




















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Advanced programming language principles with a focus on Haskell's Algebraic Data Types (ADT), types, kinds, and typeclasses. It includes examples of Maybe and Either types, their usage, and how they help prevent runtime errors. The document also discusses Null Pointer Exceptions, the Maybe and Either types in Haskell, and creating custom ADTs.
What you will learn
Typology: Slides
1 / 30

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!























Algebraic Data Types, Kinds, & Typeclasses
public class Maybe { public static String reverse(String s) { return new StringBuilder(s).reverse(); } public static void main(String[] args) { String rev = reverse("Racecar"); System.out.println(rev); } }
$ javac Maybe.java Maybe.java:3: error: incompatible types: StringBuilder cannot be converted to String return new StringBuilder(s).reverse(); ^ 1 error We needed a String but tried to return a StringBuilder.
$ javac Maybe.java $ java Maybe racecaR $ The types match, so:
public class Maybe { public static String reverse(String s) { return ""
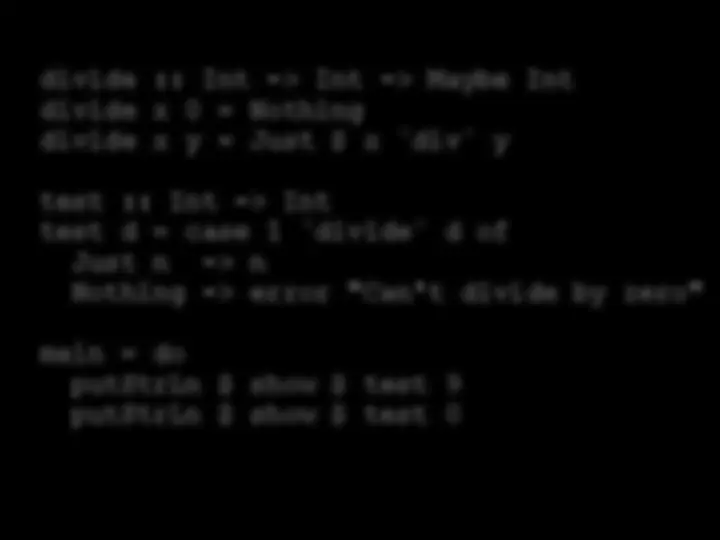
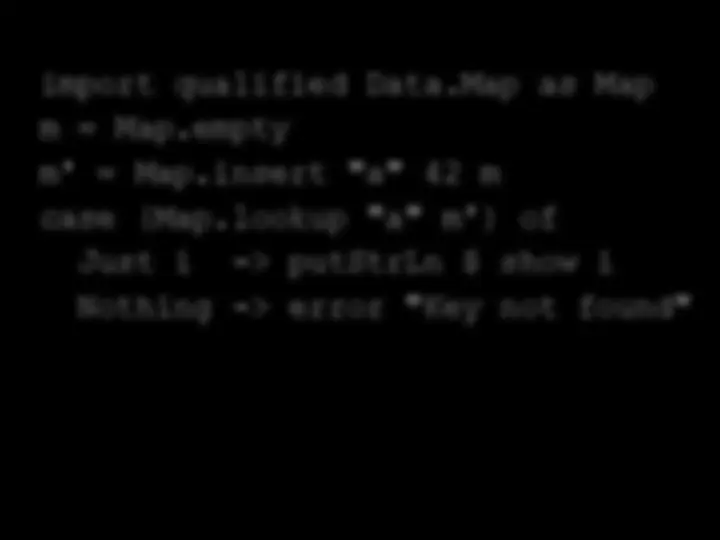
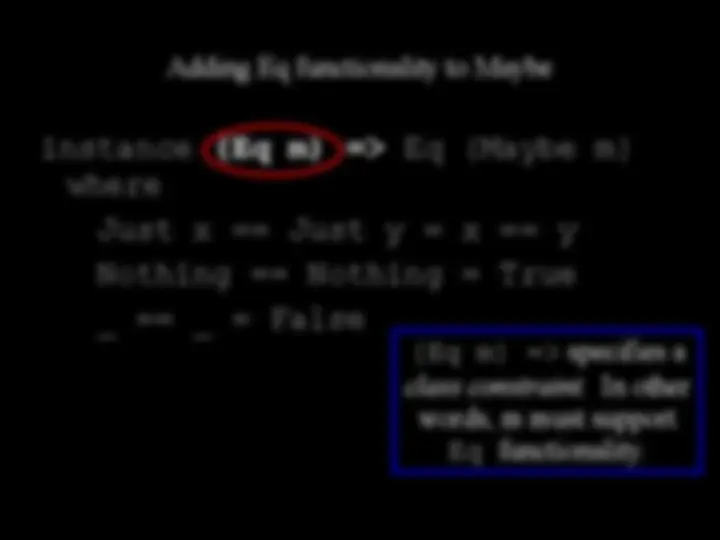
div ydivide d ofMaybe is an algebraic data type (ADT) An ADT is a composite data type; a type made up of other types. Can we create our own ADTs?
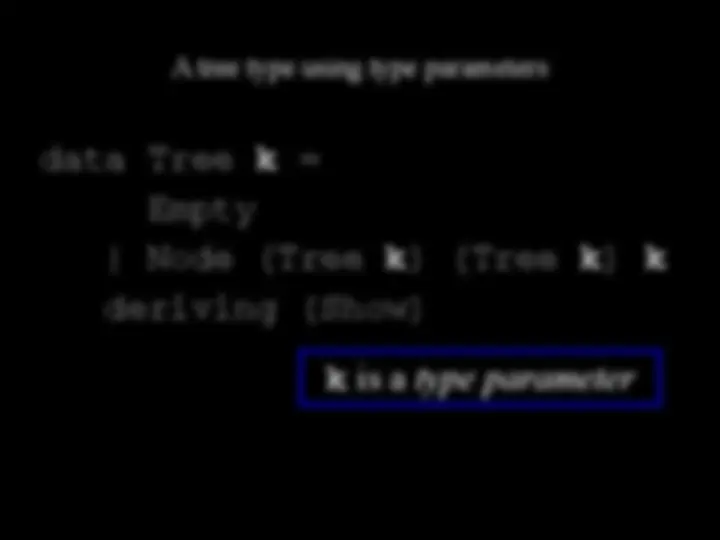
data Tree = Empty | Node Tree Tree String deriving (Show)
data keyword lets us define a new type.
*Main> :t (++) (++) :: [a] -> [a] -> [a] ++ takes a list of a's and returns… a function that takes a list of a's and returns… a list of a's.