




































































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
introduction to computer network slides
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 91

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




















































































By: Sanjeev Patel Asst. Professor, CSE& IT Department JIIT, Noida Sector- Unit-1 1
Test 1 : 20 (21 Hrs.) Test 2 : 20 (11 Hrs.) Test 3 : 35 (10 Hrs.) Quiz/Test : 10 Attendance: 5 Assignments/Tutorial: 10 Unit-1 2
Introduction 1- 4
1.1 Basics of Network. What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge 1.3 Network core 1.4 Network access and physical media 1.5 Internet structure and ISPs 1.6 Delay & loss in packet-switched networks 1.7 Protocol layers, service models 1.8 History
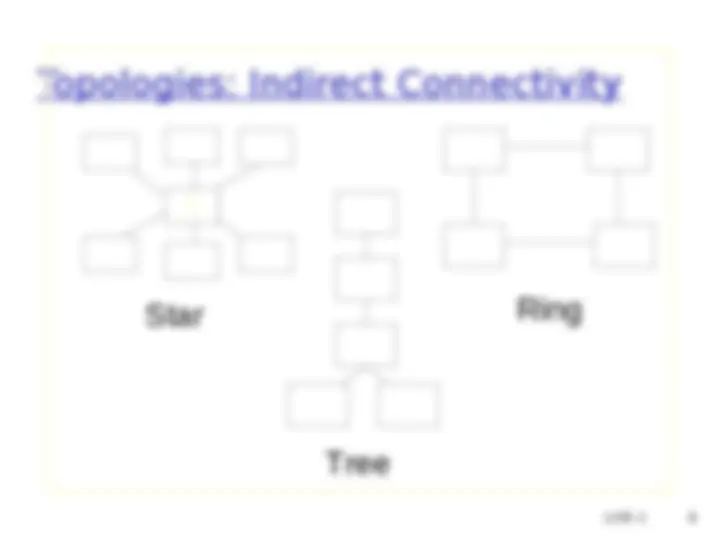
Direct or indirect access to every other node in the network (^) Connectivity is the magic needed to communicate if you do not have a direct pt-pt physical link. Unit-1 7
Unit-1 8 Ring Star S Tree
Unit-1 10
Introduction 1- 11 What’s the Internet: “nuts and bolts” view (^) millions of connected computing devices: hosts = end systems (^) running network apps (^) communication links (^) fiber, copper, radio, satellite (^) transmission rate = bandwidth (^) routers: forward packets (chunks of data) local ISP company network regional ISP router workstation server mobile
Introduction 1- 13 What’s the Internet: a service view (^) communication infrastructure enables distributed applications: (^) Web, email, games, e- commerce, file sharing (^) communication services provided to apps: (^) Connectionless unreliable (^) connection-oriented reliable
Introduction 1- 14
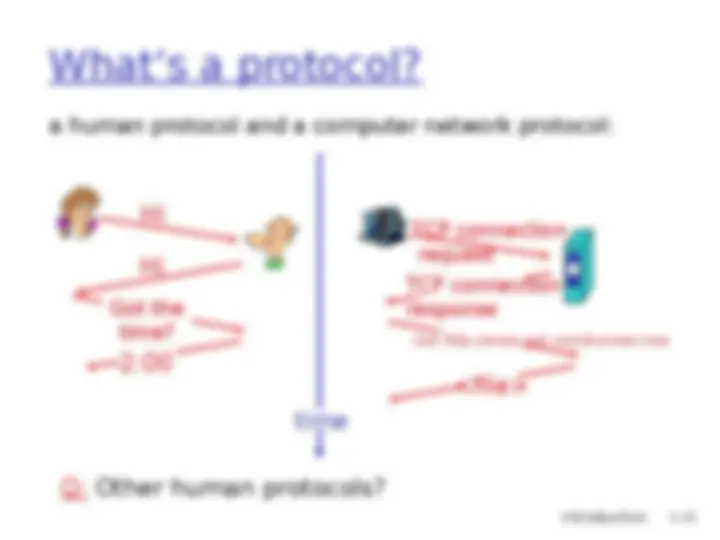
human protocols: (^) “what’s the time?” (^) “I have a question” (^) introductions … specific msgs sent … specific actions taken when msgs received, or other events network protocols: (^) machines rather than humans (^) all communication activity in Internet governed by protocols protocols define format, order of msgs sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on msg transmission, receipt
Introduction 1- 16
1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge 1.3 Network core 1.4 Network access and physical media 1.5 Internet structure and ISPs 1.6 Delay & loss in packet-switched networks 1.7 Protocol layers, service models 1.8 History
Introduction 1- 17
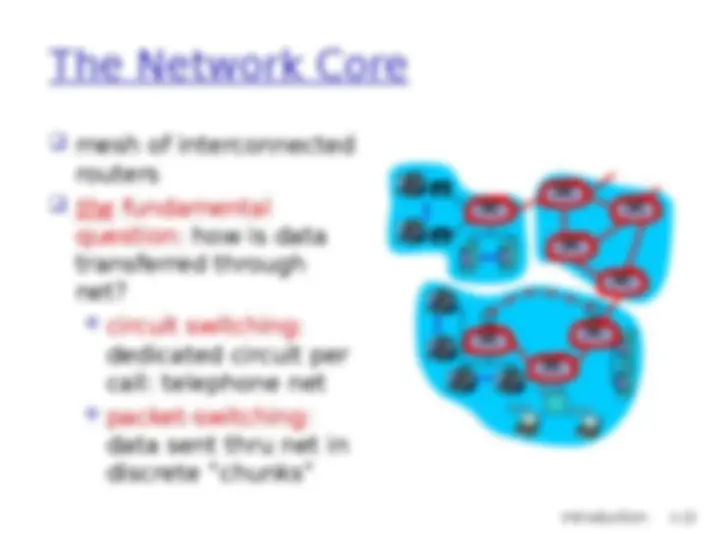
(^) network edge: applications and hosts (^) network core: (^) routers (^) network of networks (^) access networks, physical media: communication links
Introduction 1- 19 Network edge: connection-oriented service Goal: data transfer between end systems (^) handshaking: setup (prepare for) data transfer ahead of time (^) Hello, hello back human protocol (^) set up “state” in two communicating hosts (^) TCP - Transmission Control Protocol (^) Internet’s connection- oriented service TCP service [RFC 793] (^) reliable, in-order byte- stream data transfer (^) loss: acknowledgements and retransmissions (^) flow control: (^) sender won’t overwhelm receiver (^) congestion control: (^) senders “slow down sending rate” when network congested
Introduction 1- 20 Network edge: connectionless service Goal: data transfer between end systems (^) same as before! (^) UDP - User Datagram Protocol [RFC 768]: connectionless (^) unreliable data transfer (^) no flow control no congestion control App’s using TCP: (^) HTTP (Web), FTP (file transfer), Telnet (remote login), SMTP (email) App’s using UDP: (^) streaming media, teleconferencing, DNS, Internet telephony