



































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
These lecture slides are delivered at The LNM Institute of Information Technology by Dr. Sham Thakur for subject of Mathematical Modeling and Simulation. Its main points are: Modeling, Reasoning, Developing, Project, Flowchart, System, Examples, Nuclear, Representation
Typology: Slides
1 / 44

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





































1
Docsity.com
The Marks distribution:
**1. Quizzes 5%
Recommended Text:
1. B. S. Bennett, “Simulation Fundamentals, ” **Prentice Hall.
Docsity.com
What is Model-based Reasoning?
Docsity.com
Steps for Developing a Model
Docsity.com
What is a System!
What exactly is a system? ??
Examples of Systems
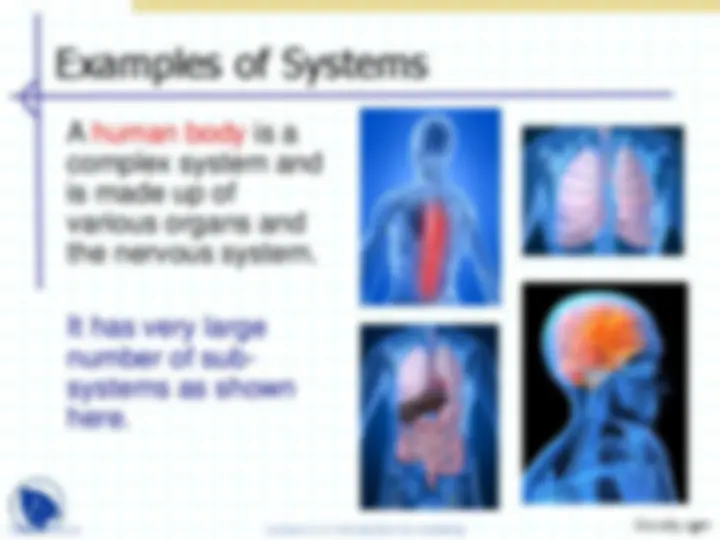
A human body is a complex system and is made up of various organs and the nervous system.
It has very large number of sub- systems as shown here.
Docsity.com
Examples of Systems
A bicycle is also
complex system and is made up of various parts:
tyres, seats, handles, chain system, paddles,
brake system, wheels and support structure
Docsity.com
Examples of Systems
A nuclear power plant is also a complex system that has reactor vessel, pumps, pressurizing system, steam generators, turbines, cooling towers, and containment building among many other sub- systems
Docsity.com
Representation of a System
A system is a set of elements that are united by some interactions or inter-dependences to perform at least one specified function. A system is generally described in two types:
In first type, we identify all possible sub-systems to be included in the model without bringing about any change to the system. Here we eliminate the effect of time.
Then, in second type changes in the state of the system are allowed. Docsity.com
If we look at the system from viewpoints of its purpose,
then it can be classified it in the following four main types:
Classification: Purpose is the Viewpoint
Docsity.com
The Goal Seeking Systems
devised to find possible new states or goals.
with automatic pilot is a goal seeking system.
keep on changing with time, the system keeps on updating its goal states.
Docsity.com
The Purposeful Systems
defined purpose and they can device methods to seek their goals under changing conditions.
Trains are most familiar example of such systems.
Docsity.com
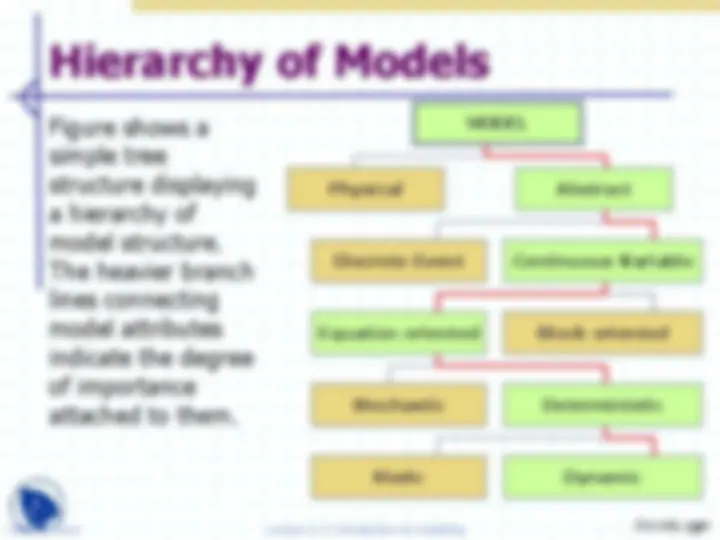
Figure shows a simple tree structure displaying a hierarchy of model structure. The heavier branch lines connecting model attributes indicate the degree of importance attached to them.
MODEL
Discrete Event
Physical Abstract
Continuous Variable
Equation oriented Block oriented
Stochastic Deterministic
Static Dynamic
Docsity.com
Hierarchy: Physical or Replica Models
Docsity.com