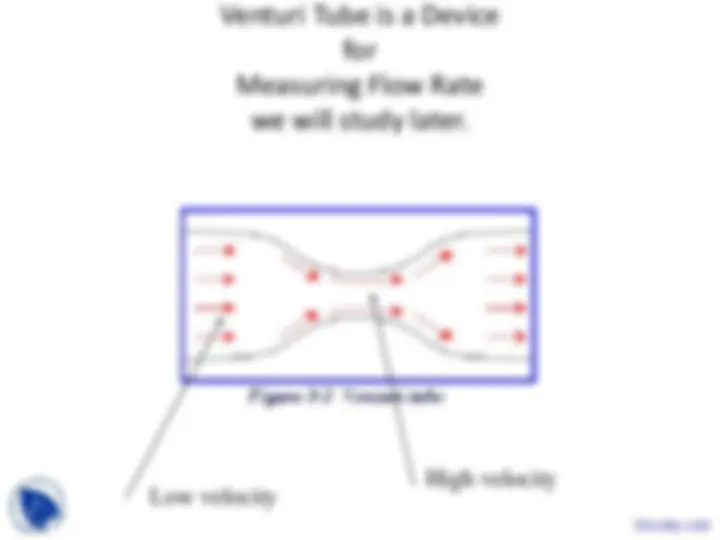
If Area between streamlines is high, the velocity is low and vice versa.
In regions where the streamlines squeeze together, velocity is high.
High Velocity
Low Velocity
Venturi Tube is a Device for Measuring Flow Rate we will study later.
Low velocity
High velocity
Momentum Equation (Contd..)
Density ρ velocity V
Density ρ+dρ velocity V+dV Area =A+dA
Momentum rate in= Mass flow rate times velocity = ρV 2 A
Momentum Rate out= Mass flow rate times velocity = ρ VA (V+dV)
Rate of change of momentum within this element = Momentum rate out - Momentum rate in = ρ VA (V+dV) - ρV 2 A = ρ VA dV
Momentum Equation (Contd..)
Area =A
Density ρ+dρ velocity V+dV Area =A+dA
Rate of change of momentum as fluid particles flow through this element= ρ VA dV
By Newton’s law, this momentum change must be caused by forces acting on this stream tube.
Forces acting on the Stream tube
Pressure times area=pA
(p+dp)(A+dA)
Horizontal Force = Pressure times area of the ring=(p+dp/2)dA
Area of this ring = dA
Net force = pA + (p+dp/2)dA-(p+dp)(A+dA)=- Adp - dp • dA/2≈-Adp
Product of two small numbers
From the previous slides,
Rate of change of momentum when fluid particles flow through the stream tube = ρAVdV
Forces acting on the stream tube = -Adp
We have neglected all other forces - viscous, gravity, electrical and magnetic forces.
Equating the two factors, we get: ρVdV+dp=
This equation is called the Euler’s Equation
Actuator Disk Theory: Background
V
Disk area is A
Total area S
Station
Station 2
Station 3
Station 4
V- v (^2)
V-v (^3)
Stream tube area is A 4 Velocity is V-v (^4)
( )
4 4
1
4 4 4
ρv A
Inflowat thetop Outflowat the bottom
Ouflowthrough theside m
Outflowthrough thebottom ρV S-A ρ(V v )A
Inflowthrough thetop ρVS
=
= −
=
= + −
=