



Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Solutions to various programming exercises in MATLAB related to mathematical functions, vectors, and matrices. It covers topics such as piecewise functions, maximum/minimum values, summation, products, iteration, recursion, and more. Students can use these solutions as a reference to understand the coding patterns and apply them to solve similar problems.
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 6

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




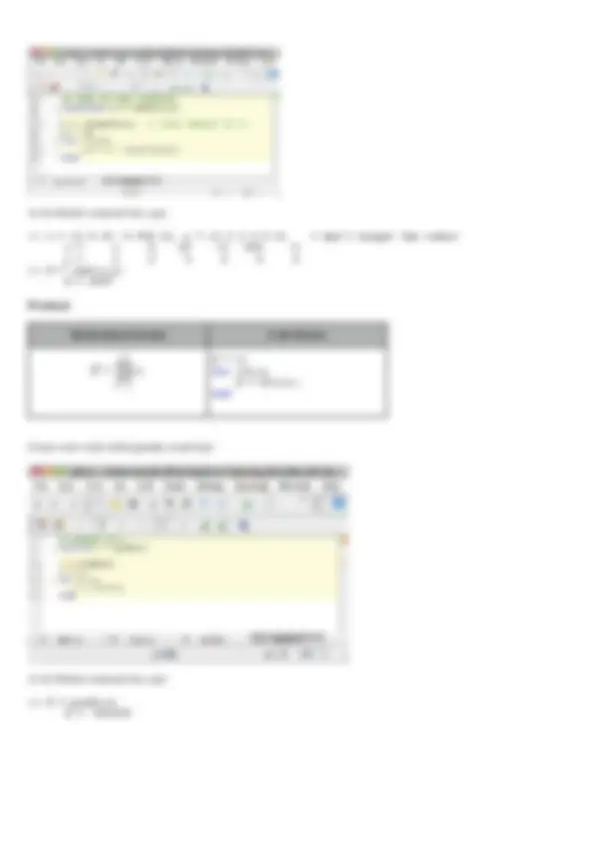
When writing programs, it is a good idea to write your code in a file. This can be done using any editor or by using the built-in editor. The files should always be saved with the extension .m File names cannot begin with numbers or include hyphens. Open the editor by clicking on the icon underneath the File menu (labeled New M-File) and type the following lines in it:
a(1)=1; for n=2: a(n)=a(n-1)+1/n^2; end plot(a,'r*')
Click on the Save and Run button in the menubar of the editor to save the program and to run it in Matlab. Remember to use the extension .m for the saved file. Alternatively, if the file was created with another editor and saved as filename.m, then it can be run in Matlab by typing filename
Programming patterns are standard segments of code that form parts of larger algorithms. These patterns allow us to represent standard mathematical expressions and tasks e.g. sums in mathematics can be evaluated using for-loops in programming.
Mathematical formula Code Pattern
if condition Y = a; else Y = b; end
The simplest example of a piecewise-function is |x| :
Create a new script and type:
Save this script as absx.m in your working directory. At the Matlab command line type:
ls % check that I am in my working directory absx.m Y = absx(-2) Y = 2 Y = absx(2) Y = 2
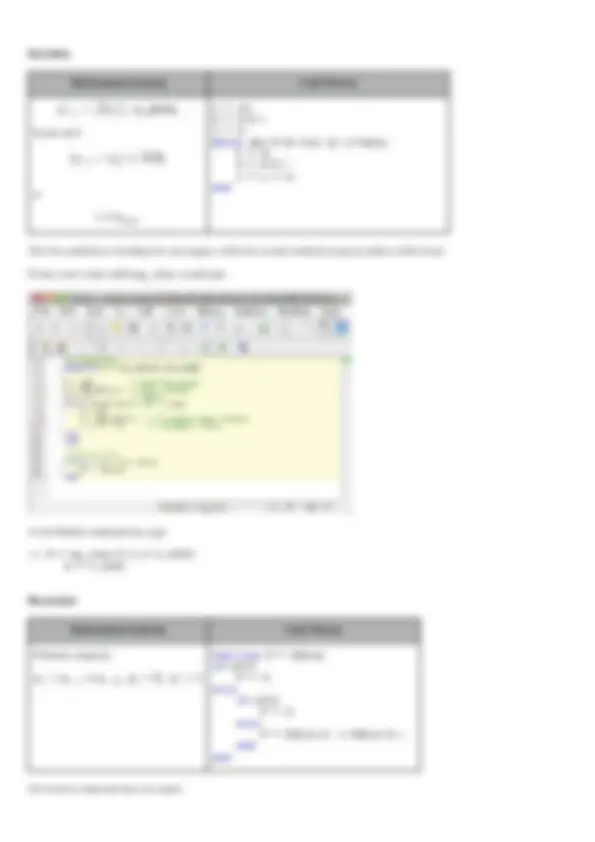
Mathematical formula Code Pattern
Y = x(1); for i = 2:n if Y < x(i) Y = x(i); end end
Create a new script called maxx.m and type:
At the Matlab command line, type:
x = [1 5 20 -4 500 2] % a (row) vector of numbers x = 1 5 20 -4 500 2
Y = maxx(x) Y = 500
Mathematical formula Code Pattern
z = 0; for i=1:n z = z + x(i)*y(i); end
Create a new script called sum2.m and type:
Mathematical formula Code Pattern
Iterate until:
or
Y = x0; Z = f(Y); i = 1; while abs(Y-Z)>tol && i<=imax Y = Z; Z = f(Y); i = i + 1; end
The first condition is checking for convergence while the second condition stops an endless while-loop!
Create a new script called my_iter.m and type:
At the Matlab command line, type:
Z = my_iter(0.2,0.1,1000) Z = 0.
Mathematical formula Code Pattern
Fibonacci sequence function F = Fib(n) if n== F = 0; else if n== F = 1; else F = Fib(n-1) + Fib(n-2); end end
All recursive functions have two parts:
Create a new script called Fib.m and type:
and at the Matlab command line type:
F = Fib(6) F = 8
Combining the above code patterns, we can solve more complex problems e.g. find the infinity norm of a matrix A
To solve this problem, one first finds the vector
and then you can apply the “max” code pattern to find Y. The Matlab script looks like this: