









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Main points of Local and Wide Area Networks are: Medium Access Sublayer Two, Multiple Access Protocols, Ieee, Standard, Ethernet, Wireless, Protocols, Misc, Channel Efficiency, Complicated Stuff Skipped
Typology: Slides
1 / 18

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!











)
)
)
)
)
)
c
)
)
)
)
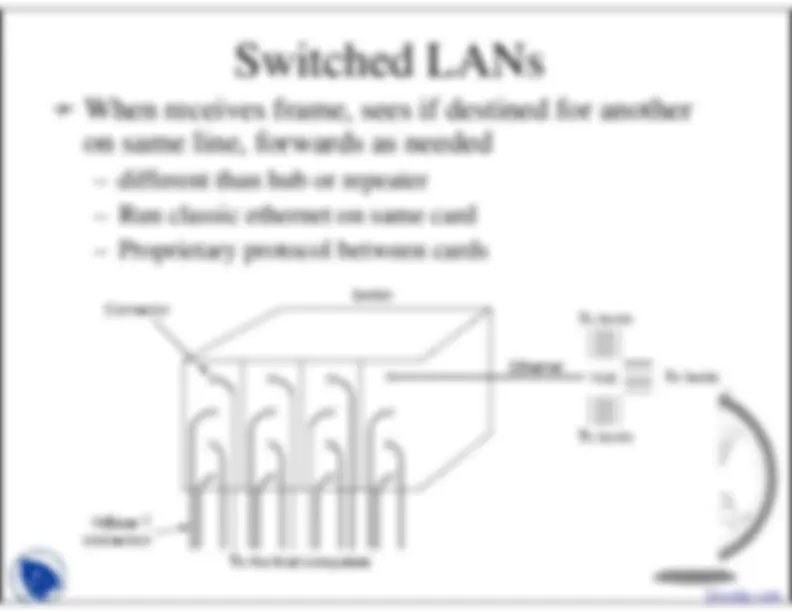
Switched LANs
)
)
)
)
)
When receives frame, sees if destined for anotheron same line, forwards as needed
)
FDDI, Fibre channel too complicated, didn’tbecome LAN )
Used as backbones, no widespread success )
Made 802.3 committee think tank (in 1992)
)
Reasons 802.3 won:
)
(a) A two-station Ethernet. (b) A multistation Ethernet.
)
Two modes:
)
Full duplex used when a switch is used (b) )
No contention since line is FD, so no CSMA/CD
)
Half-duplex used when a hub is used instead of aswitch )
Hub cannot buffer packets, switch can )
Collisions are possible so CSMA/CD )
Higher bandwidth means shorter longest distance )
Solutions:
)
Result: extends network radius to 200 meters
IEEE 802.2: Logical Link Control(a) Position of LLC. (b) Protocol formats.
)
So far Ethernet and MAC protocols offer no reliableservice (e.g. stop-and-wait, etc) )
IEEE defined LLC to run above MAC to providethese services )
Closely based on HDLC
)
)
)