










Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This lecture is part of lecture series for Engineering Economics course at M. J. P. Rohilkhand University. It was delivered by Dr. Badrinath Singh to cover following points: Introduction, Land, Labor, Capital, Scarcity, Flow, Planning, Technical, Efficiency, Productivity
Typology: Slides
1 / 15

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










Economics is a social science that analyzes the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.
It studies the economics behavior of the people and economic phenomenon.
Economic Behavior is a conscious effort to derive maximum gain from scarce resources and opportunities available to them.
Economic Phenomenon deals with the production and consumption of goods & services and distribution & rendering of these for human welfare.
Economics is the study of how people allocate their limited resources to their alternative uses to produce and consume goods and services to satisfy their endless wants or to maximize their gains.
While maximizing their gains people as producers and consumers
have to make choices regarding the use of resources and spending their earnings due to following basic facts of economic life.
Scarcity: means that society has limited resources and therefore
cannot produce all the goods and services people wish to have. Resources scarcity is a relative term it implies that resources are scarce in relation to demand for resources. Scarcity is a mother of all economic problems
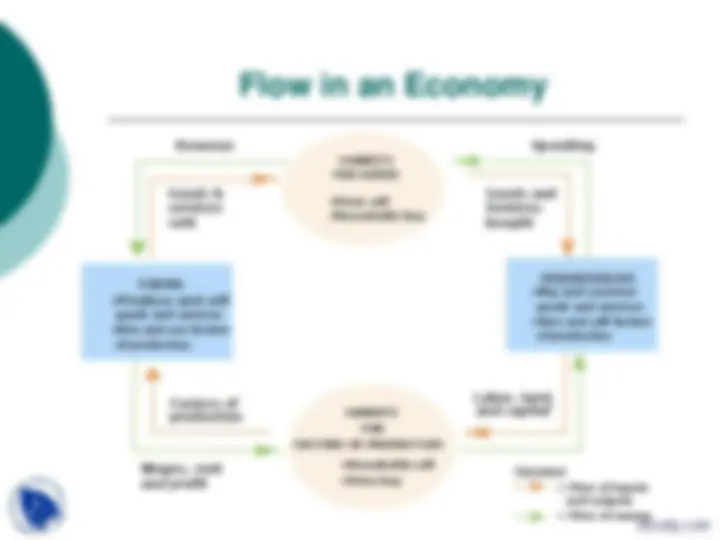
Spending
Goods and Services bought
Revenue
Goods & services sold
Labor, land, and capital
Income = Flow of inputs and outputs = Flow of money
Factors of production
Wages, rent and profit
FIRMS
HOUSEHOLDS
MARKETS FOR FACTORS OF PRODUCTION
MARKETS FOR GOODS
Long Range Planning
Long Range planning in Business. The most aspect of management is long range planning.
The need for long range planning is directed by the increasing no. of economic, social and technological factors which effect the performance of all enterprises. Managerial functions in long range planning Identifying & forecasting a set of objectives and organization’s goals. Establishing an overall strategy for achieving those goals Developing a comprehensive set of plans to integrate and coordinate organizational work. Committing the required resources to achieve the set objectives. Planning is concerned with both ends and means.
Introduction of new product/service/software, the expansion of product facilities, changes in product mix, adoption of new technology.
Generally Engineering Economics deals with methods that
enable organizations to achieve their goals efficiently (Doing things right) and effectively (Doing the right things)
Technical efficiency is the effectiveness with which a given
set of inputs is used to produce an output.
A firm is said to be technically efficient if a firm is producing
the maximum output from the minimum quantity of inputs, such as labor, capital and technology.
The concept of technical efficiency is related to productive
efficiency.
It is the ratio of the effective or useful output to the total input
in any physical system.
The ratio of the energy delivered by a machine to the energy
supplied for its operation.
Increased output for the same input. Decreased input for the same output. By a proportionate increase in the output which is more than the proportionate increase in input. By proportionate decrease in input which is more than the proportionate decrease in output Through simultaneous increase in output with decrease in input
There are two concepts of efficiency: Technological efficiency
occurs when it is not possible to increase output without increasing inputs.
Economic efficiency occurs when the cost of producing a given
output is as low as possible.
Technological efficiency is an engineering matter. Given what
is technologically feasible, something can or cannot be done.
Economic efficiency depends on the prices of the factors of
production.
Something that is technologically efficient may not be
economically efficient.
But something that is economically efficient is always
technologically efficient.