

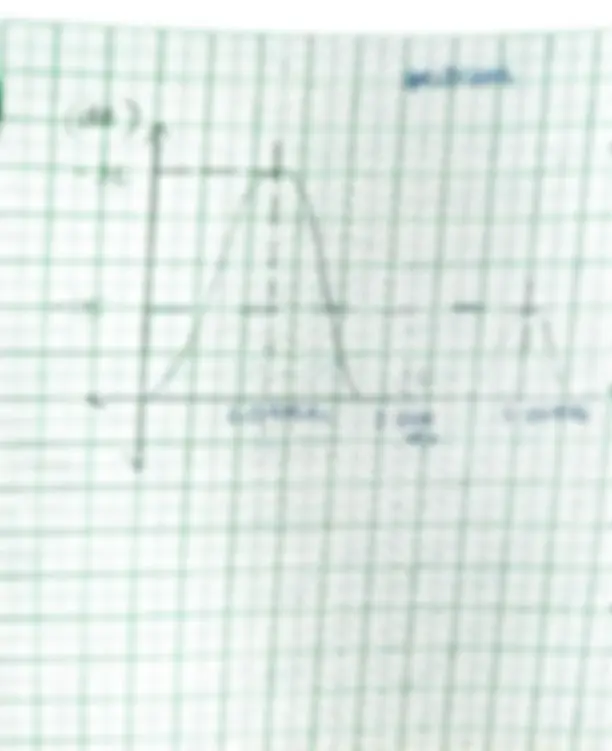


Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Graphs of different waveforms: modulating signal, carrier signal, modulated wave, frequency spectrum Observations made on wave readings End of lab questions answers
Typology: Lab Reports
1 / 7

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



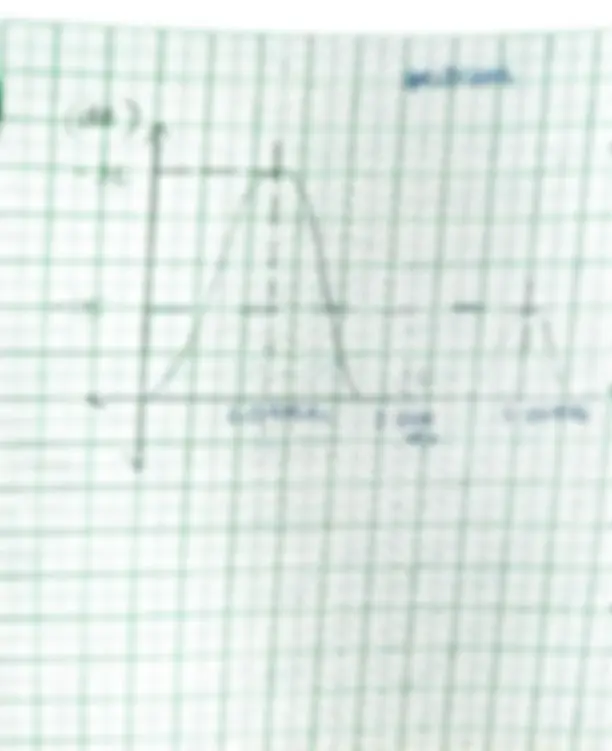
Name: Reet Shinde (^) Class: Roll No: PA-33 Batch: Al Experiment No: 03 Name of the Experiment: Generation, detection and spectral analysis of SSB. Performed on: 24/02/2023 Marks^ Teacher's^ Signature^ with^ date Submitted on: 04/03/
Aim: To study Single Side Band (SSB) modulation using Phase Shift method and its detection.
Prerequisite: Analog Modulation, Time and Frequency domain representation
Objectives: To generate SSB Suppressed Carrier (SSB-SC) modulated signal To observe the time and frequency domain waveforms and calculate its bandwidth To (^) detect the SSB-SC (^) signal and observe the recovered (^) signal.
Components and Equipment required: SSB Modem, CRO/DSO, Spectrum Analyser,
Theory:Single side band suppressed carrier (SSB-SC) Modulation
In amplitude modulation, two-thirds of the transmitted power is in the carrier, which itself conveys no information. The real information is contained within the sidebands. One way to
sideband. The result is a single-sideband (SSB) signal. The first step in generating an SSB signal is to suppress the carrier, leaving the upper and lower sidebands. In DSB transmission, since the
Expt. 3-
Date Expt. No./ Name:3 Page^ No.
Deperiment 3 Name d Dxperimend Gtneraiom dottthm and specral analysiS o SSB.
Aun:Jo study single Side Band (sSB) MDdulanion uDing_ Phase (^) SLuift mthod andta clotechonm
Dbseryation Iable 105 M Hz V1-6V(P-p) Vm 4 [P-P)
Sr Modulatng signo reg uonu LSB No frequeny (fm) VSB +amplitudli 3-4 dg
Bandwidtn (BN)_
z Sd kHz
nuuusion IhA we arnd to gengrate SSB (Single SideBand ) modulake. Siana Dbserved th time_and freq wareforma f modulakd and corrier signo Lwith its phase shift, the D6BSCL and DSBSC2 rom baanced Modulator 1 and 2, the domodulatai s1gno and the SSB ware Speutrum
50 KH 2
DSBC
4 H (^) V 43V
3KM (^) H4V
emtodiulakkd SS
Expt. No. / Name Date PageNo.
Sstabuu (^) and (^) selediviu (^) weu (^) neuond tnat (^) on u siye AM (^) ReLvers (^) whinLin_whu (^) broa d.caDters (^) rarely vse SSE_ fDr broodcading enorothias NI_mihantcoL iltts i most common ued n SSB MecnanLcal es_purpose Dama aa tmoL G namio
4
lelectromic (^) rsSuch aA tn^ pass^ mnge^ sianol^ frequoncien
but to block otnors^ Tho r^ actn^ om_mochanical^
lunidn ae tne anaLoguo d eloukrical signak