










Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The concept of direct and indirect pest interactions in integrated pest management (ipm). Direct interactions refer to the immediate effect of pests on each other or on the crop, while indirect interactions involve the role of other factors such as natural enemies, environmental conditions, or management practices. The document also covers the importance of biodiversity in ipm and the challenges and benefits of implementing ecologically-based pest management systems.
Typology: Slides
1 / 17

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










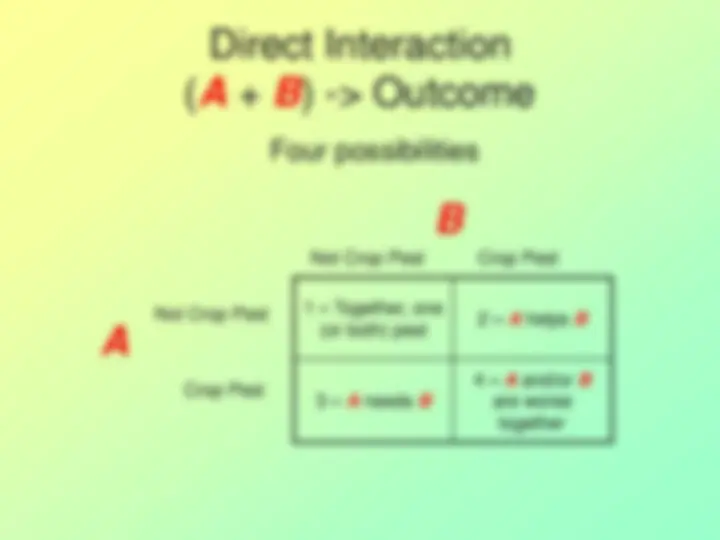
Four possibilities
1 – Together, one (or both) pest 2 –^ A^ helps^ B
3 – A needs B
4 – A and/or B are worse together
Not Crop Pest
Crop Pest
Not Crop Pest Crop Pest
Overwintering hosts for aphids.
Contrast with benefits noted on p. 158
Here‘s a small sample. Follow the links to read a little about each one & get the idea.