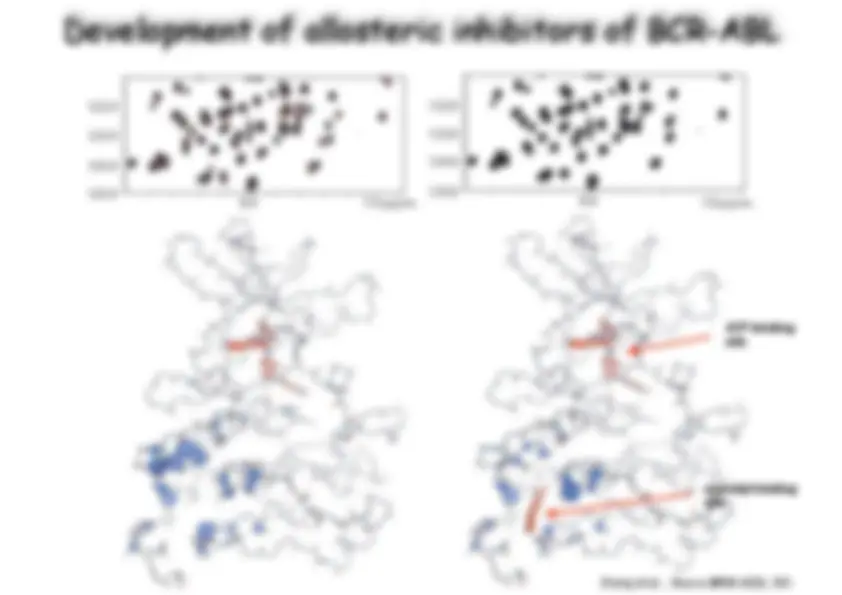
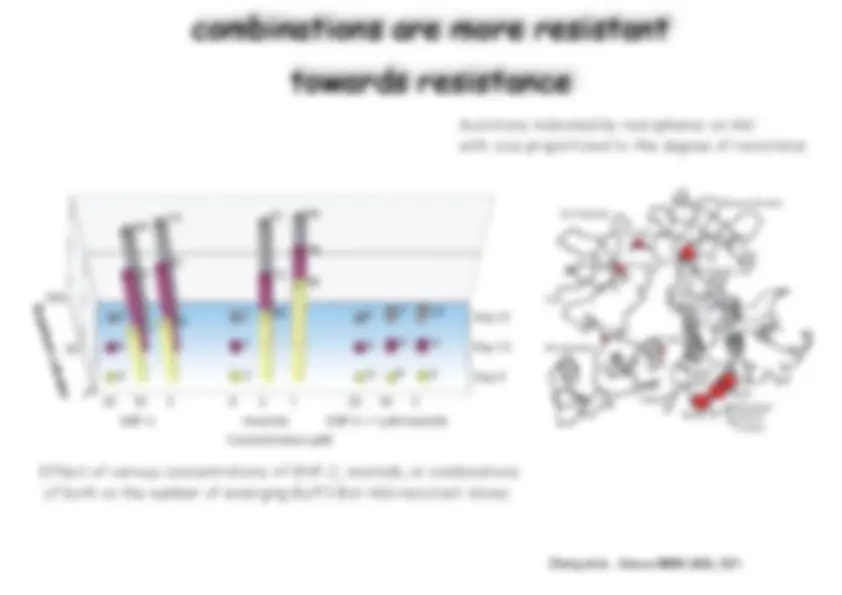
Download Medicinal Chemistry and more Exams Chemistry in PDF only on Docsity!
Medicinal Chemistry
all material is available online as pdf files
under the following URL:
http://www.chem.uzh.ch/zerbe/MedChem/Course_MedChem.html
Books and other information sources
Monographs :
- G. Patrick: Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry, Oxford University Press, 2005 (very good introduction)
- H.-J. Böhm, G. Klebe, H. Kubinyi: Wirkstoffdesign. Der Weg zum Arzneimittel (Spektrum Lehrbuch) (very interesting, easy to read)
- G. Thomas: Medicinal Chemistry: An Introduction (Wiley), (inexpensive introduction)
- H. P. Rang, M. M. Dale, J. M. Ritter: Pharmacology, Churchill Livingstone; 6th ed.
- E.J. Corey, B. Czakó, L. Kürti, Molecules and Medicine (Wiley)
- D.S. Johnson, J.J. Li: The Art of Drug Synthesis (Wiley)
Journals :
- Nature Reviews Drug Discovery
- Drug Discovery Today
- ACS Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
- Trends in Pharmacological Sciences
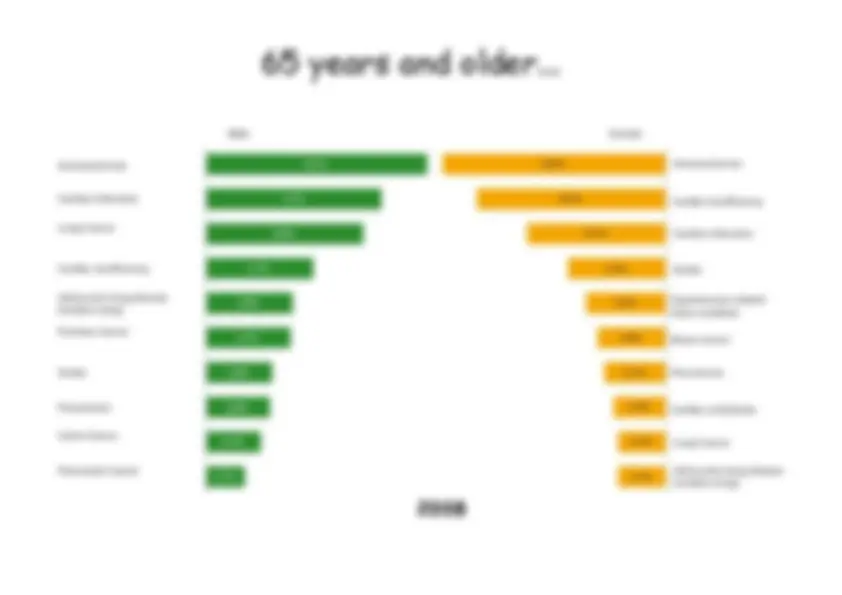
age quality of life childbed fever of the mother 1 (^1) infection of appendix 2 2 3 (^3) accidents
Society before 1800
Medicine after ~ 1950
age quality of life
most common cause of death for 22-44 year old people
Medicine in the antiquity
- Chinese medicine: (3500 BC)
- chinese herbs, some of the ingredients are still in use today, e.g. Reserpin (blood high pressure; emotional and mental control), Ephedrine (Asthma)
- Egyptian medicine (3000 BC)
- Papyrus Ebers, 877 descriptions and recipes
- Greek medicine (from 700 BC)
- illness is no punishment from God, medicine is considered a science
- diseases are due to natural causes
- Hippocratic oath
- Roman medicine (from approx. 200 BC):
- invention of hospitals
- large influence of greek medicine
- Materia Medica: pharmaceutical descriptions
Medicine in the Middle Ages (400 to 1500 AC)
- The church preserves greek traditional recipes
- Era of horrible epidemics (e.g. Pest, Lepra, Pox, Tuberculosis)
- Arabic medicine: Development of medical procedures for drug preparation (distillation) afterwards....
- Development of scientific approaches:
- Pox: Edward Jenner discovered that people who worked with cattle and had caught the cowpox disease (a mild disease related to smallpox) were immune and never caught smallpox. He inoculated a boy with blister fluid from a woman with cowpox. He later inoculated the same boy with fluid from smallpox, and discovered that the boy was immune against the disease.
- Bill Withering introduces extracts of Digitalis for treatment of heart problems
- Louis Pasteur discovers that microorganisms are responsible for diseases and develops vaccinations against rabies. He introduces attenuated viruses for treatment of rabies.
Discovery of Penicillin
- Alexander Flemming discovers in 1928 that a fungus grew on a bacterial plate containing staphylococci. Close to the fungus all bacteria were killed.
- Biotechnological production of penicillins was established during the second world war and helped saving the life of many soldiers
Robert Koch
Nobel laureate 1905 "for his discovery and treatment of tuberculosis"
Since then....
- Early 1900: synthetic drugs, foundation of pharmaceutical industry
- since 1930: screening of natural products, isolation of their bioactive ingredients
- late 70 ies: Development of recombinant drugs (proteins, e.g. interferons). Development of biotechnology
- 2000: Deciphering of the human genom, gene therapy (?), Investigation of the molecular basis of disease
- future: Personalized medicine?
Complexity
accidential
observation
focus on
biochemistry
focus on
cell-biology
focus on
molecular function
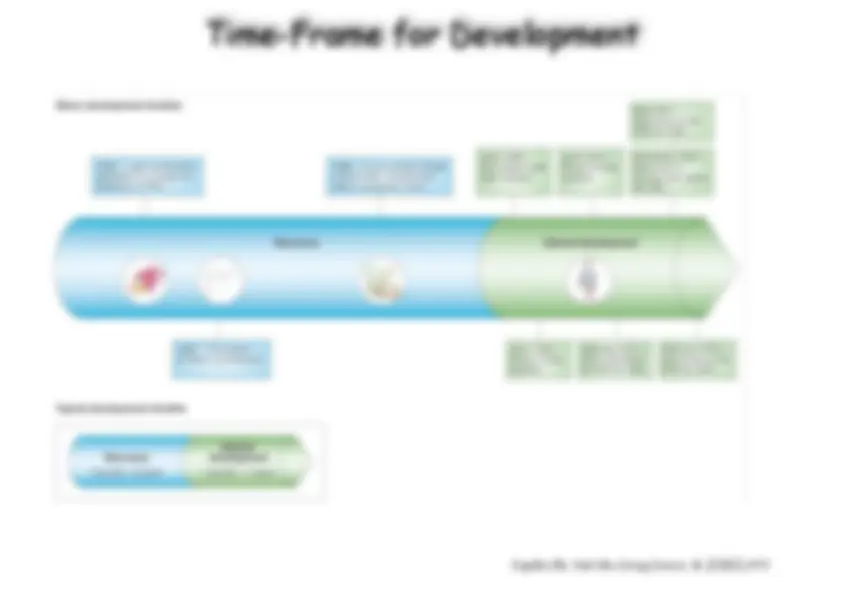
History of drug development
taken from: Real World Drug Discovery , R. Rydzewski, Elsevier 2008
Blockbusters 2013 (C&N news, supl. 09/14)
name disease area company drug class sales 2013
1 Humira (adalimumab) Rheumatoid
arthritis
AbbVie antibody $11 billion
2 Enbrel (etanercept) Rheumatoid
arthritis
Amgen recombinant
fusion protein
$8.75 billion
3 Advair (fluticasone
propionate and salmeterol)
Asthma, chronic
obstructive
pulmonary disease
GSK small molecule $8.3 billion
4 Remicade (infliximab) Rheumatoid
arthritis
Johnson &
Johnson/Janssen
antibody $8.3 billion
5 Rituxan (rituximab) Lymphoma,
leukemia and
rheumatoid
Roche/Genentech antibody $8 billion
6 Lantus (insulin glargine) Diabetes Sanofi insulin analogue $7.5 billion
7 Avastin (bevacizumab) Cancer Roche antibody $6.5 billion
8 Herceptin (trastuzumab) Cancer Roche/Genentech antibody $6.5 billion
9 Crestor (rosuvastatin) high cholesterol AstraZeneca small molecule $6 billion
10 Januvia (sitagliptin) diabetes Merck small molecule $6 billion
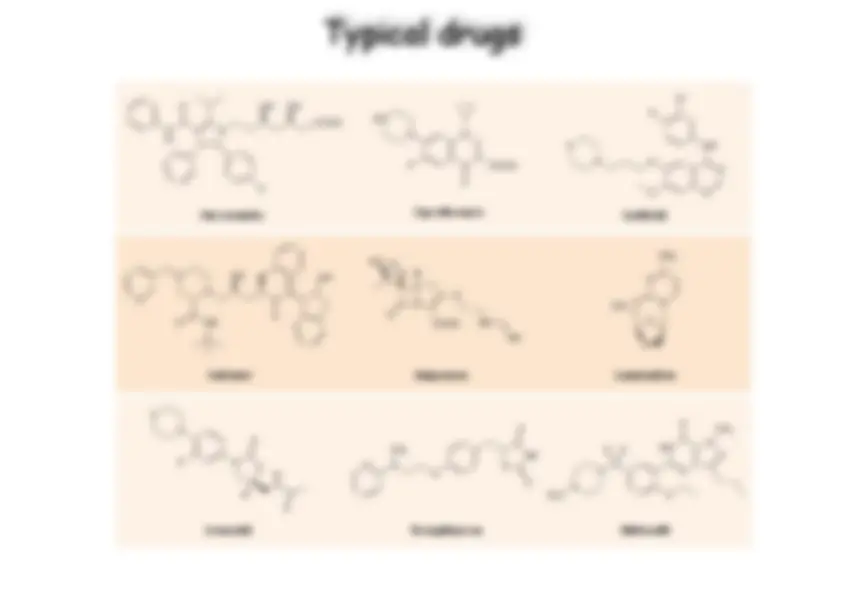
Top small molecule drugs
Salmeterol (CH 2 ) 6 (CH 2 ) (^4) HO HO OH O N H Rosuvastatin CH (^3) CH (^3) H 3 C H 3 C HO 2 C HO OH N F N O O S N Sitagliptin CF (^3) NH 2 O N N N N F F F Imatinib mesylate CH (^2) H 3 C N N C O N H CH (^3) N N N H N Aripiprazole (CH 2 ) (^4) Cl Cl O O H N N N Duloxetine CH 3 NH O S Pregabalin CH (^3) H 3 C CO^2 H NH (^2) Lenalidomide NH (^2) H N N O O O Tiotropium bromide CH (^3) O CH (^3) O S +N Br - S O HO Esomeprazole OCH (^3) CH (^3) CH 3 O CH (^3) S N N H N O Valsartan CH (^3) CH (^3) HO 2 C N N N N H N O Budesonide H 3 C (^) CH (^3) O O O O H O H O H H H H Formoterol CH 3 O CH^3 N H OH OH OHC NH Tenofovir NH (^2) CH (^3) N PO 3 H 2 N N O N Celecoxib NH (^2) F 3 C O O S N N CH (^3) Telmisartan N N N N CH (^3) HO 2 C CH (^3) CH (^2)