




























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The metabolism of l-arginine, the role of nitric oxide, and the effects of arginine supplementation. It covers the synthesis of nitric oxide, the three isoforms of nitric oxide synthase, the effects of arginine supplementation, and the structure of l-arginine and its circulatory analogues. The document also discusses the methylation of l-arginine, the removal of methylated analogues, and the enzymes involved in their metabolism.
Typology: Slides
1 / 44

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





































•L-Arginine metabolism•Nitric oxide
•Synthases•Dimethylarginines•Effects
•Arginine Supplementation
•Infusion/ Oral•Endothelial Function
•Epidemiology
L-Arginine is considered a semi-essential amino acid: it becomesessential in growing children, duringpregnancy or after injury. A Western diet provides about 4-6g/day of which 40-50% is absorbed.
•The liver produces considerable
amounts of arginine during the ureacycle, but little is available forsynthesis.
which is converted by other tissues(kidney, 80%) into L-arginine whichis then made available to othertissues.
Three Isoforms
Neuronal (constitutive, calcium dependent)
Endothelial (constitutive, calcium dependent)
Macrophages (inducible, calcium independent). Can lead to highlevels of NO being formed.
Relaxes smooth muscle Inhibits platelet aggregation andactivation Neurotransmitter Tumoricidal and bactericidal agentfrom macrophages (excess candamage healthy tissue)
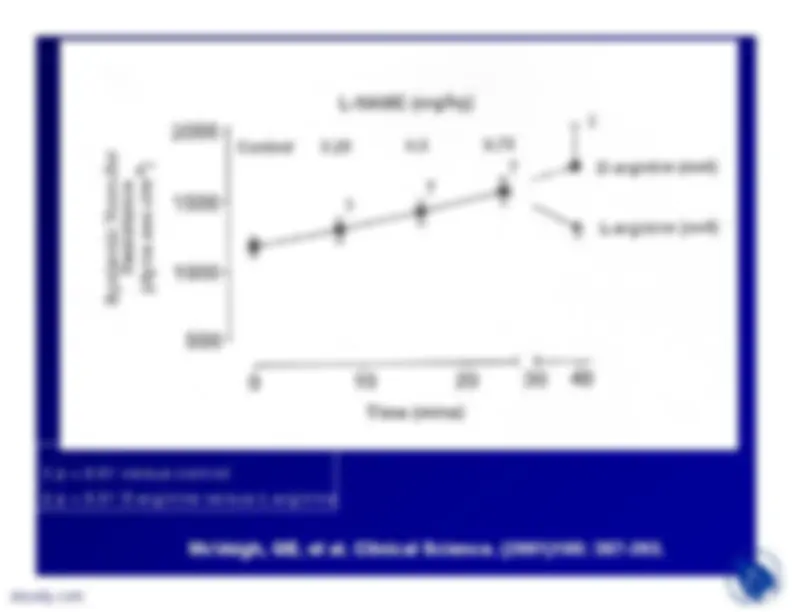
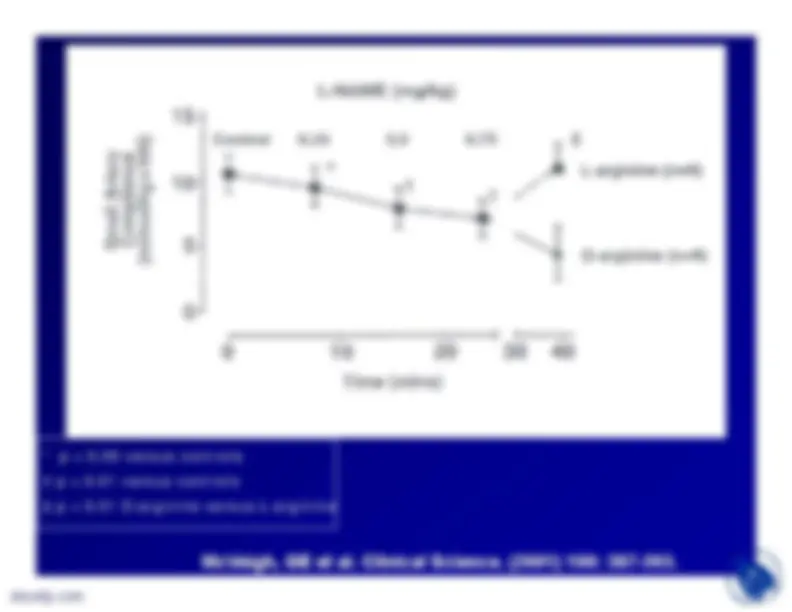
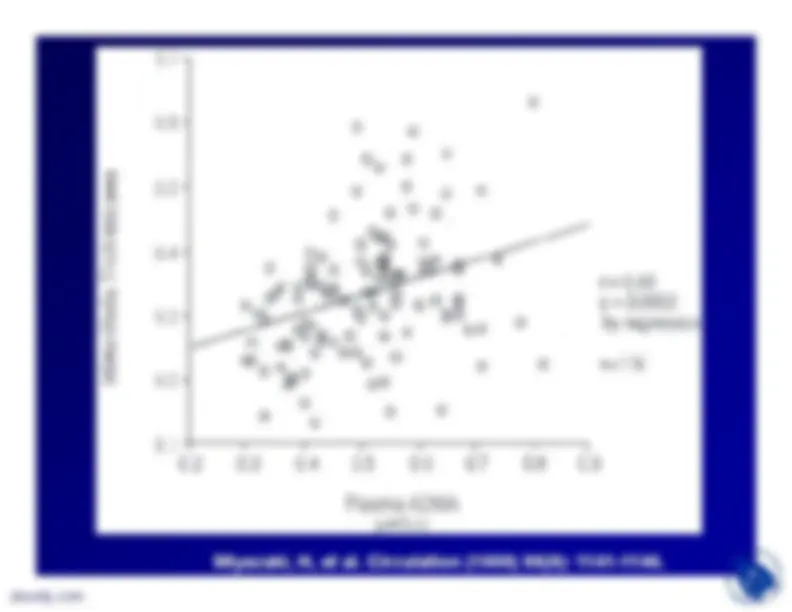
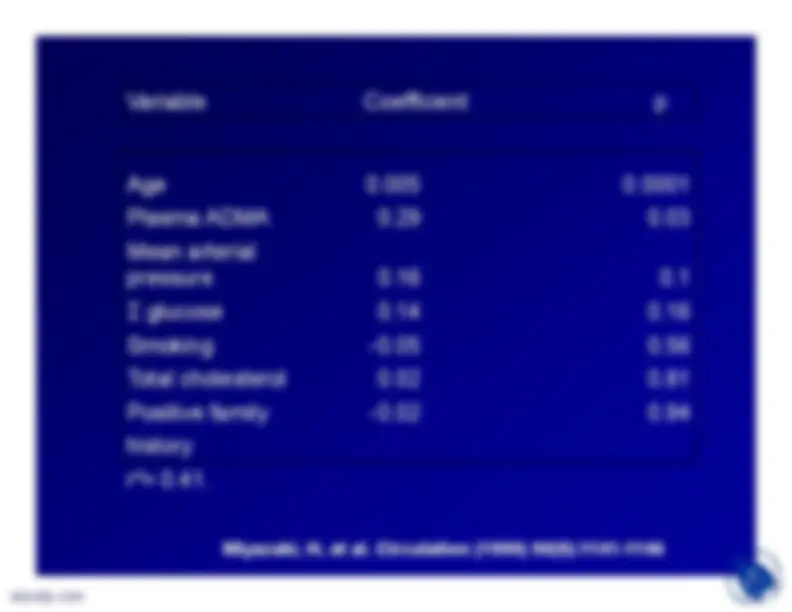
presence of naturally occurringinhibitors of NOS (ADMA and NMA).These two analogues of L-arginineplus SDMA are also competitors forthe y
transport system that delivers
L-arginine to NOS.
Structure of L-arginine and Circulatory Analogues
NH
NH
2
C NH CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
NH
2
COOH
L-ARGININE
L-NMA
ADMA
SDMA
NH
CHNH
3
C NH CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
NH
2
COOH
NH
N
CH
3
CH
3
C NH
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
NH
2
COOH
C
N
NH
CH
3
CH
3
NH
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
NH
2
COOH
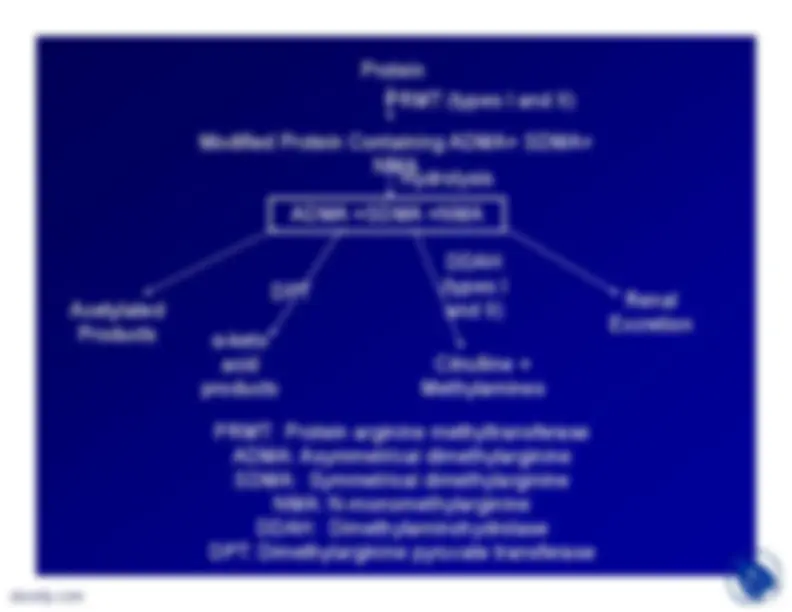
by renal excretion or catabolism•DDAH type I associated with neuralNOS•DDAH type II associated withendothelial NOS•Neither DDAH is active on SDMA•DPT (a minor pathway) acts on allthree analogues•The enzymes are particularly active inkidney
Protein
PRMT (types I and II)
Modified Protein Containing ADMA+ SDMA+
NMA
Hydrolysis
ADMA +SDMA +NMA
Acetylated
Products
α
-ketoacid
products
Citrulline +
Methylamines
DDAH (types I
and II)
Renal
Excretion
PRMT: Protein arginine methyltransferase
ADMA: Asymmetrical dimethylarginineSDMA: Symmetrical dimethylarginine
NMA: N-monomethylarginine
DDAH: Dimethylaminohydrolase
DPT: Dimethylarginine pyruvate transferase
DPT
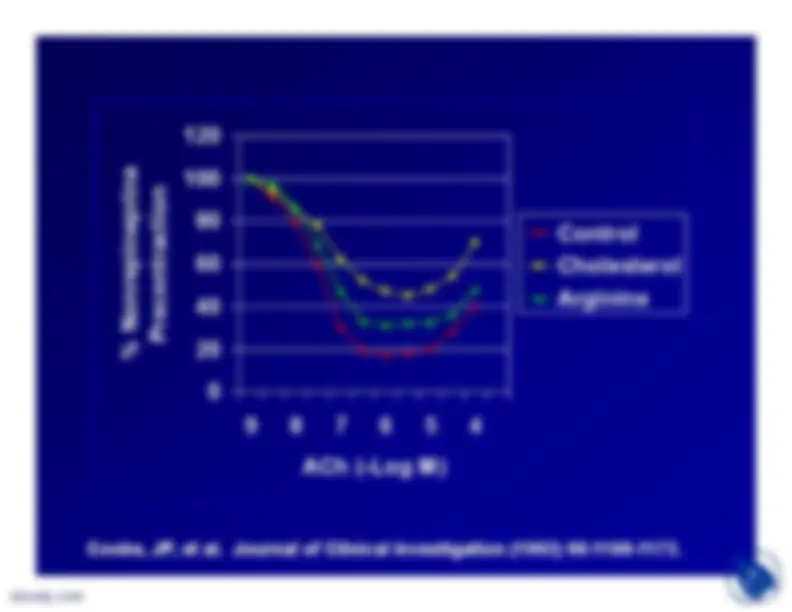
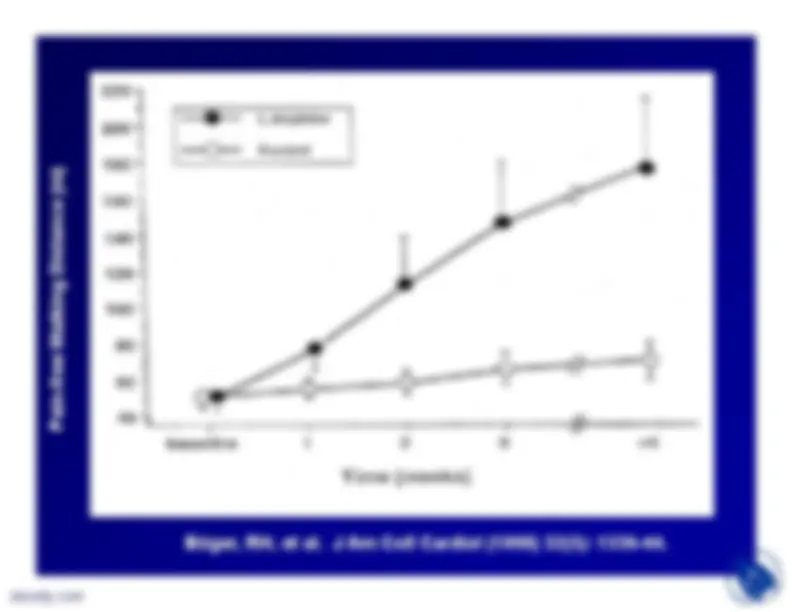
In slides 18 and 19, results from
Cooke et al (1992) are shown. Theinvestigators fed male rabbits either (a)normal chow (control) or (b) 1%cholesterol diet; or (c) 1% cholesteroldiet supplemented with drinking watercontaining 2.25% L-arginine HCl. After10 weeks of dietary intervention,analyses indicated:
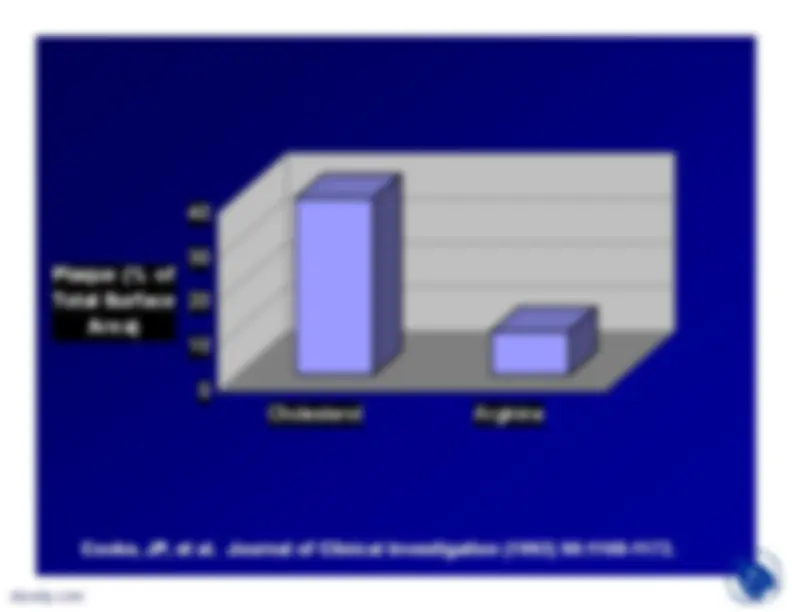
Endothelium dependent relaxation ofthe thoracic aortae elicited byacetylcholine was reduced incholesterol-fed animals and theresponse was significantlyameliorated by L-arginine. L-arginine also significantly reducedthe lesion surface area in thedescending thoracic aorta elicited bycholesterol diets (intima thicknessalso reduced)
0
40 30 20 10
Plaque (% ofTotal Surface
Area)
Cholesterol
Arginine
Cooke, JP, et al. Journal of Clinical Investigation (1992) 90:1168-1172.
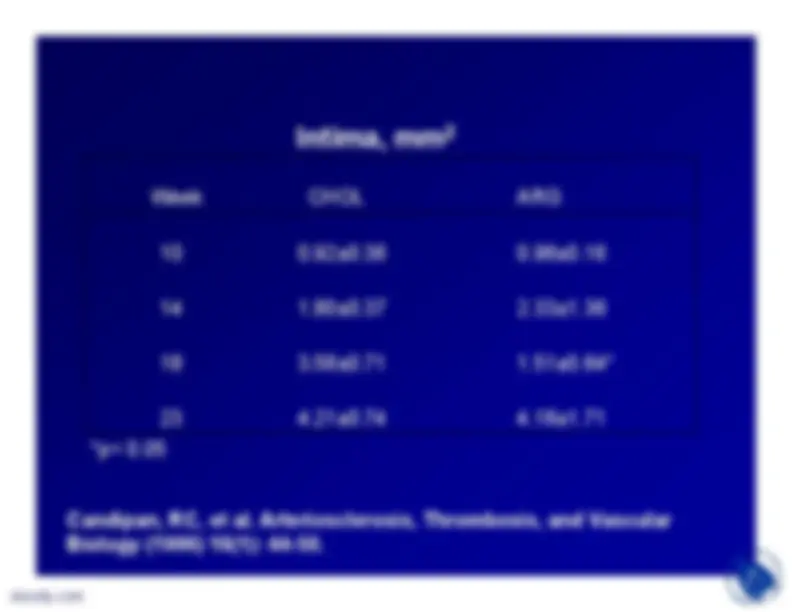
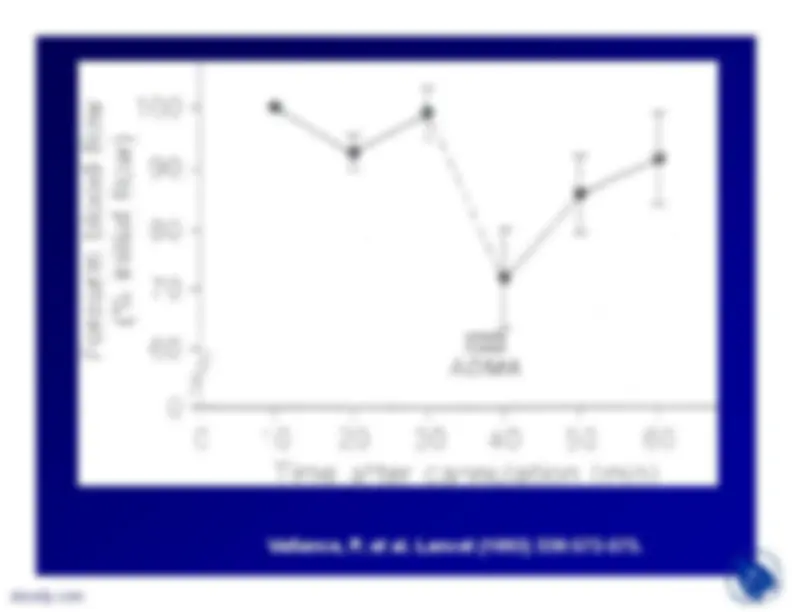
•Candipan et al (1996) fed rabbitseither normal chow (controls) or 0.5%cholesterol chow for 10 weeks andthen the cholesterol group receivedeither vehicle or L-arginine (2.25% inwater) (arginine group) for anadditional 13 weeks.