










Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
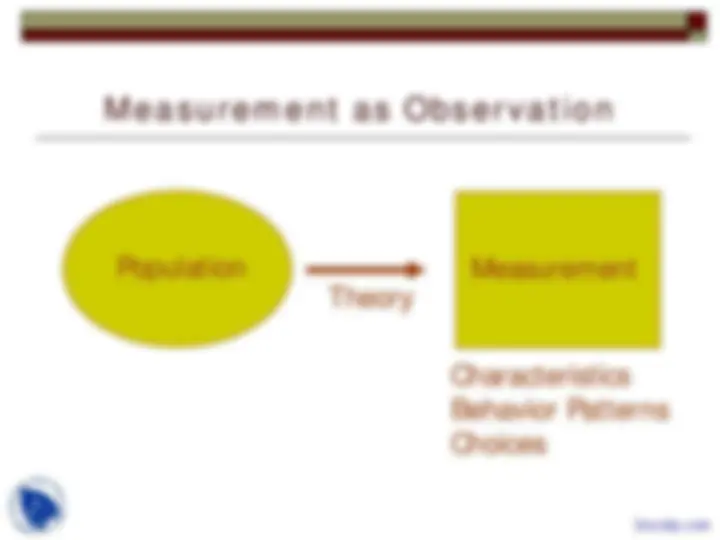
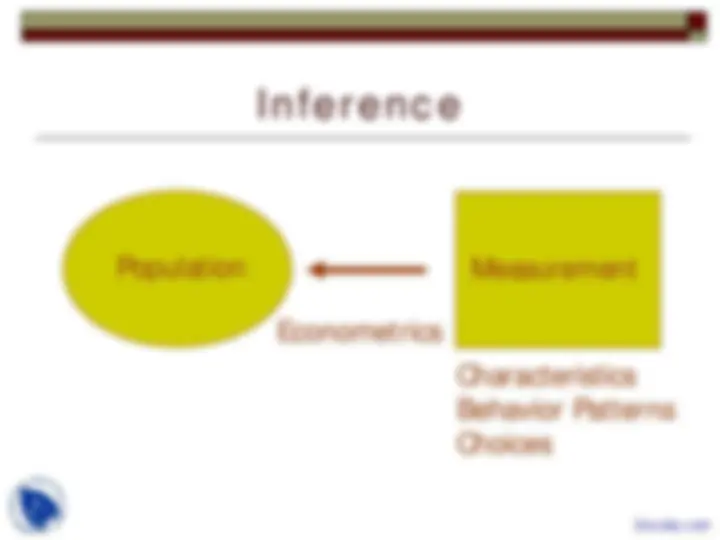
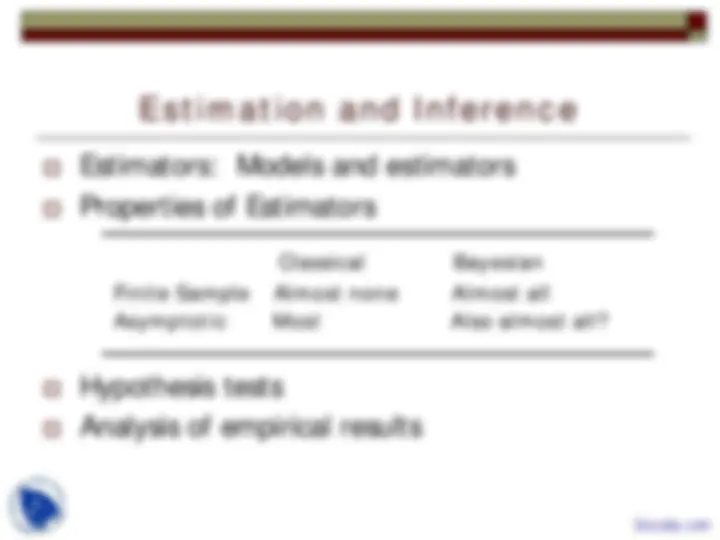
Introduction to Econometrics, Theoretical foundations, Statistical foundations, Mathematical Elements, Model building, Inference, Semiparametric Regression, Data Structures are points which describes this lecture importance in Econometric Analysis of Panel Data course.
Typology: Slides
1 / 20

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!













Nonparametric Regression of Investment on Capital Stock
KC
500
1000
1500
2000
0 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500
Invstmnt
What are the assumptions?
What are the conclusions?
λ (^) λ
λ =
N
i=1 i i
N
i=1 i
i
.
Kernel Regression
w (z)y ˆ F(z)=
w (z)
1 x -z
( ) K
(t) (t)[1 (t)]
exp(t) (t)
1 exp(t)
i
i,t
i,t
i,t
i,t
i,t
Least Absolute Deviations Regression of I on C
C
320
640
960
1280
1600
0 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500
I ILAD
= (^) Invstmnt
− ∑
N
a,b (^) i 1 i i
Least Absolute Deviations
ˆ ˆ F(x)=a+bxˆ
ˆ ˆa,b=ArgMin |y a-bx |
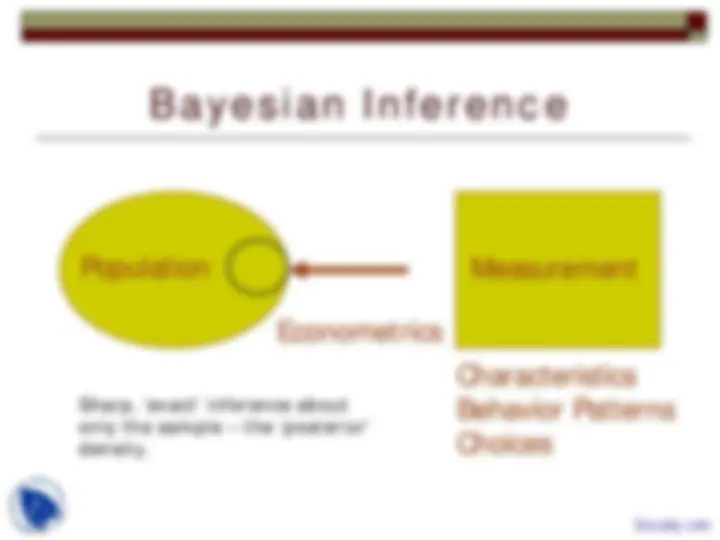
Sharp, ‘exact’ inference about
only the sample – the ‘posterior’
density.