Download Introduction to Csharp.ppt and more Slides Technical Writing in PDF only on Docsity!
Introduction to C#Introduction to C#
Anders Hejlsberg Anders Hejlsberg
Distinguished Engineer Distinguished Engineer
Developer Division Developer Division
Microsoft Corporation Microsoft Corporation
C# – The Big IdeasC# – The Big Ideas
The first component orientedThe first component oriented
language in the C/C++ familylanguage in the C/C++ family
Everything really is an objectEverything really is an object
Next generation robust andNext generation robust and
durable softwaredurable software
Preservation of investmentPreservation of investment
C# – The Big IdeasC# – The Big Ideas
Everything really is an object Everything really is an object
Traditional viewsTraditional views
C++, Java: Primitive types are “magic” and doC++, Java: Primitive types are “magic” and do
not interoperate with objectsnot interoperate with objects
Smalltalk, Lisp: Primitive types are objects, butSmalltalk, Lisp: Primitive types are objects, but
at great performance costat great performance cost
C# unifies with no performance costC# unifies with no performance cost
Deep simplicity throughout systemDeep simplicity throughout system
Improved extensibility and reusabilityImproved extensibility and reusability
New primitive types: Decimal, SQL…New primitive types: Decimal, SQL…
Collections, etc., work for allCollections, etc., work for all typestypes
C# – The Big IdeasC# – The Big Ideas
Robust and durable software Robust and durable software
Garbage collectionGarbage collection
No memory leaks and stray pointersNo memory leaks and stray pointers
ExceptionsExceptions
Error handling is not an afterthoughtError handling is not an afterthought
Type-safetyType-safety
No uninitialized variables, unsafe castsNo uninitialized variables, unsafe casts
VersioningVersioning
Pervasive versioning considerations inPervasive versioning considerations in
all aspects of language designall aspects of language design
Hello WorldHello World
using System; using System;
class Hello class Hello
static void Main() { static void Main() {
Console.WriteLine("Hello world"); Console.WriteLine("Hello world");
C# Program StructureC# Program Structure
NamespacesNamespaces
Contain types and other namespacesContain types and other namespaces
Type declarationsType declarations
Classes, structs, interfaces, enums,Classes, structs, interfaces, enums,
and delegatesand delegates
MembersMembers
Constants, fields, methods, properties, indexers,Constants, fields, methods, properties, indexers,
events, operators, constructors, destructorsevents, operators, constructors, destructors
OrganizationOrganization
No header files, code written “in-line”No header files, code written “in-line”
No declaration order dependenceNo declaration order dependence
Type SystemType System
Value typesValue types
Directly contain dataDirectly contain data
Cannot be nullCannot be null
Reference typesReference types
Contain references to objectsContain references to objects
May be nullMay be null
int int ii == 123;123; stringstring ss == "Hello"Hello world";world";
ii (^123123)
s s (^) "Hello"Hello world"world"
Type SystemType System
Value typesValue types
PrimitivesPrimitives int i;int i;
EnumsEnums enum State { Off, On }enum State { Off, On }
StructsStructs struct Point { int x, y; }struct Point { int x, y; }
Reference typesReference types
ClassesClasses class Foo: Bar, IFoo {...}class Foo: Bar, IFoo {...}
InterfacesInterfaces interface IFoo: IBar {...}interface IFoo: IBar {...}
ArraysArrays string[]string[] aa == newnew string[10];string[10];
DelegatesDelegates delegate void Empty();delegate void Empty();
ClassesClasses
Single inheritanceSingle inheritance
Multiple interface implementationMultiple interface implementation
Class membersClass members
Constants, fields, methods, properties,Constants, fields, methods, properties,
indexers, events, operators,indexers, events, operators,
constructors, destructorsconstructors, destructors
Static and instance membersStatic and instance members
Nested typesNested types
Member accessMember access
public, protected, internal, privatepublic, protected, internal, private
StructsStructs
Like classes, exceptLike classes, except
Stored in-line, not heap allocatedStored in-line, not heap allocated
Assignment copies data, not referenceAssignment copies data, not reference
No inheritanceNo inheritance
Ideal for light weight objectsIdeal for light weight objects
Complex, point, rectangle, colorComplex, point, rectangle, color
int, float, double, etc., are all structsint, float, double, etc., are all structs
BenefitsBenefits
No heap allocation, less GC pressureNo heap allocation, less GC pressure
More efficient use of memoryMore efficient use of memory
InterfacesInterfaces
Multiple inheritanceMultiple inheritance
Can contain methods, properties,Can contain methods, properties,
indexers, and eventsindexers, and events
Private interface implementationsPrivate interface implementations
interface interface IDataBoundIDataBound {{ voidvoid Bind(IDataBinderBind(IDataBinder binder);binder); }}
classclass EditBox:EditBox: (^) Control,Control, (^) IDataBoundIDataBound {{ voidvoid IDataBound.Bind(IDataBinderIDataBound.Bind(IDataBinder binder)binder) (^) {...}{...} }}
EnumsEnums
Strongly typedStrongly typed
No implicit conversions to/from intNo implicit conversions to/from int
Operators: +, -, ++, --, &, |, ^, ~Operators: +, -, ++, --, &, |, ^, ~
Can specify underlying typeCan specify underlying type
Byte, short, int, longByte, short, int, long
enum enum (^) Color:Color: bytebyte {{ RedRed == 1,1, GreenGreen == 2,2, BlueBlue == 4,4, BlackBlack == 0,0, WhiteWhite == RedRed || GreenGreen || Blue,Blue, }}
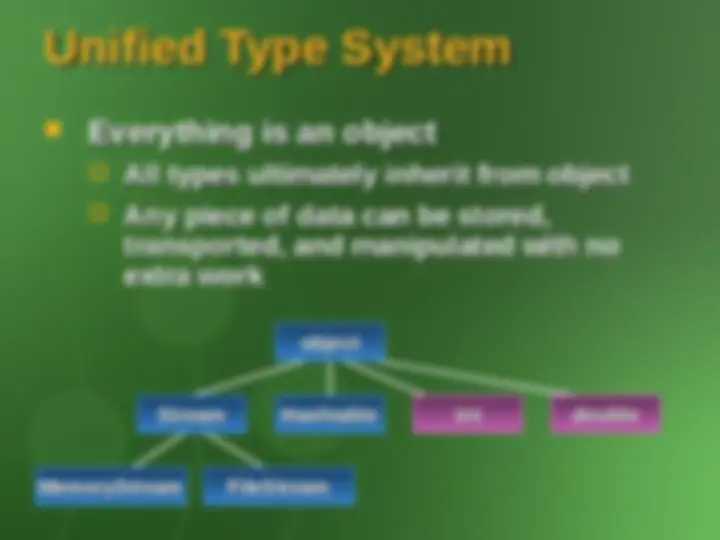
Unified Type SystemUnified Type System
Everything is an objectEverything is an object
All types ultimately inherit from objectAll types ultimately inherit from object
Any piece of data can be stored,Any piece of data can be stored,
transported, and manipulated with no transported, and manipulated with no
extra work extra work
Stream Stream
MemoryStream MemoryStream FileStreamFileStream
Hashtable Hashtable intint doubledouble
objectobject
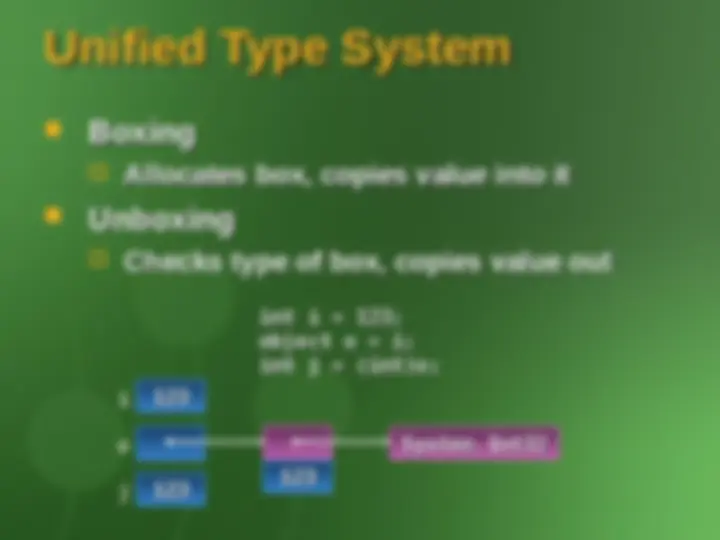
Unified Type SystemUnified Type System
BoxingBoxing
Allocates box, copies value into itAllocates box, copies value into it
UnboxingUnboxing
Checks type of box, copies value outChecks type of box, copies value out
int int ii == 123;123; objectobject oo == i;i; intint (^) jj == (int)o;(int)o; i^123123
o (^123123)
System.Int32 System.Int
j^123123