



















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Introduction to Severe Sepsis, Septic Shock, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, Tachypnea, Acute Organ Dysfunction, Metabolic Acidosis, Refractory Hypotension, Fluid Resucitation are some points in Introduction to General Medicine lecture. This lecture is one of 61 lectures you can find here for this course.
Typology: Slides
1 / 26

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



















2 o more of:
SIRS in response to documented infection
SEVERE SEPSIS:
Sepsis with evidence of acute organ dysfunction
NEJM 2001; 345:1368-
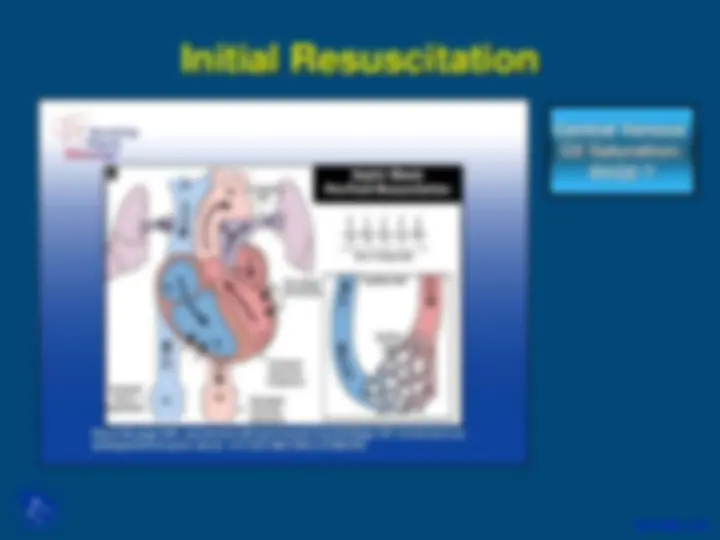
Early-Goal Directed Therapy in Sepsis
During the first 6 hours, goals are:
Grade 1-B
During the first 6 hours, goals are:
Grade 1-B
Critical Care Medicine 2006. 34, 6
Evidence 1-C